Summary.
AP-1 dependent genes, e.g., matrix-metallo-proteinases, are involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Therefore, the transcription factor AP-1 and its subunits, proteins of the Jun and Fos proto-oncogene families, are interesting targets for analysis in RA. In this study, we analyzed the mRNA expression of junB in synovial membrane (SM) samples and isolated synovial fibroblasts of patients with RA, osteoarthritis (OA), and normal, non-inflammatory controls.
To address the suitability of real-time RT-PCR for the quantitation of Jun proto-oncogene family members, conventional RTPCR and real-time PCR were comparatively applied for junD, a gene representing a major challenge because of its high GC-content (70%, increasing the probability of secondary structures interfering with the PCR) and its sequence homology to other Jun proto-oncogenes. In addition, a comparison was performed concerning the precision, reproducibility, costs, as well as labor and time consumption of the two PCR methods.
Real-time RT-PCR proved superior to conventional PCR in terms of precision (mean deviation of measured from employed concentration 58% for real-time PCR vs 225% for conventional PCR), reproducibility, as well as labor and time consumption (4 times less for real-time RT-PCR). Experimental cDNA normalization for equivalent cDNA concentrations by sample dilution was more reliable than mathematical cDNA normalization. However, real-time PCR was 3.6-fold more expensive.
Applying the more reliable real-time RT-PCR for the ex vivo analysis of junB mRNA-expression, no significantly different expression of junB was observed in SM or isolated synovial fibroblasts from RA as compared to OA.
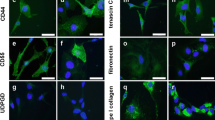
Interestingly, however, junBmRNA expression was significantly lower in RA SM and borderline significantly lower in OA SM than in normal/non-inflammatory SM, with potential effects on the functional properties of the resulting AP-1 complexes. Immunohistochemical staining of the SM with JunB-specific antibodies showed comparable JunB protein expression in SFB (collagen III mRNA-positive) of RA and OA samples.
Thus, real-time RT-PCR appears suitable and time-saving for the quantitation of jun proto-oncogene mRNA-expression in tissue and cell samples with high precision and reproducibility.
Zusammenfassung.
AP-1-abhängige Gene, z. B. Matrix-Metallo- Proteinasen, sind an der Pathogenese der rheumatoiden Arthritis (RA) beteiligt. Deshalb sind der Transkriptionsfaktor AP-1 und seine Untereinheiten – die Proteine der Jun- und Fos-Proto-Onkogen-Familien – interessante Ziele für die Analyse in der RA. In dieser Studie wurde die mRNA-Expression von JunB in Synovialmembran-Gewebeproben (SM) und primären synovialen Fibroblasten von Patienten mit RA und Osteoarthritis (OA), sowie normalen, nicht entzündlichen Kontrollen analysiert.
Um die Eignung der Real-time PCR für die Quantifizierung von Mitgliedern der Jun-Genfamilie zu überprüfen, wurde ein Vergleich der konventionellen RT-PCR mit der Real-time PCR für das Gen junD durchgeführt. Dieses stellt aufgrund seines hohen GC-Gehaltes (70%, wodurch die mögliche Bildung von mit der Polymerase- Reaktion interferierenden Sekundärstrukturen deutlich erhöht wird) und der Sequenzhomologien zu anderen Jun-Genen eine große methodische Herausforderung dar. Außerdem wurde in die Untersuchung ein Vergleich in Hinblick auf die Präzision, die Reproduzierbarkeit, die Kosten, sowie den Arbeits- und Zeitaufwand der beiden Methoden einbezogen.
Die Real-time PCR erwies sich der konventionellen PCR in den Punkten Präzision (die mittlere Abweichung der gemessenen von der eingesetzten Konzentration betrug bei der Real-time PCR 58% gegenüber 225% bei der konventionellen PCR), Reproduzierbarkeit und Arbeits-/Zeitaufwand (4-fach geringer bei der Real-time RT-PCR) überlegen. Eine experimentelle Normalisierung durch Verdünnung der untersuchten cDNA-Proben auf äquivalente cDNA-Konzentrationen stellte sich gegenüber einer rein mathematischen Normalisierung als genauer heraus. Allerdings waren die Kosten der Realtime PCR 3,6-mal so hoch wie die der konventionellen PCR.
Die zuverlässigere Real-time PCR wurde anschließend zur Ex-vivo- Analyse der junB mRNA-Expression eingesetzt. Dabei konnten keine signifikanten Unterschiede zwischen den Expressionsniveaus von junB in SM oder primären synovialen Fibroblasten von RA- und OA-Patienten nachgewiesen werden.
Interessanterweise wurde allerdings eine signifikant niedrigere junB-Expression in der RA-SM und eine grenzwertig signifikant niedrigere junB-Expression in der OA-SM im Vergleich zu den Normalkontrollen beobachtet, was die Funktion der resultierenden AP-1 Komplexe beeinflussen könnte. Die immunhistologische Färbung der SM mit JunB-spezifischen Antikörpern zeigte eine vergleichbare JunB Proteinexpression in SFB (Kollagen III mRNA positiv) bei RA- und OA-Proben.
Insgesamt erwies sich die Realtime RT-PCR in dieser Studie als eine geeignete und zeitsparende Methode für die Quantifizierung der mRNA-Expression von jun- Proto-Onkogenen in Gewebe und Zellproben mit hoher Präzision und Reproduzierbarkeit.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, ., Kunisch, E., Glück, B. et al. Comparison of conventional and real-time RT-PCR for the quantitation of jun protooncogene mRNA and analysis of junB mRNA expression in synovial membranes and isolated synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Z Rheumatol 62, 378– 389 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-003-0472-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-003-0472-4