Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the influence of organic cation transporter 3 (OCT3) expression on the effect of the combination regimen of 5-fluorouracil, folinic acid and oxaliplatin ((m)FOLFOX6) in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
Methods
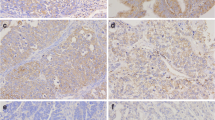
This is a retrospective study conducted at a single centre (Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, China). Patients with stage IIb-IV resectable CRC who were being postoperatively treated with (m)FOLFOX6 as a first-line adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for at least 5 cycles and had resected primary tumour samples available were eligible for the study. Patients who preoperatively received chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy or were treated with targeted drugs or other anticancer drugs were excluded from the study. Immunohistochemical staining and digital image analysis were used to assess OCT3 expression in tumour samples. According to OCT3 expression level, the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) was used to divide the patients into two groups. Cox proportional risk regression was performed with the forward LR (forward stepwise regression based on maximum likelihood estimation) method using SPSS17.0 software. The primary endpoint was the 2-year progression-free survival.
Results
In total, 57 patients were included between 2014 and 2016 according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria (22 had low OCT3 expression, and 35 had high OCT3 expression). The mean age was 55.7 (30–74) years, and 37 of the total patients were male. According to TNM stage, 5 patients had stage IV disease, 44 patients had stage III disease, and 8 patients had stage II disease. Through Cox regression analysis, we found that among patients receiving the (m)FOLFOX6 regimen, those with higher OCT3 expression had a higher two-year progression-free survival rate than those with lower OCT3 expression (P = 0.038). The hazard ratio of patients with high OCT3 expression compared with patients with low OCT3 expression was 0.247. Besides, it was found that the age of patients was negatively correlated with expression level of OCT3, which can explain why patients over 70 years do not benefit from oxaliplatin-containing chemotherapy.
Conclusions
High OCT3 expression in CRC tissues may be a protective factor for CRC patients treated with (m)FOLFOX6.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brody H (2015) Colorectal cancer. Nature 521:S1
Perego P, Robert J (2016) Oxaliplatin in the era of personalized medicine: from mechanistic studies to clinical efficacy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 77:5–18
Madi A, Fisher D, Wilson RH, Adams RA, Meade AM, Kenny SL, Nichols LL, Seymour MT, Wasan H, Kaplan R, Maughan TS (2012) Oxaliplatin/capecitabine vs oxaliplatin/infusional 5-FU in advanced colorectal cancer: the MRC COIN trial. Br J Cancer 107:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.384 published Online First: 2012/09/01
Bahrami A, Amerizadeh F, Hassanian SM, ShahidSales S, Khazaei M, Maftouh M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA, Avan A (2018) Genetic variants as potential predictive biomarkers in advanced colorectal cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. J Cell Physiol 233:2193–2201. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25966
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025 published Online First: 2014/07/25
Hector S, Bolanowska-Higdon W, Zdanowicz J, Hitt S, Pendyala L (2001) In vitro studies on the mechanisms of oxaliplatin resistance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800100363 published Online First: 2002/01/05
Hall MD, Okabe M, Shen DW, Liang XJ, Gottesman MM (2008) The role of cellular accumulation in determining sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:495–535. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.080907.180426 published Online First: 2007/10/17
Buss I, Kalayda GV, Lindauer A et al (2012) Effect of reactivity on cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of oxaliplatin analogues. J Biol Inorg Chem 17:699–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-012-0889-9 published Online First: 2012/03/30
Gupta S, Burckhardt G, Hagos Y (2011) SLC22 transporter family proteins as targets for cytostatic uptake into tumor cells. Biol Chem 392:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1515/bc.2011.014 published Online First: 2011/01/05
Yokoo S, Masuda S, Yonezawa A, Terada T, Katsura T, Inui KI (2008) Significance of organic cation transporter 3 (SLC22A3) expression for the cytotoxic effect of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Drug Metab Dispos 36:2299–2306. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.108.023168 published Online First: 2008/08/20
Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Yokoo S, Katsura T, Inui KI (2006) Cisplatin and oxaliplatin, but not carboplatin and nedaplatin, are substrates for human organic cation transporters (SLC22A1-3 and multidrug and toxin extrusion family). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.110346 published Online First: 2006/08/18
Cheng-Ming Hsu HL, Lin P-M, Chang J-G, Lin H-C, Lin S-F, Yang M-Y (2017) Upregulated SLC22A3 has a potential for improving survival of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma receiving cisplatin treatment. Oncotarget 8:74348–74358
Cui R, Okada Y, Jang SG, Ku JL, Park JG, Kamatani Y, Hosono N, Tsunoda T, Kumar V, Tanikawa C, Kamatani N, Yamada R, Kubo M, Nakamura Y, Matsuda K (2011) Common variant in 6q26-q27 is associated with distal colon cancer in an Asian population. Gut 60:799–805. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.215947 published Online First: 2011/01/19
