Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine whether endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
A meta-analysis was conducted on associations between the 4b/a, T786C, and G894T polymorphisms of eNOS and SLE or RA using the following methods: (1) allele contrast, (2) recessive model, (3) dominant model, and (4) homozygous contrast.
Results
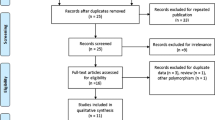
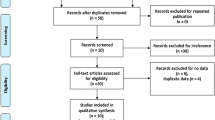
Nineteen studies were included in this meta-analysis, comprising eleven studies on SLE (1561 patients and 1565 controls) and eight on RA (1624 patients and 2118 controls). Meta-analysis showed a significant association between SLE and the 4b/a polymorphism using the recessive model and the homozygous contrast (odds ratio [OR] = 1.836, 95 % confidence interval [CI] = 1.171–2.878, p = 0.008; OR = 2.055, 95 % CI = 1.302–3.243, p = 0.002). Ethnicity-specific meta-analysis showed a significant association between the aa vs. bb of the 4b/a polymorphism and SLE in European populations (OR = 2.096, 95 % CI = 1.288–4.0, p = 0.027), but not in Arab populations. Stratification by presence of lupus nephritis (LN) indicated a significant association between the a allele and the aa + ab genotype of the 4b/a polymorphism and LN in SLE patients (OR = 2.125, 95 % CI = 1.289–3.054, p = 0.003; OR = 2.655, 95 % CI = 1.509–4.671, p = 0.001). Meta-analysis indicated no association between SLE and the T786C and G894T polymorphisms. No association was found between the eNOS 4b/a, T786C, and G894T polymorphisms and RA
Conclusions
This meta-analysis of published studies shows that the eNOS 4b/a polymorphism may be associated with the development of SLE, but the 4b/a, T786C, and G894T polymorphisms may be not associated with RA susceptibility.
Zusammenfassung
Ziel
Ziel dieser Studie war es, festzustellen, ob Polymorphismen der endothelialen Stickstoffmonoxid-Synthase (eNOS) mit einer Suszeptibilität für systemischen Lupus erythematodes (SLE) und rheumatoide Arthritis (RA) assoziiert sind.
Methoden
Eine Metaanalyse wurde hinsichtlich der Assoziationen zwischen den eNOS-Polymorphismen 4b/a, T786C sowie G894T und SLE oder RA unter Verwendung der folgenden Methoden durchgeführt: (1) Allel-Kontrast-Modell, (2) rezessives Modell, (3) dominantes Modell und (4) homozygotes Kontrast-Modell.
Ergebnisse
Neunzehn Studien wurden in diese Metaanalyse eingeschlossen, die 11 SLE-Studien (1561 Patienten und 1565 Kontrollpersonen) und 8 RA-Studien (1624 Patienten und 2118 Kontrollpersonen) umfasste. Die Metaanalyse zeigte eine signifikante Assoziation zwischen SLE und dem 4b/a-Polymorphismus unter Anwendung des rezessiven und des homozygoten Kontrast-Modells (Odds-Ratio [OR] = 1,836, 95 % Konfidenzintervall [CI] = 1,171–2,878; p = 0,008; OR = 2,055, 95 % CI = 1,302–3,243; p = 0,002).
Eine ethnizitätsbezogene Metaanalyse zeigte eine signifikante Assoziation zwischen dem aa und dem bb des 4b/a-Polymorphismus und SLE in der europäischen Population (OR = 2,096, 95 % CI = 1,288–4,0; p = 0,027), jedoch nicht in der arabischen Population. Die Stratifizierung bei Vorliegen einer Lupusnephritis (LN) zeigte eine signifikante Assoziation zwischen dem a‑Allel und dem aa+ ab-Genotyp des 4b/a-Polymorphismus und LN bei SLE-Patienten (OR = 2,125, 95 % CI = 1,289–3,054; p = 0,003; OR = 2,655, 95 % CI = 1,509–4,671; p = 0,001). Die Metaanalyse zeigte keine Assoziation zwischen SLE und den Polymorphismen T786C und G894T. Es wurde keine Assoziation zwischen den eNOS-Polymorphismen 4b/a, T786C sowie G894T und RA gefunden.
