Abstract
Introduction
Probiotics are defined as live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. These probiotic effects are considered to be displayed through the mediation of effective molecules derived from these bacteria because live bacteria as well as their conditioned media exhibit beneficial effects in many cases. However, many of the probiotic-derived molecules which mediate such benefits have so far been poorly characterized. We previously found that competence and sporulation factor (CSF) activates the Akt and p38 MAPK pathways and protects epithelial cells from oxidant stress in the mammalian intestine. The purpose of this study is to determine the CSF effect on reducing intestinal inflammation.
Methods and results
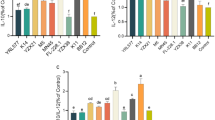
A protein array demonstrated that CSF induced the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10, and decreased the release of pro-inflammatory mediators, IL-4, IL-6 and CXCL-1, induced by TNF-α in Caco2/bbe cells. CSF also induced the cytoprotective protein Hsp 27 in Caco2/bbe cells. The histological score of intestinal inflammation in 2% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-treated mice with the administration of 10 nM CSF was significantly lower than that of control mice. CSF also improved the survival rate of mice treated with a lethal concentration of DSS.
Conclusion
Therefore, CSF is a potentially effective treatment for intestinal inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hooper LV, Wong MH, Thelin A, Hansson L, Falk PG, Gordon JI (2001) Molecular analysis of commensal host-microbial relationships in the intestine. Science 291(5505):881–884. doi:10.1126/science.291.5505.881
Sudo N, Sawamura S, Tanaka K, Aiba Y, Kubo C, Koga Y (1997) The requirement of intestinal bacterial flora for the development of an IgE production system fully susceptible to oral tolerance induction. J Immunol 159(4):1739–1745
Guarner F, Malagelada JR (2003) Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361(9356):512–519. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12489-0
Rousseaux C, Thuru X, Gelot A, Barnich N, Neut C, Dubuquoy L, Dubuquoy C, Merour E, Geboes K, Chamaillard M, Ouwehand A, Leyer G, Carcano D, Colombel JF, Ardid D, Desreumaux P (2007) Lactobacillus acidophilus modulates intestinal pain and induces opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Nat Med 13(1):35–37. doi:10.1038/nm1521
Kruis W, Schutz E, Fric P, Fixa B, Judmaier G, Stolte M (1997) Double-blind comparison of an oral Escherichia coli preparation and mesalazine in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 11(5):853–858
Rembacken BJ, Snelling AM, Hawkey PM, Chalmers DM, Axon AT (1999) Non-pathogenic Escherichia coli versus mesalazine for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a randomised trial. Lancet 354(9179):635–639
Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, Brigidi P, Matteuzzi D, Bazzocchi G, Poggioli G, Miglioli M, Campieri M (2000) Oral bacteriotherapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 119(2):305–309
Kato K, Mizuno S, Umesaki Y, Ishii Y, Sugitani M, Imaoka A, Otsuka M, Hasunuma O, Kurihara R, Iwasaki A, Arakawa Y (2004) Randomized placebo-controlled trial assessing the effect of bifidobacteria-fermented milk on active ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20(10):1133–1141. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02268.x
Bibiloni R, Fedorak RN, Tannock GW, Madsen KL, Gionchetti P, Campieri M, De Simone C, Sartor RB (2005) VSL#3 probiotic-mixture induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 100(7):1539–1546. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41794.x
Surawicz CM, Elmer GW, Speelman P, McFarland LV, Chinn J, van Belle G (1989) Prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea by Saccharomyces boulardii: a prospective study. Gastroenterology 96(4):981–988
McFarland LV, Surawicz CM, Greenberg RN, Fekety R, Elmer GW, Moyer KA, Melcher SA, Bowen KE, Cox JL, Noorani Z et al (1994) A randomized placebo-controlled trial of Saccharomyces boulardii in combination with standard antibiotics for Clostridium difficile disease. JAMA: J Am Med Assoc 271(24):1913–1918
Bin-Nun A, Bromiker R, Wilschanski M, Kaplan M, Rudensky B, Caplan M, Hammerman C (2005) Oral probiotics prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates. J Pediatr 147(2):192–196. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.03.054
Lin HC, Hsu CH, Chen HL, Chung MY, Hsu JF, Lien RI, Tsao LY, Chen CH, Su BH (2008) Oral probiotics prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight preterm infants: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 122(4):693–700. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-3007
Wehkamp J, Harder J, Wehkamp K, Wehkamp-von Meissner B, Schlee M, Enders C, Sonnenborn U, Nuding S, Bengmark S, Fellermann K, Schroder JM, Stange EF (2004) NF-kappaB- and AP-1-mediated induction of human beta defensin-2 in intestinal epithelial cells by Escherichia coli Nissle 1917: a novel effect of a probiotic bacterium. Infect Immun 72(10):5750–5758. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.10.5750-5758.2004
