Abstract
Purpose
Pleiotrophin (PTN) is an important developmental secretory cytokine expressed in many types of cancer and involved in angiogenesis and tumor growth; however, the significance of PTN expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) has not been established.
Methods
Immunohistochemistry, western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were used to detect PTN expression in CRC patients. The relationship between PTN expression and clinicopathological characteristics and survival time was statistically analyzed, and the relationship between PTN and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in tumor angiogenesis was further analyzed.
Results
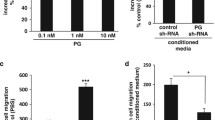
Of CRC tissues, 74.70% (62/83) stained positive, with a strong positive ratio of 60.24% (50/83). The expression of PTN in CRC tissues was much higher than in normal colorectal tissues. PTN serum levels in CRC patients (mean = 254.59 ± 261.76 pg/ml) were significantly higher than those of normal volunteers (mean = 115.23 ± 79.53 pg/ml; p < 0.001). PTN expression was related to CRC differentiation and TNM staging. High level of PTN is a predictor of a poor prognosis and high expression of PTN is accompanied by high expression of VEGF in CRC patients. Investigation of the relationship between PTN and VEGF revealed that PTN, through the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ signaling pathway, increased tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin, leading to an increase in VEGF.
Conclusions
Our study identifies PTN as an essential growth factor for CRC. PTN promotes VEGF expression and cooperates with VEGF in promoting CRC angiogenesis. PTN could serve as a prognostic factor for this cancer. Considering that PTN shows very limited expression in normal tissue, it may represent an attractive new target for CRC therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YS, Milner PG, Chauhan AK, Watson MA, Hoffman RM, Kodner CM, Milbrandt J, Deuel TF (1990) Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated protein that induces mitogenic and neurite outgrowth activity. Science 250(4988):1690–1694
Polykratis A, Delbé J, Courty J, Papadimitriou E, Katsoris P (2004) Identification of Heparin affin regulation peptide domains with potential role on angiogenesis. Int J Biochen Cell Biol 36(10):1954–1966
Chang Y, Zuka M, Perez-Pinera P, Astudillo A, Mortimer J, Berenson JR, Deuel TF (2007) Secretion of pleiotrophin stimulates breast cancer progression through remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(26):10888–10893
Souttou B, Juhl H, Hackenbruck J, Röckseisen M, Klomp HJ, Raulais D, Vigny M, Wellstein A (1998) Relationship between serum concentrations of the growth factor pleiotrophin and pleiotrophin-positive tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(19):1468–1473
Calvet L, Geoerger B, Regairaz M, Opolon P, Machet L, Morizet J, Joseph JM, Elie N, Vassal G (2006) Pleiotrophin, a candidate gene for poor tumor vasculature and in vivo neuroblastoma sensitivityto irinotecan. Oncogene 25(22):3150–3159
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM (1995) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 55(18):3964–3968
Lee JC, Chow NH, Wang ST, Huang SM (2000) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colorectal cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 36(6):748–753
Meng K, Rodriguez-Peña A, Dimitrov T, Chen W, Yamin M, Noda M, Deuel TF (2000) Pleiotrophin signals increased tyrosine phosphorylation of beta-catenin through inactivation of the intrinsic catalytic activity of the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(6):2603–2608
Skurk C, Maatz H, Rocnik E, Bialik A, Force T, Walsh K (2005) Glycogen-Synthase Kinase3beta/beta-catenin axis promotes angiogenesis through activation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 96(3):308–318
Easwaran V, Lee SH, Inge L, Guo L, Goldbeck C, Garrett E, Wiesmann M, Garcia PD, Fuller JH, Chan V, Randazzo F, Gundel R, Warren RS, Escobedo J, Aukerman SL, Taylor RN, Fantl WJ (2003) ß-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res 63(12):3145–3153
Héroult M, Bernard-Pierrot I, Delbé J, Hamma-Kourbali Y, Katsoris P, Barritault D, Papadimitriou E, Plouet J, Courty J (2004) Heparin affin regulatory peptide binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)and inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Oncogene 23(9):1745–1753