Schlussfolgerungen
Diese Metaanalyse publizierter Studien zeigt, dass der eNOS-Polymorphismus 4a/b mit dem Entstehen eines SLE assoziiert sein könnte. Die Polymorphismen 4b/a, T786C sowie G894T sind jedoch vermutlich nicht mit einer Suszeptibilität für RA assoziiert.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayanglambam C, Kumar U, Chosdol K, Das N (2014) Endothelial nitricoxide synthase gene intron-4 27 bp repeat polymorphism is not associated with rheumatoidarthritis among Asian Indians. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 5(3(B)):908–912
AlFadhli S (2013) Influence of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene intron-4 27 bp repeat polymorphism on its expression in autoimmune diseases. Dis Markers 34(5):349–356
Alfadhli S, AlTamimy B, AlSaeid K et al (2011) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene haplotype association with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 20(7):700–708
An JD, Li XY, Yu JB et al (2012) Association between the eNOS gene polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis risk in a northern Chinese population. Chin Med J 125(8):1496–1499
Belmont HM, Abramson SB, Lie J (1996) Pathology and pathogenesis of vascular injury in systemic lupus erythematosus. Interactions of inflammatory cells and activated endothelium. Arthritis Rheum 39(1):9–22
Brenol CV, Chies JA, Brenol JC et al (2009) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase T‑786C polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis: association with extraarticular manifestations. Clin Rheumatol 28(2):201–205
Bunjevacki V, Maksimovic N, Jekic B et al (2015) Polymorphisms of the eNOS gene are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int :. doi:10.1007/s00296-015-3401-3
Choi S, Rho Y, Ji J et al (2006) Genome scan meta-analysis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45(2):166–170
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Douglas G, Reilly C, Dooley MA et al (2004) Angiotensin-converting enzyme (insertion/deletion) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 31(9):1756–1762
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56(2):455–463
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M et al (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Förstermann U, Münzel T (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease from marvel to menace. Circulation 113(13):1708–1714
Fowkes FG, Lee AJ, Hau CM et al (2000) Methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and nitric oxide synthase (ecNOS) genes and risks of peripheral arterial disease and coronary heart disease: Edinburgh Artery Study. Atherosclerosis 150(1):179–185
Gilkeson G, Cannon C, Oates J et al (1999) Correlation of serum measures of nitric oxide production with lupus disease activity. J Rheumatol 26(2):318–324
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Llorca J, Sanchez E et al (2004) Inducible but not endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in northwest Spain. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(9):1182–1185
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
Kolb H, Kolb-Bachofen V (1998) Nitric oxide in autoimmune disease: cytotoxic or regulatory mediator? Immunol Today 19(12):556–561
Lee YH, Kim HJ, Rho YH et al (2004) Intron 4 polymorphism of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene is associated with the development of lupus nephritis. Lupus 13(3):188–191
Lee YH, Lee H‑S, Choi SJ et al (2012) Associations between eNOS polymorphisms and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Res 61(2):135–141
Lee YH, Nath SK (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility loci defined by genome scan meta-analysis. Hum Genet 118(3–4):434–443
Li X, An J, Guo R et al (2010) Association of the genetic polymorphisms of the ACE gene and the eNOS gene with lupus nephropathy in northern Chinese population. Bmc Med Genet 11:94
Markiewski MM, Lambris JD (2007) The role of complement in inflammatory diseases from behind the scenes into the spotlight. Am J Pathol 171(3):715–727
Melchers I, Blaschke S, Hecker M et al (2006) The -786C/T single-nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter of the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase: insensitivity to physiologic stimuli as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. Arthritis Care Res 54(10):3144–3151
Mucenic T, Brenol JC, Bredemeier M et al (2009) Glu298Asp eNOS polymorphism is not associated with SLE. Lupus 18(5):448–451
Pober JS, Cotran RS (1990) The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation 50(4):537–544
Rolla G, Brussino L, Bertero M et al (1997) Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 24(6):1066–1071
Salvarani C, Boiardi L, Casali B et al (2002) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms in Behcet’s disease. J Rheumatol 29(3):535–540
Sandoughi M, Salimi S, Zakeri Z et al (2014) Association of eNOS gene polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus in southeast Iran. Int J Rheum Dis :. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12510
Serrano NC, Paez C, Correa PA et al (2004) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 31(11):2163–2168
Suarez-Gestal M, Calaza M, Dieguez-Gonzalez R et al (2009) Rheumatoid arthritis does not share most of the newly identified systemic lupus erythematosus genetic factors. Arthritis Rheum 60(9):2558–2564
Tang FY, Xie XW, Ling GH et al (2010) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase and nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase p22phox gene (C242T) polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese Population. Lupus 19(2):192–196
Tesauro M, Thompson WC, Rogliani P et al (2000) Intracellular processing of endothelial nitric oxide synthase isoforms associated with differences in severity of cardiopulmonary diseases: cleavage of proteins with aspartate vs. glutamate at position 298. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(6):2832–2835
Tsukada T, Yokoyama K, Arai T et al (1998) Evidence of association of the ecNOS gene polymorphism with plasma NO metabolite levels in humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245(1):190–193
Van’t Hof R, Hocking L, Wright P et al (2000) Nitric oxide is a mediator of apoptosis in the rheumatoid joint. Rheumatology 39(9):1004–1008
Vazgiourakis V, Sidiropoulos P, Bertsias G et al (2007) Association of the nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene polymorphism with increased risk for both lupus glomerulonephritis and rheumatoid arthritis in a single genetically homogeneous population. Lupus 16(11):867–874
Yki-Järvinen H, Bergholm R, Leirisalo-Repo M (2003) Increased inflammatory activity parallels increased basal nitric oxide production and blunted response to nitric oxide in vivo in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(7):630–634
Zervou MI, Vazgiourakis VM, Yilmaz N et al (2011) TRAF1/C5, eNOS, C1q, but not STAT4 and PTPN22 gene polymorphisms are associated with genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Turkey. Hum Immunol 72(12):1210–1213
Zhou XJ, Cheng FJ, Zhu L et al (2014) Association of systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility genes with IgA nephropathy in a Chinese cohort. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(4):788–797
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI15C2958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y.H. Lee and S.-C. Bae declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
The accompanying manuscript does not include studies on humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Redaktion
U. Müller-Ladner, Bad Nauheim
U. Lange, Bad Nauheim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.H., Bae, S. Associations between eNOS polymorphisms and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Z Rheumatol 76, 708–715 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0157-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-016-0157-4
Keywords
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- Polymorphism
- Meta-analysis