Abstract.
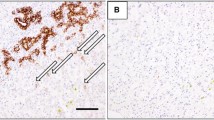
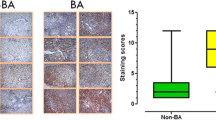
The aim of the present study was to examine the clinical significance of c-kit expression in biliary atresia (BA) using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from 21 patients with BA. Patients were divided into group I (n = 8) with good liver function; group II (n = 8) with moderate liver dysfunction; and group III (n = 5) with severe liver dysfunction. Choledochal cysts (CDC, n = 5) and normal liver samples (NL, n = 4) served as controls. The results were analyzed and compared among the groups. Most c-kit + cells were present in the portal tracts, and their numbers in BA were significantly higher than in the controls (11.12 ± 1.64 vs 2.15 ± 0.15 [mean ± standard error], P = 0.02, BA vs CDC; 11.12 ± 1.64 vs 1.66 ± 0.52, P = 0.03, BA vs NL). Clinical correlation revealed a significantly higher number of c-kit + cells in group III versus group I (18.10 ± 3.62 vs 8.86 ± 2.51, P = 0.02). These results suggest that c-kit overexpression is associated with an adverse clinical outcome in BA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 1 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, A., Nio, M., Ohtani, H. et al. Clinical significance of c-kit expression in biliary atresia. Pediatr Surg Int 17, 601–603 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830100002
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003830100002