Gorreta F, Runfola TP, VanMeter AJ, Barzaghi D, Chandhoke V, Del Giacco L (2005) Identification of thioredoxin reductase 1-regulated genes using small interference RNA and cDNA microarray. Cancer Biol Ther 4(10):1079–1088
Muramatsu T (2002) Midkine and pleiotrophin: two related proteins involved in development, survival, inflammation and tumorigenesis. J Biochem 132(3):359–371
Yamakawa T, Kurosawa N, Kadomatsu K, Matsui T, Itoh K, Maeda N, Noda M, Muramatsu T (1999) Levels of expression of pleiotrophin and protein tyrosine phosphatasez are decreased in human colorectal cancers. Cancer Lett 135(1):91–96
Vacherot F, Delbé J, Heroult M, Barritault D, Fernig DG, Courty J (1999) Glycosaminoglycans differentially bind HARP and modulate its biological activity. J Biol Chem 274(12):7741–7747
Isemura M, Sato N, Munakata H, Aikawa J, Ototani N, Yosizawa Z, Sakuma A, Masuda T, Aoyagi Y, Ichida F (1984) Glycosaminoglycans of human colonic mucosa and colonic adenocarcinoma. Tohoku J Exp Med 142(1):89–95
Dai J, Rabie AB (2007) VEGF:an essential mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondral ossification. J Dent Res 86(10):937–950
Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Cervi D, Haeri M, Li Y, Nagy A, Ben-David Y (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor—a positive and negative regulator of tumor growth. Cancer Res 70(3):863–867
Novotny WF, Maffi T, Mehta RL, Milner PG (1993) Identification of novel heparin-releasable proteins, as well as the cytokines midkine and pleiotrophin, in human postheparin plasma. Arterioscler Thromb 13(12):1798–1805
Polytarchou C, Hatziapostolou M, Papadimitriou E (2005) Hydrogen peroxide stimulates proliferation and migration of human prostate cancer cells through activation of activator protein-1 and up-regulation of the heparin affin regulatory peptide gene. J Biol Chem 280(49):40428–40435
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE, Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM, Schumacker PT (2000) Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of O2 sensing. J Biol Chem 275(33):25130–25138
Coothankandaswamy V, Liu Y, Mao SC, Morgan JB, Mahdi F, Jekabsons MB, Nagle DG, Zhou YD (2010) The alternative medicine pawpaw and its acetogenin constituents suppress tumor angiogenesis via the HIF-1/VEGF pathway. J Nat Prod 73(5):956–961
Clark DE, Lord EA, Suttie JM (2006) Expression of VEGF and pleiotrophin in deer antler. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 288(12):1281–1293
Perez-Pinera P, Zhang W, Chang Y, Vega JA, Deuel TF (2007) Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is activated through the pleiotrophin/receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta signaling pathway: an alternative mechanism of receptor tyrosine kinase activation. J Biol Chem 282(39):28683–28690
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Miagkov A, Skeel A, Nakaigawa N, Zbar B, Leonard EJ (2001) Oncogenic mutants of RoN and MET receptor tyrosine kinases cause activation of the β-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Biol 21(17):5857–5868
Podar K, Anderson KC (2010) A therapeutic role for targeting c-Myc/Hif-1-dependent signaling pathways. Cell Cycle 9(9):1722–1728
Li G, Hu Y, Huo Y, Liu M, Freeman D, Gao J, Liu X, Wu DC, Wu H (2006) PTEN deletion leads to up-regulation of a secreted growth factor pleiotrophin. J Biol Chem 281(16):10663–10668
Gu D, Yu B, Zhao C, Ye W, Lv Q, Hua Z, Ma J, Zhang Y (2007) The effect of pleiotrophin signaling on adipogenesis. FEBS Lett 581(3):382–388
Tian Q, He XC, Hood L, Li L (2005) Bridging the BMP and Wnt pathways by PI3K/AKT and 14-3-3zeta. Cell Cycle 4(2):215–216
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the fine work performed by American Journal Experts (AJE) in the correction of the English text. This work was supported by funds from Science and technology projects of Xi’an city (SF08009(3)) and Science and technology projects of Shaanxi Province (2008K09-06). We thank Prof. Chen Huang for technical assistance and other members of the Department of Oncology, First Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University for advice and suggestions.
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest is declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Bai, Ps., Nan, Kj. et al. Pleiotrophin is a potential colorectal cancer prognostic factor that promotes VEGF expression and induces angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 287–298 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1344-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1344-z