Abstract
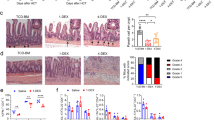
Background: The acute murine semiallogenic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is known to be associated with Th1 cytokines secreting lymphocytes in the spleen and lymph nodes. However, whether this cytokine secretion pattern is also involved in the intestinal manifestations of acute GvHD (crypt hyperplasia and villous atrophy) is not known, so far. Methods: We first investigated the secretion of interleukin (IL) 4 (indicative of Th2-type differentiation) and interferon (IFN) γ (Th1-type differentiation) by splenic and by small bowel lamina propria lymphocytes. In addition, animals were treated with neutralizing antibodies to IL-4 or IL-12. The effect of this treatment on the intestinal morphology was examined. Second, we also investigated the effect of donor-derived IFN-γ by using donor lymphocytes from IFN-γ knock-out animals. Third, animals were treated with the fusion protein OX40-Ig which interferes with the OX40-OX40L interaction and thereby inhibits the intestinal manifestations of acute GvHD. Results: We found that, whereas splenic lymphocytes secrete an excess of IFN-γ, lymphocytes of the intestinal lamina propria secrete less IFN-γ and IL-4 than control animals. When OX40-Ig is administered to animals with acute GvHD, the intestinal histology normalizes as well as the secretion of IFN-γ and IL-4, indicating that the intestinal morphology is not affected by the secretion of IFN-γ by lamina propria lymphocytes. The treatment of animals suffering from acute GvHD with anti-IL-4 and anti-IL-12, which blocks the differentiation of IFN-γ secreting T-lymphocytes, did not significantly affect the development of crypt hyperplasia or villous atrophy. Furthermore, donor lymphocytes of IFN-γ knock-out animals also induced the intestinal manifestations of acute GvHD. Conclusions: These findings indicate that IFN-γ is not crucial for the development of crypt hyperplasia and villous atrophy in the murine semiallogenic GvHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stüber, E., Schlenger, P., Freier, A. et al. Interferon-γ is not involved in the intestinal manifestations of the acute murine semiallogenic graft-versus-host disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 16, 346–351 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003840100322
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003840100322