Schlee M, Harder J, Koten B, Stange EF, Wehkamp J, Fellermann K (2008) Probiotic lactobacilli and VSL#3 induce enterocyte beta-defensin 2. Clin Exp Immunol 151(3):528–535. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03587.x
Mondel M, Schroeder BO, Zimmermann K, Huber H, Nuding S, Beisner J, Fellermann K, Stange EF, Wehkamp J (2009) Probiotic E. coli treatment mediates antimicrobial human beta-defensin synthesis and fecal excretion in humans. Mucosal Immunol 2(2):166–172. doi:10.1038/mi.2008.77
Yan F, Polk DB (2002) Probiotic bacterium prevents cytokine-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 277(52):50959–50965. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207050200
Tao Y, Drabik KA, Waypa TS, Musch MW, Alverdy JC, Schneewind O, Chang EB, Petrof EO (2006) Soluble factors from Lactobacillus GG activate MAPKs and induce cytoprotective heat shock proteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(4):C1018–C1030. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00131.2005
Morita H, He F, Fuse T, Ouwehand AC, Hashimoto H, Hosoda M, Mizumachi K, Kurisaki J (2002) Adhesion of lactic acid bacteria to caco-2 cells and their effect on cytokine secretion. Microbiol Immunol 46(4):293–297
Hosoi T, Hirose R, Saegusa S, Ametani A, Kiuchi K, Kaminogawa S (2003) Cytokine responses of human intestinal epithelial-like Caco-2 cells to the nonpathogenic bacterium Bacillus subtilis (natto). Int J Food Microbiol 82(3):255–264
Kelly D, Campbell JI, King TP, Grant G, Jansson EA, Coutts AG, Pettersson S, Conway S (2004) Commensal anaerobic gut bacteria attenuate inflammation by regulating nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of PPAR-gamma and RelA. Nat Immunol 5(1):104–112. doi:10.1038/ni1018
Petrof EO, Kojima K, Ropeleski MJ, Musch MW, Tao Y, De Simone C, Chang EB (2004) Probiotics inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB and induce heat shock proteins in colonic epithelial cells through proteasome inhibition. Gastroenterology 127(5):1474–1487
Jijon H, Backer J, Diaz H, Yeung H, Thiel D, McKaigney C, De Simone C, Madsen K (2004) DNA from probiotic bacteria modulates murine and human epithelial and immune function. Gastroenterology 126(5):1358–1373
Zhang L, Li N, Caicedo R, Neu J (2005) Alive and dead Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decrease tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced interleukin-8 production in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 135(7):1752–1756
Otte JM, Podolsky DK (2004) Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286(4):G613–G626. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00341.2003
O'Hara AM, O'Regan P, Fanning A, O'Mahony C, Macsharry J, Lyons A, Bienenstock J, O'Mahony L, Shanahan F (2006) Functional modulation of human intestinal epithelial cell responses by Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus salivarius. Immunology 118(2):202–215. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02358.x
Broekaert IJ, Nanthakumar NN, Walker WA (2007) Secreted probiotic factors ameliorate enteropathogenic infection in zinc-deficient human Caco-2 and T84 cell lines. Pediatr Res 62(2):139–144. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e31809fd85e
Lopez M, Li N, Kataria J, Russell M, Neu J (2008) Live and ultraviolet-inactivated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decrease flagellin-induced interleukin-8 production in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 138(11):2264–2268. doi:10.3945/jn.108.093658
Candela M, Perna F, Carnevali P, Vitali B, Ciati R, Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Campieri M, Brigidi P (2008) Interaction of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains with human intestinal epithelial cells: adhesion properties, competition against enteropathogens and modulation of IL-8 production. Int J Microbiol 125(3):286–292. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.04.012
Zeuthen LH, Fink LN, Frokiaer H (2008) Epithelial cells prime the immune response to an array of gut-derived commensals towards a tolerogenic phenotype through distinct actions of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and transforming growth factor-beta. Immunology 123(2):197–208. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02687.x
Ueno N, Fujiya M, Segawa S, Nata T, Moriichi K, Tanabe H, Mizukami Y, Kobayashi N, Ito K, Kohgo Y (2011) Heat-killed body of Lactobacillus brevis SBC8803 ameliorates intestinal injury in a murine model of colitis by enhancing the intestinal barrier function. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(11):2235–2250. doi:10.1002/ibd.21597
Lievin V, Peiffer I, Hudault S, Rochat F, Brassart D, Neeser JR, Servin AL (2000) Bifidobacterium strains from resident infant human gastrointestinal microflora exert antimicrobial activity. Gut 47(5):646–652
