Summary
Background
Indian Asians living in Western Countries have an over 50 % increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) relative to their Caucasians counterparts. The atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype (ALP), which is more prevalent in this ethnic group, may in part explain the increased risk. A low dietary long chain n-3 fatty acid (LC n-3 PUFA) intake and a high dietary n-6 PUFA intake and n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio in Indian Asians have been proposed as contributors to the increased ALP incidence and CHD risk in this subgroup.
Aim
To examine the impact of dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio on membrane fatty acid composition, blood lipid levels and markers of insulin sensitivity in Indian Asians living in the UK.
Methods
Twentynine males were assigned to either a moderate or high n-6:n-3 PUFA (9 or 16) diet for 6 weeks. Fasting blood samples were collected at baseline and 6 weeks for analysis of triglycerides, total-, LDL- and HDL-cholesterol, non-esterified fatty acids, glucose, insulin, markers of insulin sensitivity and C-reactive protein.
Results
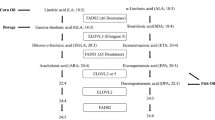
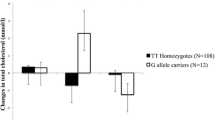
Group mean saturated fatty acid, MUFA, n-6 PUFA and n-3 PUFA on the moderate and high n-6:n-3 PUFA diets were 26 g/d, 43 g/d, 15 g/d, 2 g/d and 25 g/d, 25 g/d, 28 g/d, 2 g/d respectively. A significantly lower total membrane n-3 PUFA and a trend towards lower EPA and DHA levels were observed following the high n-6:n-3 PUFA diet. However no significant effect of treatment on plasma lipids was evident. There was a trend towards a loss of insulin sensitivity on the high n-6:n- 3 PUFA diet, with the increase in fasting insulin (P = 0.04) and HOMA IR [(insulin x glucose)/ 22.5] (P = 0.02) reaching significance.
Conclusion
The results of the current study suggest that, within the context of a western diet, it is unlikely that dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio has any major impact on the levels of LC n-3 PUFA in membrane phospholipids or have any major clinically relevant impact on insulin sensitivity and its associated dyslipidaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Source of support: This project was funded by the Food Standards Agency (FSA), UK.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minihane, A.M., Brady, L.M., Lovegrove, S.S. et al. Lack of effect of dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio on plasma lipids and markers of insulin responses in Indian Asians living in the UK. Eur J Nutr 44, 26–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0488-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0488-9