Abstract
Background
Insulin resistance is a common symptom of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
Aim of the study
We investigated whether Gastrodia elata Blume water extract(GEB), containing phenolic compounds, had a beneficial action on insulin resistance in male Sprague–Dawley rats fed a high fat diet(HFD) and determined how this effect was produced. In addition, the bioactive candidates involved were identified.
Methods
Rats fed HFD were daily administered with 0.3 g GEB(GEB-L), 1 g GEB(GEB-H), or 1 g cellulose(control) per kg body weight for 8 weeks, while rats in the fourth group were fed a low fat diet(LFD). In vitro study, 4 major components of GEB were tested for their impact on fat accumulation.
Results
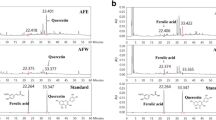
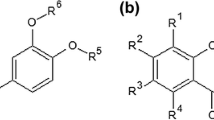
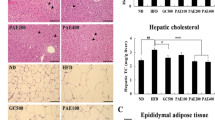
Rats in the control group exhibited a higher weight gain of epididymal and retroperitoneal fat pads than those fed LFD, while GEB prevented such an increment in a dose-dependent manner. GEB-H significantly decreased energy intake partly through potentiating STAT3 phosphorylation and attenuating AMPK phosphorylation in the hypothalamus. GEB-H also increased energy expenditure with the increase in fat oxidation. GEB-H increased whole body glucose disposal rates and decreased hepatic glucose output compared to the control. Among the major components of GEB, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and vanillin decreased triglyceride accumulation by modulating the expression of genes involved in fat metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. They increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake to reduce insulin resistance.
Conclusions
GEB-H, mainly as a result of the action of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and vanillin, reduces insulin resistance by decreasing fat accumulation in adipocytes by activating fat oxidation and potentiating leptin signaling in diet-induced obese rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO (2009) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:1925–1932
Figlewicz DP, Benoit SC (2009) Insulin, leptin, and food reward: update 2008. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R9–R19
Minokoshi Y, Alquier T, Furukawa N, Kim YB, Lee A, Xue B, Mu J, Foufelle F, Ferré P, Birnbaum MJ, Stuck BJ, Kahn BB (2004) AMP-kinase regulates food intake by responding to hormonal and nutrient signals in the hypothalamus. Nature 428:569–574
Ropelle ER, Pauli JR, Fernandes MF, Rocco SA, Marin RM, Morari J, Souza KK, Dias MM, Gomes-Marcondes MC, Gontijo JA, Franchini KG, Velloso LA, Saad MJ, Carvalheira JB (2008) A central role for neuronal AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in high-protein diet-induced weight loss. Diabetes 57:594–605
Ojemanna LM, Nelsonb WL, Shinc DS, Rowed AO, Buchanane RA (2006) Tian ma, an ancient Chinese herb, offers new options for the treatment of epilepsy and other conditions. Epilepsy Behav 8:376–383
Yang XD, Zhu J, Yang R, Liu JP, Li L, Zhang HB (2007) Phenolic constituents from the rhizomes of Gastrodia elata. Nat Prod Res 21:180–186
Shuchang H, Qiao N, Piye N, Mingwei H, Xiaoshu S, Feng S, Sheng W, Opler M (2008) Protective effects of Gastrodia elata on aluminium-chloride-induced learning impairments and alterations of amino acid neurotransmitter release in adult rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci 26:467–473
Huang NK, Chern Y, Fang JM, Reed GW, Peters JC, Hill JO (2007) Neuroprotective principles from Gastrodia elata. J Nat Prod 70:571–574
Shuaib A, Murabit MA, Kanthan R, Howlett W, Wishart T (1996) The neuroprotective effects of gamma-vinyl GABA in transient global ischemia: a morphological study with early and delayed evaluations. Neurosci Lett 204:1–4
Gainetdinov RR (2007) Mesolimbic dopamine in obesity and diabetes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R601–R602
Goudie AJ, Cooper GD, Halford JC (2005) Antipsychotic-induced weight gain. Diabetes Obes Metab 7:478–487
Tong Q, Ye CP, Jones JE, Elmquist JK, Lowell BB (2008) Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance. Nat Neurosci 11:998–1000
Bellido GG, Beta T (2009) Anthocyanin composition and oxygen radical scavenging capacity (ORAC) of milled and pearled purple, black, and common barley. J Agric Food Chem 57:1022–1028