Fujiya M, Musch MW, Nakagawa Y, Hu S, Alverdy J, Kohgo Y, Schneewind O, Jabri B, Chang EB (2007) The Bacillus subtilis quorum-sensing molecule CSF contributes to intestinal homeostasis via OCTN2, a host cell membrane transporter. Cell Host Microbe 1(4):299–308. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2007.05.004
Yan F, Cao H, Cover TL, Whitehead R, Washington MK, Polk DB (2007) Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth. Gastroenterology 132(2):562–575. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.022
Alexopoulos C, Georgoulakis IE, Tzivara A, Kyriakis CS, Govaris A, Kyriakis SC (2004) Field evaluation of the effect of a probiotic-containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis spores on the health status, performance, and carcass quality of grower and finisher pigs. J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med 51(6):306–312. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0442.2004.00637.x
D'Arienzo R, Maurano F, Mazzarella G, Luongo D, Stefanile R, Ricca E, Rossi M (2006) Bacillus subtilis spores reduce susceptibility to Citrobacter rodentium-mediated enteropathy in a mouse model. Res Microbiol 157(9):891–897. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2006.06.001
Solomon JM, Lazazzera BA, Grossman AD (1996) Purification and characterization of an extracellular peptide factor that affects two different developmental pathways in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev 10(16):2014–2024
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero MG, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Borchert S, Borriss R, Boursier L, Brans A, Braun M, Brignell SC, Bron S, Brouillet S, Bruschi CV, Caldwell B, Capuano V, Carter NM, Choi SK, Codani JJ, Connerton IF, Danchin A et al (1997) The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390(6657):249–256. doi:10.1038/36786
Lazazzera BA, Solomon JM, Grossman AD (1997) An exported peptide functions intracellularly to contribute to cell density signaling in B. subtilis. Cell 89(6):917–925
Tam NK, Uyen NQ, Hong HA, le Duc H, Hoa TT, Serra CR, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (2006) The intestinal life cycle of Bacillus subtilis and close relatives. J Bacteriol 188(7):2692–2700. doi:10.1128/JB.188.7.2692-2700.2006
Musch MW, Kaplan B, Chang EB (2001) Role of increased basal expression of heat shock protein 72 in colonic epithelial c2BBE adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ: Mol Biol J Am Assoc Cancer Res 12(8):419–426
Ropeleski MJ, Tang J, Walsh-Reitz MM, Musch MW, Chang EB (2003) Interleukin-11-induced heat shock protein 25 confers intestinal epithelial-specific cytoprotection from oxidant stress. Gastroenterology 124(5):1358–1368
Ropeleski MJ, Riehm J, Baer KA, Musch MW, Chang EB (2005) Anti-apoptotic effects of L-glutamine-mediated transcriptional modulation of the heat shock protein 72 during heat shock. Gastroenterology 129(1):170–184
Berg DJ, Davidson N, Kuhn R, Muller W, Menon S, Holland G, Thompson-Snipes L, Leach MW, Rennick D (1996) Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4(+) TH1-like responses. J Clin Invest 98(4):1010–1020. doi:10.1172/JCI118861
Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W (1993) Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75(2):263–274
McFarland LV (2006) Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhea and the treatment of Clostridium difficile disease. Am J Gastroenterol 101(4):812–822. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00465.x
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Rahimi F, Elahi B, Derakhshani S, Vafaie M, Abdollahi M (2008) A meta-analysis on the efficacy of probiotics for maintenance of remission and prevention of clinical and endoscopic relapse in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci 53(9):2524–2531. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-0171-0
Hu S, Ciancio MJ, Lahav M, Fujiya M, Lichtenstein L, Anant S, Musch MW, Chang EB (2007) Translational inhibition of colonic epithelial heat shock proteins by IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha in intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 133(6):1893–1904. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.026
Schroeder BO, Wu Z, Nuding S, Groscurth S, Marcinowski M, Beisner J, Buchner J, Schaller M, Stange EF, Wehkamp J (2011) Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human beta-defensin 1. Nature 469(7330):419–423. doi:10.1038/nature09674
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research no. 20590734 (M.F.) and the Intractable Disease, the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, K., Fujiya, M., Nata, T. et al. Competence and sporulation factor derived from Bacillus subtilis improves epithelial cell injury in intestinal inflammation via immunomodulation and cytoprotection. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 1039–1046 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1416-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1416-8