Abstract
Background
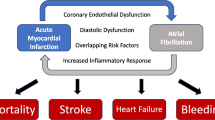
Aim of the current study was to analyse the impact of atrial fibrillation (AF) on prognosis in patients with cardiogenic shock (CS) complicating acute myocardial infarction (AMI), which has never been investigated yet.
Methods
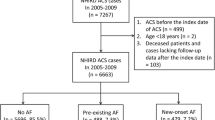
The current analysis is a substudy of the IABP-SHOCK II trial. Patients were grouped according to the presence or absence of AF. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality at 30-day follow-up. Secondary endpoints included all-cause mortality, recurrent myocardial infarction, repeat revascularisation, and stroke at 12 months.
Results
AF was documented in 28.2% (n = 169) of all 600 patients initially enrolled in the IABP-SHOCK II trial. There were no significant differences with respect to mortality at 30 days and 12 months between patients with and without AF (p = 0.81, p = 0.74). Similarly, the rates of recurrent myocardial infarction, repeat revascularisation, and stroke did not differ between groups (all p > 0.05). There was no interaction of intraaortic balloon counterpulsation (IABP) and no IABP in patients with or without AF with respect to clinical outcome at 30 days and 12 months (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
AF is not associated with clinical outcome at 30 days and 12 months in CS complicating AMI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Herpen G, Stricker BH et al (2006) Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J 27:949–953
Rich MW (2009) Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 25:3–8
Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV et al (2001) Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and risk factors in atrial fibrillation (ATRIA) study. JAMA 285:2370–2375
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D (1998) Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 98:946–952
Chopard R, Teiger E, Meneveau N, Chocron S, Gilard M, Laskar M et al (2015) Baseline characteristics and prognostic implications of pre-existing and new-onset atrial fibrillation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: results from the FRANCE-2 registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 8:1346–1355
Tarantini G, Mojoli M, Windecker S, Wendler O, Lefevre T, Saia F et al (2016) Prevalence and impact of atrial fibrillation in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: an analysis from the SOURCE XT prospective multicenter registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 9:937–946
Schmitt J, Duray G, Gersh BJ, Hohnloser SH (2009) Atrial fibrillation in acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review of the incidence, clinical features and prognostic implications. Eur Heart J 30:1038–1045
Jabre P, Roger VL, Murad MH, Chamberlain AM, Prokop L, Adnet F et al (2011) Mortality associated with atrial fibrillation in patients with myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 123:1587–1593
LaPar DJ, Speir AM, Crosby IK, Fonner E Jr, Brown M, Rich JB et al (2014) Postoperative atrial fibrillation significantly increases mortality, hospital readmission, and hospital costs. Ann Thorac Surg 98:527–533 (discussion 33)
Saxena A, Dinh DT, Smith JA, Shardey GC, Reid CM, Newcomb AE (2012) Usefulness of postoperative atrial fibrillation as an independent predictor for worse early and late outcomes after isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (multicenter Australian study of 19,497 patients). Am J Cardiol 109:219–225
Clark DM, Plumb VJ, Epstein AE, Kay GN (1997) Hemodynamic effects of an irregular sequence of ventricular cycle lengths during atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1039–1045
Thiele H, Schuler G, Neumann FJ, Hausleiter J, Olbrich HG, Schwarz B et al (2012) Intraaortic balloon counterpulsation in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock: design and rationale of the intraaortic balloon pump in cardiogenic shock II (IABP-SHOCK II) trial. Am Heart J 163:938–945
Thiele H, Zeymer U, Werdan K (2013) Intraaortic balloon support for cardiogenic shock. N Engl J Med 368:81
Thiele H, Zeymer U, Neumann FJ, Ferenc M, Olbrich HG, Hausleiter J et al (2013) Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock (IABP-SHOCK II): final 12 month results of a randomised, open-label trial. Lancet 382:1638–1645
Werdan K, Ruß M, Buerke M, Engelmann L, Ferrari M, Friedrich I et al (2011) Deutsch-österreichische S3-Leitlinie “Infarktbedingter kardiogener Schock—diagnose, monitoring und Therapie”. Intensivmed Notf 48:291–344
Kopecky SL (1999) Idiopathic atrial fibrillation: prevalence, course, treatment, and prognosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis 7:27–31
Rienstra M, Smit MD, Nieuwland W, Tan ES, Wiesfeld AC, Anthonio RL et al (2007) Persistent atrial fibrillation is associated with appropriate shocks and heart failure in patients with left ventricular dysfunction treated with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Am Heart J 153:120–126
Rathore SS, Berger AK, Weinfurt KP, Schulman KA, Oetgen WJ, Gersh BJ et al (2000) Acute myocardial infarction complicated by atrial fibrillation in the elderly: prevalence and outcomes. Circulation 101:969–974
Bang CN, Gislason GH, Greve AM, Bang CA, Lilja A, Torp-Pedersen C et al (2014) New-onset atrial fibrillation is associated with cardiovascular events leading to death in a first time myocardial infarction population of 89,703 patients with long-term follow-up: a nationwide study. J Am Heart Assoc 3:e000382
Kotecha D, Piccini JP (2015) Atrial fibrillation in heart failure: what should we do? Eur Heart J 36:3250–3257
Sakamoto T, Arai H, Maruyama T, Suzuki A (1995) New algorithm of intra aortic balloon pumping in patients with atrial fibrillation. ASAIO J 41:79–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The IABP-SHOCK II trial was supported by grants from the German Research Foundation, the German Heart Research Foundation, the German Cardiac Society, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Leitende Kardiologische Krankenhausärzte, the University of Leipzig–Heart Centre, and by unrestricted grants from Maquet Cardiopulmonary as well as Teleflex Medical.
Conflict of interest
None relevant to the current study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Waha, S., Schoene, K., Fuernau, G. et al. Prognostic impact of atrial fibrillation in cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction: a substudy of the IABP-SHOCK II trial. Clin Res Cardiol 107, 233–240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-017-1175-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-017-1175-1