Abstract
Objective
Body packers smuggle cocaine by swallowing containers filled with the drugs, whilst body pushers conceal the containers in the rectum or vagina. In a collaborative effort between the Department of General Surgery, two major airports and Poisons Centre, we performed a retrospective study to develop an algorithm for the treatment of ruptured cocaine-filled containers.
Materials and methods
The data of all cocaine body packers and body pushers who were identified at the airports of Frankfurt and Paris from 1985 to 2002 were evaluated concerning incidence, demographics and surgical aspects.
Results
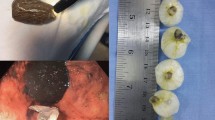
From 1985 to 2002, 312 body pushers and 4,660 body packers were identified. The sex ratio was 1:1. Sixty-four “mules” (1.4%) developed life-threatening symptoms of cocaine overdose after the rupture of a container. In 20 patients, an emergency laparotomy was performed and the containers were removed; all of these patients survived. Forty-four body packers died before surgical treatment could be performed. Only one body pusher required medical attention.
Conclusion
Cocaine overdose can be life-threatening. If the cause is the rupture of a container in a body packer, the only possible treatment is immediate laparotomy for the removal of the container.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fishbain DA, Wetli CV (1981) Cocaine intoxication, delirium, and death in a body packer. Ann Emerg Med 10:531–532
Wetli CV, Mittlemann RE (1981) The “body packer syndrome”—toxicity following ingestion of illicit drugs packaged for transportation. J Forensic Sci 26:492–500
McCarron MM, Wood JD (1983) The cocaine ‘body packer’ syndrome. Diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 250:1417–1420
Haugen OA, Dalaker M, Svindland A (1994) Smuggling of narcotics in body cavities. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 10:2501–2502
Gill JR, Graham SM (2002) Ten years of “body packers” in New York City: 50 deaths. J Forensic Sci 47(4):843–846
MAHSAN Diagnostika (2005) MAHSAN catalogue for quick tests, p 42
Beermann R, Nunez D Jr, Wetli CV (1986) Radiographic evaluation of the cocaine smuggler. Gastrointest Radiol 11:351–354
Hartoko DJ, Demey HE, De Schepper AM, Beaucourt LE, Bossaert LL (1988) The body packer syndrome—cocaine smuggling in the gastro-intestinal tract. Klin Wochenschr 66:1116–1120
Marc B, Baud FJ, Aelion MJ, Gherardi R et al (1990) The cocaine body-packer syndrome: evaluation of a method of contrast study of the bowel. J Forensic Sci 35:345–355
Gherardi R, Marc B, Alberti X, Baud F, Diamant-Berger O (1990) A cocaine body packer with normal abdominal plain radiograms. Value of drug detection in urine and contrast study of the bowel. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 11:154–157
Hierholzer J, Cordes M, Tantow H, Keske U, Maurer J, Felix R (1995) Drug smuggling by ingested cocaine-filled packages: conventional X-ray and ultrasound. Abdom Imaging 20(4):333–338
Hoffman RS, Smilkstein MJ, Goldfrank LR (1990) Whole bowel irrigation and the cocaine body-packer: a new approach to a common problem. Am J Emerg Med 8:523–527
Gomez Antunez M, Cuenca Carvajal C, Farfan Sedano A, Villalba MV, del Toro Cervera J, Garcia Castano J (1998) Complications of intestinal transporting of cocaine packets. Study of 215 cases. Med Clin (Barc) 26:336–337
John H, Schoenenberger R, Renner N, Ritz R (1992) Cocaine poisoning from transport of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract (the body-packer syndrome). Dtsch Med Wochenschr 117:1952–1955
John H, Renner N, Schoenenberger R, Harder F (1994) Intestinal drug transport: a surgical problem? Helv Chir Acta 60:935–938
Aldrighetti L, Paganelli M, Giacomelli M, Villa G, Ferla G (1996) Conservative management of cocaine-packet ingestion: experience in Milan, the main Italian smuggling center of South American cocaine. Panminerva Med 38(2):111–116
Schaper A, Hofmann R, Ebbecke M, Desel H, Langer C (2003) Cocaine-body-packing. Infrequent indication for laparotomy. Chirurg 74(7):626–631
Aldrighetti L, Graci C, Paganelli M, Vercesi M et al (1993) Intestinal occlusion in cocaine-packet ingestion. Minerva Chir 48:1233–1237
Traub SJ, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS (2003) Body packing—the internal concealment of illicit drugs. N Engl J Med 349(26):2519–2526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaper, A., Hofmann, R., Bargain, P. et al. Surgical treatment in cocaine body packers and body pushers. Int J Colorectal Dis 22, 1531–1535 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-007-0324-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-007-0324-9