Abstract
Background
Previous research demonstrated that the crude saponins of Platycodi radix improve glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic animals; however, which individual saponins are the most potent insulin sensitizers is unknown.
Objectives
This study investigated which saponin(s) have anti-diabetic action in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
The insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and PPAR-γ agonistic actions of six saponins from Platycodi radix were investigated in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion was determined in Min6 cells. Four individual saponins (20 mg/kg body weight) were orally administered to low-dose streptozotocin-injected diabetic mice fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks to evaluate glucose tolerance by oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT), insulin sensitivity by insulin tolerance testing, and insulin signaling in the liver and adipose tissues.
Results
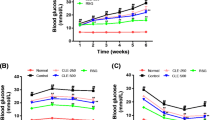
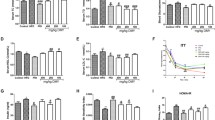
Platyconic acid (PA) most effectively increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, possibly in part by working as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR)-γ activator; however, none of the saponins improved glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in insulinoma cells. PA-treated diabetic mice exhibited the lowest peak serum glucose levels and highest serum insulin levels during the first part of OGTT. PA also improved insulin sensitivity: PA increased glycogen accumulation and decreased triacylglycerol storage in liver, which was associated with enhanced hepatic insulin signaling, while PA potentiated the expression of adiponectin and PPAR-γ in adipose tissue, and improved insulin signaling and increased GLUT4 translocation into the membranes.
Conclusions
PA improves glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetic mice, partly by enhancing hepatic and adipocyte insulin sensitivity, possibly by activating PPAR-γ.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E (2001) Regulation of intermediary metabolism during fasting and feeding. In: DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL (eds) Endocrinology. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, pp 737–775
Taylor SI (1999) Deconstructing type 2 diabetes. Cell 97:9–12
Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY (2006) Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet 368:1681–1688
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB (2009) Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors and pathophysiology. JAMA 301:2129–2140
Hui H, Tang G, Go VLW (2009) Hypoglycemic herbs and their action mechanisms. Chin Med 4:11
Han LK, Xu BJ, Kimura Y, Zheng Y, Okuda H (2000) Platycodi radix affects lipid metabolism in mice with high fat diet-induced obesity. J Nutr 130:2760–2764
Kim KS, Seo EK, Lee YC, Lee TK, Cho YW, Ezaki O, Kim CH (2000) Effect of dietary Platycodon grandiflorum on the improvement of insulin resistance in obese zucker rats. J Nutr Biochem 11:420–424
Kwon DY, Kim YS, Hong SM, Park S (2009) Long-term consumption of saponins derived from Platycodi radix (22 years old) enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in 90% pancreatectomized diabetic rats fed a high-fat diet. Br J Nutr 101:358–366
Kim HK, Choi JS, Yoo DS, Choi YH, Yeon KH, Hong KS, Lee BH, Kim HJ, Kim EJ, Roh SW, Jeong YC, Kim YS, Ryu SY (2007) HPLC analysis of saponins in Platycodi radix. Kr J Pharm 38:1–18
Choi JH, Yoo KY, Park OK, Lee CH, Won MH, Hwang IK, Ryu SY, Kim YS, Yi JS, Bae YS, Kang IJ (2009) Platycodin D and 2″-O-acetyl-polygalacin D2 isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum protect ischemia/reperfusion injury in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res 1279:197–208
Chung JW, Noh EJ, Zhao HL, Sim JS, Ha YW, Shin EM, Lee EB, Cheong CS, Kim YS (2008) Anti-inflammatory activity of prosapogenin methyl ester of platycodin D via nuclear factor-kappa B pathway inhibition. Biol Pharm Bull 31:2114–2120
Ahn KS, Noh EJ, Zhao HL, Jung SH, Kang SS, Kim YS (2005) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci 76:2315–2328
Choi YH, Yoo DS, Choi CW, Cha MR, Kim YS, Lee HS, Lee KR, Ryu SY (2008) Platyconic acid A, a genuine triterpenoid saponin from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum. Molecules 13:2871–2879
Shimaya A, Kovacina KS, Roth RA (2004) On the mechanism for neomycin reversal of wortmannin inhibition of insulin stimulation of glucose uptake. J Biol Chem 279:55277–55282
Park S, Ahn IS, Kwon DY, Ko BS, Jun WK (2008) Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 suppress triacylglycerol accumulation in 3T3–L1 adipocytes and enhance β-cell insulin secretion and viability in Min6 cells via PKA dependent pathways. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:2815–2823
Letter EH (1982) Multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia and insulinitis in C57BL mice: influence of inbred background, sex, and thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:630–634
