Abstract
Introduction
In colorectal cancer (CRC), no biological marker is known that could serve both as a marker for detection and prognosis. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy of spin-labeled fatty acid (FA) molecules binding to human serum albumin is a suitable method for the detection of conformational changes and alterations of transport function of albumin through changes in its FA binding capabilities.
Objective
The aim of this study was to examine whether the FA binding to albumin is detectably and significantly altered in CRC patients when compared with patients having benign colorectal diseases.
Materials and methods
One hundred four patients operatively or endoscopically treated for CRC, sigmoid diverticulitis, or a colorectal adenoma were examined before procedure. Albumin was analyzed by ESR with spin-labeled FA. A determination ratio (DR) was calculated from the measured ESR spectra as ratios of the fraction of FA that is tightly bound vs. the fractions that are loosely interacting with albumin or are unbound.
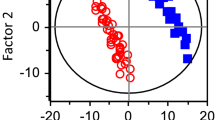
Results and discussions
Patients with CRC showed significantly lower DR values (DR, −0.09 ± 0.98 vs. 0.61 ± 1.43) than patients with benign colorectal diseases, consistent with a change of conformation and transport function of albumin in CRC. Within the CRC group, with advanced tumor stage, the difference in DR values increased. ESR of FA binding to albumin thus seems to be suitable for detection of patients with CRC. Furthermore, a correlation with advanced tumor stage can be established.
Conclusions
These results suggest that a further evaluation of the role of ESR in patients with all stages of CRC should take place. It should also be examined whether ESR might play a role in detecting CRC in a larger panel of patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahi CJ, Rex DK, Imperiale FI (2008) Screening, surveillance and primary prevention for colorectal cancer: a review of the recent literature. Gastroenterology 135:380–399
Hundt S, Haug U, Brenner H (2007) Blood markers for early detection of colorectal cancer: a systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:1935–1953
Duffy MJ, van Dalen A, Haglund C, Hansson L, Holinski-Feder E, Klapdor R, Lamerz R, Peltomaki P, Sturgeon C, Topolcan O (2007) Tumor markers in colorectal cancer: European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM) guidelines for clinical use. Eur J Cancer 43:1348–1360
Greene FL, Balch CM, Fleming ID (2002) AJCC cancer staging handbook, 6th edn. Springer, New York
Allegra C, Sargent DJ (2005) Adjuvant therapy for colon cancer—the pace quickens. N Engl J Med 352:2746–2748
Peters T (1996) All about albumin. Biochemistry, genetics, and medical application. Academic, San Diego
Curry S, Mandelkow H, Brick P, Franks N et al (1998) Crystal structure of human serum albumin complexed with fatty acid reveals an asymmetric distribution of binding sites. Nat Struct Biol 5:827–835
Simard JR, Zunszain PA, Hamilton JA, Curry S (2006) Location of high and low affinity fatty acid binding sites on human serum albumin revealed by NMR drug-competition analysis. J Mol Biol 361:336–351
Kragh-Hansen U, Chuang VT, Otagiri M (2002) Practical aspects of the ligand-binding and enzymatic properties of human serum albumin. Biol Pharm Bull 25:695–704
Mehta AI, Ross S, Lowenthal MS, Fusaro V, Fishman DA, Petricoin EF, Liotta LA (2003) Biomarker amplification by serum carrier protein binding. Dis Markers 19:1–10
Liotta LA, Ferrari M, Petricoin E (2003) Clinical proteomics: written in blood. Nature 425:905
Ge MT, Rananavare SB, Freed JH (1990) ESR studies of stearic acid binding to bovine serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1036:228–236
Livshits VA, Marsh D (2000) Fatty acid binding sites of serum albumin probed by non-linear spin-label EPR. Biochim Biophys Acta 1466:350–360
Matthes G, Seibt G, Muravsky V, Hersmann G, Dornheim G (2002) Albumin transport analysis of different collected and processed plasma products by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Transfer Apheresis Sci 27:129–135
Hinderberger D, Jeschke G (2006) Site-Specific Characterization of Structure and Dynamics of Complex Materials by EPR Spin Probes. Modern Magnetic Resonance 3:1509–1517
Muravsky VA, Matthes G, Seibt G, Milutin A (2000) Verfahren zur Diagnose und/oder Überwachung physiologischer oder pathologischer Veränderungen im menschlichen oder tierischen Körper und ESR-Spektrometer zur Durchführung des Verfahrens. Patent DE10011163 (28.02.2000) (PCT/EP01/02248), (WO 01/65270)
Gurachevsky A, Muravskaya E, Gurachevskaya T, Smirnova L, Muravsky V (2007) Cancer-associated alteration in fatty acid binding to albumin by spin-lapel electron spin resonance. Cancer Invest 25:378–383
Kazmierczak SC, Gurachevsky A, Matthes G, Muravsky V (2006) Electron spin resonance spectroscopy of serum albumin: a novel test for cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Clin Chem 52:2129–2134
Hansen O, Stock W (1999) Prophylaktische Operation bei der Divertikelkrankheit des Kolons—Stufenkonzept durch exakte Stadieneinteilung. Langenbecks Arch Chir (Suppl II):1257–1260
Compton C, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Pettigrew N, Fielding LP (2000) American Joint Committee on Cancer Prognostic Factors Consensus Conference. Cancer 88:1739–1757
Li J, Zhang Z, Rosenzweig J, Wang YY, Chan DW (2002) Proteomics and bioinformatics approaches for identification of serum biomarkers to detect breast cancer. Clin Chem 48:1296–1304
Mashevsky A, Muravsky V, Milutin A, Javrid E, Korotkevich E, Prokchorova V et al (1994) Dynamics of ESR spectra of the spin labeled blood serum under neoplastic process. Ukr Radiol Zh 4:268–270
Afanas'eva AN, Evtushenko VA (2004) Conformation changes in albumin molecule as a marker of dissemination of the tumor process. Bull Exp Biol Med 138:177–178
Hinderberger D, Schmelz O, Rehahn M, Jeschke G (2004) Electrostatic site attachment of divalent counterions to rodlike ruthenium(II) coordination polymers characterized by ESR spectroscopy. Angewandte Chemie 116:4716–4721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Gelos and D. Hinderberger contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelos, M., Hinderberger, D., Welsing, E. et al. Analysis of albumin fatty acid binding capacity in patients with benign and malignant colorectal diseases using electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. Int J Colorectal Dis 25, 119–127 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0777-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0777-0