American Institute of Nutrition (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Niwa H, Ogawa Y, Kido Y, Abe Y, Kobayashi M, Mori T, Tanaka T (1989) The rate of lipid oxidation in septic rat models. Jpn J Surg 19:439–445
Lusk G (1924) Analysis of the oxidation of mixtures of carbohydrate and fat. J Biol Chem 59:41
Labayen I, Forga L, Martinez JA (1999) Nutrient oxidation and metabolic rate as affected by meals containing different proportions of carbohydrate and fat, in healthy young women. Eur J Nutr 38:158–166
Frontoni S, Choi SB, Banduch D, Rossetti L (1991) In vivo insulin resistance induced by amylin primarily through inhibition of insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 40:568–573
Sebokova E, Klimes I, Moss R, Stolba P, Wiersma MM, Mitkova A (1993) Muscle GLUT 4 protein levels and impaired triglyceride metabolism in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Effect of a high sucrose diet and fish oil supplementation. Ann NY Acad Sci 683:218–227
Kim JK, Kim YJ, Fillmore JJ, Chen Y, Moore I, Lee J, Yuan M, Li ZW, Karin M, Perret P, Shoelson SE, Shulman GI (2001) Prevention of fat-induced insulin resistance by salicylate. J Clin Invest 108:437–446
Park S, Hong SM, Ahn IS (2009) Long-term ICV infusion of insulin, but not glucose, modulates body weight and hepatic insulin sensitivity through modifying hypothalamic insulin signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats. Neuroendocrinology 89:387–399
Ejaz A, Wu D, Kwan P, Meydani M (2009) Curcumin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3–L1 adipocytes and angiogenesis and obesity in C57/BL mice. J Nutr 139:919–925
Park S, Ahn IS, Kwon DY, Ko BS, Jun WK (2008) Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 suppress triacylglycerol accumulation in 3T3–L1 adipocytes and enhance β-cell insulin secretion and viability in Min6 cells via PKA dependent pathways. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:2815–2823
Lin LC, Chen YF, Lee WC, Wu YT, Tsai TH (2008) Pharmacokinetics of gastrodin and its metabolite p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in rat blood, brain and bile by microdialysis coupled to LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:909–917
Sahu A (2004) Minireview: a hypothalamic role in energy balance with special emphasis on leptin. Endocrinology 145:2613–2620
Xue B, Kahn BB (2006) AMPK integrates nutrient and hormonal signals to regulate food intake and energy balance through effects in the hypothalamus and peripheral tissues. J Physiol 574:73–83
Miller WC, Lindeman AK, Wallace J, Niederpruem M (1990) Diet composition, energy intake, and exercise in relation to body fat in men and women. Am J Clin Nutri 52:426–430
Torre-Villavazo I, Tovar AR, Ramos-Barragán VE, Cerbón-Cervantes MA, Torres N (2008) Soy protein ameliorates metabolic abnormalities in liver and adipose tissue of rats fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr 138:462–468
Fruebis J, Tsao TS, Javorschi S, Ebbets-Reed D, Lodish HF (2001) Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2005–2010
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:79–83
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1595–1599
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, Ortmeyer HK, Arita Y, Hansen BC, Matsuzawa Y (2001) Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes 50:1126–1133
DeFronzo RA (2004) Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am 88:787–835
Ha JH, Shin SM, Lee SK, Kim JS, Shin US, Huh K, Kim JA, Yong CS, Lee NJ, Lee DU (2001) In vitro effects of hydroxybenzaldehydes from Gastrodia elata and their analogues on GABAergic neurotransmission, and a structure-activity correlation. Planta Med 67:877–880
Gurnell M (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the regulation of adipocyte function: lessons from human genetic studies. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 19:501–523
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HMP-08-A-0-80958). All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Kim, D.S. & Kang, S. Gastrodia elata Blume water extracts improve insulin resistance by decreasing body fat in diet-induced obese rats: vanillin and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde are the bioactive candidates. Eur J Nutr 50, 107–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-010-0120-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-010-0120-0