Mu J, Petrov A, Eiermann GJ, Woods J et al (2009) Inhibition of DPP-4 with sitagliptin improves glycemic control and restores islet cell mass and function in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol 623:148–154
Kusakabe T, Tanioka H, Ebihara K et al (2009) Beneficial effects of leptin on glycaemic and lipid control in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes with increased adiposity induced by streptozotocin and a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 52:675–683
American Institute of Nutrition (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Frontoni S, Choi SB, Banduch D, Rossetti L (1991) In vivo insulin resistance induced by amylin primarily through inhibition of insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 40:568–573
Sebokova E, Klimes I, Moss R, Stolba P, Wiersma MM, Mitková A (1993) Muscle GLUT 4 protein levels and impaired triglyceride metabolism in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Effect of a high sucrose diet and fish oil supplementation. Ann NY Acad Sci 683:218–227
Zanquetta MM, Nascimento ME, Mori RC, D’Agord Schaan B, Young ME, Machado UF (2006) Participation of beta-adrenergic activity in modulation of GLUT4 expression during fasting and refeeding in rats. Metabolism 55:1538–1545
Hallakou S, Doaré L, Foufelle F, Kergoat M, Guerre-Millo M, Berthault MF, Dugail I, Morin J, Auwerx J, Ferré P (1997) Pioglitazone induces in vivo adipocyte differentiation in the obese zucker fa/fa rat. Diabetes 46:1393–1399
Kim JY, Moon KD, Seo KI, Park KW, Choi MS, Do GM, Jeong YK, Cho YS, Lee MK (2009) Supplementation of SK1 from Platycodi radix ameliorates obesity and glucose intolerance in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Med Food 12:629–636
Reed MJ, Meszaros K, Entes LJ, Claypool MD, Pinkett JG, Gadbois TM, Reaven GM (2000) A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism 49:1390–1394
Zhang F, Ye C, Li G (2003) The rat model of type 2 diabetic mellitus and its glycometabolism characters. Exp Anim 52:401–407
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res 52:313–320
Han LK, Zheng YN, Xu BJ, Okuda H, Kimura Y (2002) Saponins from Platycodi radix ameliorate high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J Nutr 132:2241–2245
Lee H, Kang R, Kim YS, Chung SI, Yoon Y (2010) Platycodin D inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3–L1 cells by modulating kruppel-like factor 2 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Phytother Res 24:S161–S167
DeFronzo RA (2004) Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am 88:787–835
Ide T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Matsuzaka T et al (2004) SREBPs suppress IRS-2-mediated insulin signaling in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 6:351–357
Kwon DY, Jang JS, Hong SM, Lee JE, Sung SR, Park HR, Park S (2007) Long-term consumption of fermented soybean-derived chungkookjang enhances insulinotropic action unlike soybeans in 90% pancreatectomized diabetic rats. Eur J Nutr 46:44–52
Dong X, Park S, Lin X, Copps K, Yi X, White MF (2006) Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J Clin Invest 116:101–1014
Ribon V, Johnson JH, Camp HS, Saltiel AR (1998) Thiazolidinediones and insulin resistance: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation stimulates expression of the CAP gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14751–14756
Huang TH, Kota BP, Razmovski V, Roufogalis BD (2005) Herbal or natural medicines as modulators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and related nuclear receptors for therapy of metabolic syndrome. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 96:13–14
Rangwala SM, Lazar MA (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in diabetes and metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:331–336
Olefsky JM (2000) Treatment of insulin resistance with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists. J Clin Invest 106:467–472
Ratziu V, Giral P, Jacqueminet S, Charlotte F, Hartemann-Heurtier A, Serfaty L, Podevin P, Lacorte JM, Bernhardt C, Bruckert E, Grimaldi A, Poynard T, LIDO Study Group (2008) Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled fatty liver improvement with rosiglitazone therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 135:100–110
Wu CW, Chu ES, Lam CN, Cheng AS, Lee CW, Wong VW, Sung JJ, Yu J (2010) PPAR gamma is essential for protection against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gene Ther 17:790–798
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Inter-Institutional Collaboration Research Program under the Korea Research Council for Industrial Science and Technology (KOCI), Korea.
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dae Young Kwon and Young Seob Kim equally contributed to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, D.Y., Kim, Y.S., Ryu, S.Y. et al. Platyconic acid, a saponin from Platycodi radix, improves glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Nutr 51, 529–540 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0236-x