Abstract
Purpose
Several factors may influence the risk of recurrence after an episode of acute colonic diverticulitis. Until now, a comprehensive systematic overview and evaluation of relevant risk factors have not been presented. This review aimed at assembling and evaluating current evidence on risk factors for recurrence after conservatively treated acute colonic diverticulitis.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched for studies evaluating risk factors for recurrence after acute diverticulitis treated non-surgically defined as antibiotic treatment, percutaneous abscess drainage, or by observation. Randomized clinical trials and observational studies were included. Analyzed outcome variables were extracted and grouped. No meta-analysis was performed due to low inter-study comparability. Variables were rated according to their likelihood of causing recurrence (no/low, medium, high).
Results
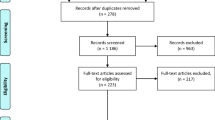
Of 1153 screened records, 35 studies were included, enrolling 396,676 patients with acute diverticulitis. A total of 50,555 patients experienced recurrences. Primary diverticulitis with abscess formation and young age increased the risk of recurrence. Readmission risk was higher within the first year after remission. In addition, the risk of subsequent diverticulitis more than doubled after two earlier episodes of diverticulitis and the risk increased further for every episode.
Conclusions
The best treatment strategy for recurrent diverticulitis is undetermined. However, the risk of a new recurrence seemed to increase after each recurrence making elective resection a viable option at some point after multiple recurrences depending on patient risk factors and preferences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parks TG (1975) Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol 4:53–69
Hall JF, Roberts PL, Ricciardi R, Read T et al (2011) Long-term follow-up after an initial episode of diverticulitis: what are the predictors of recurrence? Dis Colon rectum 54:283–288. doi:10.1007/DCR.0b013e3182028576
Nguyen GC, Sam J, Anand N (2011) Epidemiological trends and geographic variation in hospital admissions for diverticulitis in the United States. World J Gastroenterol 17:1600–1605. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i12.1600
Ünlü Ç, Daniels L, Vrouenraets BC, Boermeester MA (2012) Systematic review of medical therapy to prevent recurrent diverticulitis 27:1131–1136. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1486-7
Lopez-Borao J, Kreisler E, Millan M, Trenti L et al (2012) Impact of age on recurrence and severity of left colonic diverticulitis. Color Dis 14:e407–e412. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2012.02976.x
Haglund U, Hellberg R, Johnsén C, Hultén L (1979) Complicated diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon. An analysis of short and long term outcome in 392 patients. Ann Chir Gynaecol 68:41–46
Biondo S, Parés D, Martí Ragué J, Kreisler E et al (2002) Acute colonic diverticulitis in patients under 50 years of age. Br J Surg 89:1137–1141
Sandler RS, Everhart JE, Donowitz M, Adams E et al (2002) The burden of selected digestive diseases in the United States. Gastroenterology 122:1500–1511
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies. JAMA 283:2008–2012
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, et al. (2016) The Newcastle-Ottowa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. The Ottowa Hospital Research Institute Publishing OHRI. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 29 Sept 2016
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C et al (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Van de Wall BJ, Draaisma WA, Consten ECJ, van der Kaaij RT et al (2013) Does the presence of abscesses in diverticular disease prelude surgery? J Gastrointest Surg 17:540–547. doi:10.1007/s11605-012-2097-x
Unlü C, van de Wall BJ, Gerhards MF, Wiezer M et al (2013) Influence of age on clinical outcome of acute diverticulitis. J Gastrointest Surg 17:1651–1656. doi:10.1007/s11605-013-2240-3
Trenti L, Kreisler E, Galvez A, Golda T et al (2015) Long-term evolution of acute colonic diverticulitis after successful medical treatment. World J Surg 39:266–274
Broderick-Villa G, Burchette RJ, Collins JC, Abbas MA et al (2005) Hospitalization for acute diverticulitis does not mandate routine elective colectomy. Arch Surg 140:576–583
Parente F, Bargiggia S, Prada A, Bortoli A et al (2013) Intermittent treatment with mesalazine in the prevention of diverticulitis recurrence: a randomised multicentre pilot double-blind placebo-controlled study of 24-month duration. Int J Color Dis 28:1423–1431. doi:10.1007/s00384-013-1722-9
Raskin JB, Kamm MA, Jamal MM et al (2014) Mesalamine did not prevent recurrent diverticulitis in phase 3 controlled trials. Gastroenterology 147:793–802
Lidor AO, Segal JB, Wu AW, Yu Q et al (2011) Older patients with diverticulitis have low recurrence rates and rarely need surgery. Surgery 150:146–153. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2011.05.006
Faria GR, Almeida AB, Moreira H, Pinto-de-Sousa J et al (2011) Acute diverticulitis in younger patients: any rationale for a different approach? World J Gastroenterol 17:207–212. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.207
Bose KP, Khorshidi I, Southern WN, Brandt LJ (2009) The impact of ethnicity and obesity on the course of colonic diverticulitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 47:160–164. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e318259e71c
Binda GA, Arezzo A, Serventi A, Bonelli L et al (2012) Multicentre observational study of the natural history of left-sided acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 99:276–285. doi:10.1002/bjs.772
Li D, de Mestral C, Baxter NN, McLeod RS et al (2014) Risk of readmission and emergency surgery following nonoperative management of colonic diverticulitis: a population-based analysis. Ann Surg 260:423–431. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000000870