Chen L, Hong C, Chen EC et al (2013) Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the organic cation transporter 3, SLC22A3. Pharm J 13:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.60
Grisanzio C, Werner L, Takeda D, Awoyemi BC, Pomerantz MM, Yamada H, Sooriakumaran P, Robinson BD, Leung R, Schinzel AC, Mills I, Ross-Adams H, Neal DE, Kido M, Yamamoto T, Petrozziello G, Stack EC, Lis R, Kantoff PW, Loda M, Sartor O, Egawa S, Tewari AK, Hahn WC, Freedman ML (2012) Genetic and functional analyses implicate the NUDT11, HNF1B, and SLC22A3 genes in prostate cancer pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:11252–11257. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200853109
Vollmar J, Lautem A, Closs E, Schuppan D, Kim YO, Grimm D, Marquardt JU, Fuchs P, Straub BK, Schad A, Gründemann D, Schattenberg JM, Gehrke N, Wörns MA, Baumgart J, Galle PR, Zimmermann T (2017) Loss of organic cation transporter 3 (Oct3) leads to enhanced proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncotarget 8:115667–115680 https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23372
Xiong JX, Wang YS, Sheng J, Xiang D, Huang TX, Tan BB, Zeng CM, Li HH, Yang J, Meltzer SJ, Mori Y, Qin YR, Guan XY, Fu L (2018) Epigenetic alterations of a novel antioxidant gene SLC22A3 predispose susceptible individuals to increased risk of esophageal cancer. Int J Biol Sci 14:1658–1668. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.28482 published Online First: 2018/11/13
Fu L, Qin YR, Ming XY, Zuo XB, Diao YW, Zhang LY, Ai J, Liu BL, Huang TX, Cao TT, Tan BB, Xiang D, Zeng CM, Gong J, Zhang Q, Dong SS, Chen J, Liu H, Wu JL, Qi RZ, Xie D, Wang LD, Guan XY (2017) RNA editing of SLC22A3 drives early tumor invasion and metastasis in familial esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4631–E4E40. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1703178114
Le Roy B, Tixier L, Pereira B et al (2016) Assessment of the relation between the expression of Oxaliplatin transporters in colorectal Cancer and response to FOLFOX-4 adjuvant chemotherapy: a case control study. PLoS One 11:e0148739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148739 published Online First: 2016/02/10
Maloney JP, Stearman RS, Bull TM, Calabrese DW, Tripp-Addison ML, Wick MJ, Broeckel U, Robbins IM, Wheeler LA, Cogan JD, Loyd JE (2012) Loss-of-function thrombospondin-1 mutations in familial pulmonary hypertension. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 302(6):L541–L554
Juan G, Wang L, Li T et al (2019) Rloe and mechanism of organic cation transporter 3 in oxaliplatin treatment of colon cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep 42:1355–1364. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7267
Tournigand C, Andre T, Bonnetain F et al (2012) Adjuvant therapy with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in stage II and elderly patients (between ages 70 and 75 years) with colon cancer: subgroup analyses of the multicenter international study of Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in the adjuvant treatment of Colon Cancer trial. J Clin Oncol 30:3353–3360. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2012.42.5645 published Online First: 2012/08/24
Jiao D, Zhang R, Gong Z, Liu F, Chen Y, Yu Q, Sun L, Duan H, Zhu S, Liu F, Wang J, Jia J (2015) Fluorouracil-based preoperative chemoradiotherapy with or without oxaliplatin for stage II/III rectal cancer: a 3-year follow-up study. Chin J Cancer Res 27:588–596. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.12.05 published Online First: 2016/01/12
Wu JB, Tang YL, Liang XH (2018) Targeting VEGF pathway to normalize the vasculature: an emerging insight in cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther 11:6901–6909. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S172042
Ohkawa K, Asakura T, Tsukada Y, Matsuura T (2017) Antibody to human alpha-fetoprotein inhibits cell growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by resuscitating the PTEN molecule: in vitro experiments. Int J Oncol 50:2180–2190. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3982 published Online First: 2017/05/13
Acknowledgements
We thank to Liu Huan, Wu Xingwei for technical assistance in data collecting of patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: JG, LW, XJ. Acquisition of data: JG, EL, DD, Analysis and interpretation of data: JG, TL. Drafting the manuscript: JG, ST, SF. Final approval of the version to be published: JG, XJ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committees at Sichuan academy of medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital in China. Written informed consent was not obtained from the patients or their relatives due to the retrospective study design of using the electronic health records and no additional interventions were given to the subjects.
Competing of interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Juan Gu and Dandan Dong are Co-first author
A brief description
This study explored the relationship of transporter OCT3 protein expression level in colorectal cancer tissues and the effect of oxaliplatin on colorectal cancer. The population we investigated were patients with stage IIb-IV resectable CRC who were postoperatively treated with (m)FOLFOX6 as a first-line adjuvant chemotherapy regimen. We found that the prognosis differed between patients with high OCT3 expression level and low OCT3 expression level, and the age of patients was negatively correlated with expression level of OCT3. These findings could help in implementing appropriate CRC treatment regimens.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Dong, D., Long, E. et al. Upregulated OCT3 has the potential to improve the survival of colorectal cancer patients treated with (m)FOLFOX6 adjuvant chemotherapy. Int J Colorectal Dis 34, 2151–2159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03407-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-019-03407-x