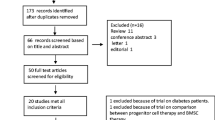
Abstract
Background
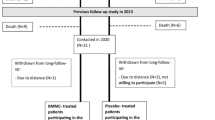
In patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the number of transplanted autologous bone-marrow cells (BMC) has been linked to improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Complete obstruction of myocardial microvasculature is indicated by microvascular obstruction (MO) in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR). We analyzed whether the number of transplanted cells and presence of MO were associated with improved LVEF in the double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized intracoronary Stem Cell therapy in patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction (SCAMI) trial.
Methods and results
Patients (N = 42) received study therapy mean 7 days after AMI. Median number of transplanted BMC was 324 × 106. CMR was performed prior to study therapy and annually up to 3 years and revealed no difference between BMC and placebo population. Patients treated with a cell number above the median experienced a significant improvement in LVEF compared with patients with cell number below the median 3.6 ± 3.4 versus −0.5 ± 6.4 % (difference 4.1, 95 % CI 0.2 to 8.1 %, p = 0.04) at 6 months. The difference in LVEF change between the groups remained with 3.8 % (p = 0.12) at 12 months, 4.5 % (p = 0.07) at 24 months and 5.6 % (p = 0.03) at 36 months. BMC treated patients without MO experienced a better improvement in LVEF compared with patients with MO at 6, 12, 24 and 36 months with 3.5, 5.3, 6.4 and 3.2 %.
Conclusions
In the randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind SCAMI trial improvement in LVEF up to 3 years was higher in BMC patients treated with a high cell number or without MO.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hombach V, Grebe O, Merkle N, Waldenmaier S, Höher M, Kochs M, Wöhrle J, Kestler HA (2005) Sequelae of acute myocardial infarction regarding cardiac structure and function and their prognostic significance as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Heart J 26:549–557
Clifford DM, Fisher SA, Brunskill SJ, Doree C, Mathur A, Watt S, Martin-Rendon E (2012) Stem cell treatment for acute myocardial infarction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 15(2):CD006536
Wöhrle J, Merkle N, Mailänder V, Nusser T, Schauwecker P, von Scheidt F, Schwarz K, Bommer M, Wiesneth M, Schrezenmeier H, Hombach V (2010) Results of intracoronary stem cell therapy after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 105:804–812
Wöhrle J, Merkle N, Kunze M, Cristea E, Mehran R, Rottbauer W, Stone GW (2012) Effect of bivalirudin compared with unfractionated heparin plus abciximab on infarct size and myocardial recovery after primary percutaneous coronary intervention: the horizons-AMI CMRI substudy. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 79:1083–1089
Hombach V, Merkle N, Torzewski J, Kraus JM, Kunze M, Zimmermann O, Kestler HA, Wöhrle J (2009) Electrocardiographic and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging parameters as predictors of a worse outcome in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 30:2011–2018
Zimmet H, Porapakkham P, Porapakkham P, Sata Y, Haas SJ, Itescu S, Forbes A, Krum H (2012) Short- and long-term outcomes of intracoronary and endogenously mobilized bone marrow stem cells in the treatment of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Eur J Heart Fail 14:91–105
Martin-Rendon E, Brunskill SJ, Hyde CJ, Stanworth SJ, Mathur A, Watt SM (2008) Autologous bone marrow stem cells to treat acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 29:1807–1818
Meluzín J, Mayer J, Groch L, Janousek S, Hornácek I, Hlinomaz O, Kala P, Panovský R, Prásek J, Kamínek M, Stanícek J, Klabusay M, Korístek Z, Navrátil M, Dusek L, Vinklárková J (2006) Autologous transplantation of mononuclear bone marrow cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction: the effect of the dose of transplanted cells on myocardial function. Am Heart J 152:975.e9-15
Traverse JH, Henry TD, Ellis SG, Pepine CJ, Willerson JT, Zhao DX, Forder JR, Byrne BJ, Hatzopoulos AK, Penn MS, Perin EC, Baran KW, Chambers J, Lambert C, Raveendran G, Simon DI, Vaughan DE, Simpson LM, Gee AP, Taylor DA, Cogle CR, Thomas JD, Silva GV, Jorgenson BC, Olson RE, Bowman S, Francescon J, Geither C, Handberg E, Smith DX, Baraniuk S, Piller LB, Loghin C, Aguilar D, Richman S, Zierold C, Bettencourt J, Sayre SL, Vojvodic RW, Skarlatos SI, Gordon DJ, Ebert RF, Kwak M, Moyé LA, Simari RD (2011) Cardiovascular Cell Therapy Research Network. Effect of intracoronary delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells 2 to 3 weeks following acute myocardial infarction on left ventricular function: the LateTIME randomized trial. JAMA 306:2110–2119
Quyyumi A, Pecora AL (2012) Intracoronary bone marrow mononuclear cells after myocardial infarction. JAMA 307:1022–1023
Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K, Malliaras K, Thomson LE, Berman D, Czer LS, Marbán L, Mendizabal A, Johnston PV, Russell SD, Schuleri KH, Lardo AC, Gerstenblith G, Marbán E (2012) Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells for heart regeneration after myocardial infarction (CADUCEUS): a prospective, randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet 379:895–904
Shen D, Cheng K, Marbán E (2012) Dose-dependent functional benefit of human cardiosphere transplantation in mice with acute myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med 16:2112–2116
Strauer BE, Steinhoff G (2011) 10 years of intracoronary and intramyocardial bone marrow stem cell therapy of the heart: from the methodological origin to clinical practice. J Am Coll Cardiol 58:1095–1104
Penn MS, Ellis S, Gandhi S, Greenbaum A, Hodes Z, Mendelsohn FO, Strasser D, Ting AE, Sherman W (2012) Adventitial delivery of an allogeneic bone marrow-derived adherent stem cell in acute myocardial infarction: phase I clinical study. Circ Res 110:304–311
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Clinical Trial Registration: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov NCT00669227.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wöhrle, J., von Scheidt, F., Schauwecker, P. et al. Impact of cell number and microvascular obstruction in patients with bone-marrow derived cell therapy: final results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled intracoronary Stem Cell therapy in patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction (SCAMI) trial. Clin Res Cardiol 102, 765–770 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0595-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0595-9