Sallinen V, Mali J, Leppäniemi A, Mentula P (2015) Assessment of risk for recurrent diverticulitis: a proposal of risk score for complicated recurrence. Medicine 94:e557. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000557
Bharucha AE, Parthasarathy G, Ditah I, Fletcher JG et al (2015) Temporal trends in the incidence and natural history of diverticulitis: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol 110:1589–1596. doi:10.1038/ajg.2015.302
Ho VP, Nash GM, Milsom JW, Lee SW (2015) Identification of diverticulitis patients at high risk for recurrence and poor outcomes. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 78:112–119. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000000466
Rose J, Parina ÃRP, Faiz ÃO, Chang DC et al (2015) Long-term outcomes after initial presentation of diverticulitis. Ann Surg 262:1046–1053
Garfinkle R, Kugler A, Pelsser V, Vasilevsky CA et al (2016) Diverticular abscess managed with long-term definitive nonoperative intent is safe. Dis Colon rectum 59:648–655
Buchs NC, Konrad-Mugnier B, Jannot AS, Poletti P et al (2013) Assessment of recurrence and complications following uncomplicated diverticulitis. Br J Surg 100:976–979. doi:10.1002/bjs.9119
Park SM, Kwon TS, Kim DJ, Lee YS et al (2014) Prediction and management of recurrent right colon diverticulitis. Int J Color Dis 29:1355–1360. doi:10.1007/s00384-014-1938-37
Mäkelä J, Vuolio S, Kiviniemi H, Laitinen S (1998) Natural history of diverticular disease: when to operate? Dis Colon rectum 41:1523–1528
Frileux P, Dubrez J, Burdy G, Roullet-Audy JC et al (2010) Sigmoid diverticulitis. Longitudinal analysis of 222 patients with a minimal follow up of 5 years. Color Dis 12:674–680. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2009.01866.x
Nelson RS, Ewing BM, Wengert TJ, Thorson AG (2008) Clinical outcomes of complicated diverticulitis managed nonoperatively. Am J Surg 196:969–974. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.07.035
Reisman Y, Ziv Y, Kravrovitc D, Negri M et al (1999) Diverticulitis: the effect of age and location on the course of disease. Int J Color Dis 14:250–254
Mueller MH, Glatzle J, Kasparek MS, Becker HD et al (2005) Long-term outcome of conservative treatment in patients with diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:649–654
Hjern F, Josephson T, Altman D, Holmström B et al (2008) Outcome of younger patients with acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 95:758–764. doi:10.1002/bjs.6137
Pittet O, Kotzampassakis N, Schmidt S, Denys A et al (2009) Recurrent left colonic diverticulitis episodes: more severe than the initial diverticulitis? World J Surg 33:547–552. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9898-9
Gatta L, Di Mario F, Curlo M, Vaira D et al (2012) Long-term treatment with mesalazine in patients with symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease. Intern Emerg Med 7:133–137. doi:10.1007/s11739-011-0509-7
Tursi A, Elisei W, Giorgetti GM, Inchingolo CD et al (2013) Effectiveness of different therapeutic strategies in preventing diverticulitis recurrence. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:342–348
Scarpa CR, Buchs NC, Poncet A, Konrad-mugnier B et al (2015) Coloproctology short-term intravenous antibiotic treatment in uncomplicated diverticulitis does not increase the risk of recurrence compared to long-term treatment. Coloproctology 31:52–56
Gaertner WB, Willis DJ, Madoff RD, Rothenberger DA et al (2013) Percutaneous drainage of colonic diverticular abscess: is colon resection necessary? Dis Colon rectum 56:622–626. doi:10.1097/DCR.0b013e31828545e3
Park HC, Kim BS, Lee K, Kim MJ et al (2014) Risk factors for recurrence of right colonic uncomplicated diverticulitis after first attack. Int J Color Dis 29:1217–1222. doi:10.1007/s00384-014-1941-8
Devaraj B, Liu W, Tatum J, Cologne K et al (2016) Medically treated diverticular abscess associated with high risk of recurrence and disease complications. Dis Colon rectum 59:208–215
Gregersen R, Andresen K, Burcharth J, Pommergaard HC et al (2016) Short-term mortality, readmission, and recurrence in treatment of acute diverticulitis with abscess formation: a nationwide register-based cohort study. Int J Color Dis 31:983–990
Biondo S, Borao JL, Kreisler E, Golda T et al (2012) Recurrence and virulence of colonic diverticulitis in immunocompromised patients. Am J Surg 204:172–179. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.09.027
Katz LH, Guy DD, Lahat A, Gafter-Gvili A et al (2013) Diverticulitis in the young is not more aggressive than in the elderly, but it tends to recur more often: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28:1274–1281. doi:10.1111/jgh.12274
Andeweg C, Peters J, Bleichrodt R, van Goor H (2008) Incidence and risk factors of recurrence after surgery for pathology-proven diverticular disease. World J Surg 32:1501–1506
Anaya D, Flum D (2005) Risk of emergency colectomy and colostomy in patients with diverticular disease. Arch Surg 140:681–685
Al-Khamis A, Abou Khalil J, Demian M et al (2016) Sigmoid colectomy for acute diverticulitis in immunosuppressed vs immunocompetent patients: outcomes from the ACS-NSQIP database. Dis Colon rectum 59:101–109. doi:10.1097/DCR.0000000000000513
Van de Wall BJ, Draaisma WA, Consten ECJ et al (2010) DIRECT trial. Diverticulitis recurrences or continuing symptoms: operative versus conservative treatment. A multicenter randomized clinical trial. BMC Surg 10:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-10-25
Thomas K, Jackson A, Bell R (2013) Prophylactic antibiotics for preventing recurrent symptomatic episodes of acute diverticulitis (Protocol). Wiley Online Library Publishing The Cochrane Library. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010635/epdf. Accessed 29 Sept 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hupfeld, L., Burcharth, J., Pommergaard, HC. et al. Risk factors for recurrence after acute colonic diverticulitis: a systematic review. Int J Colorectal Dis 32, 611–622 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2766-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2766-z