Abstract
Background
Researched and discussed the risks and outcomes of bronchopulmonary sequestrations, especially the intralobar type.
Methods
A retrospective review of our experiences with bronchopulmonary sequestrations from January 2012 to April 2015 is reported. The present study researched and discusses the risks and outcomes of bronchopulmonary sequestrations, especially the intralobar type, compared with other types of bronchopulmonary sequestrations in symptoms, surgery, pathology, and excretion.
Results
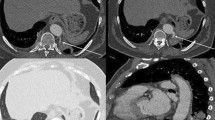
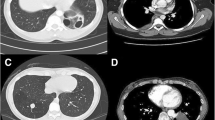
A total of 126 bronchopulmonary sequestrations were diagnosed. All fetal chest cases (18–30 weeks) of solid or high-echo masses were diagnosed antenatally and then confirmed by ultrasound. Enhanced computed tomography was used to confirm the diagnosis. Eighty-three boys and 43 girls were included. The mean age at surgery was 4.2 ± 0.5 months. There were 103 cases of left, 22 cases of right, and 1 case of bilateral sequestration. There were 62 extralobar cases, 51 intralobar cases, 13 cases within the diaphragm, and a rare bilateral case. A preoperative history of recurrent respiratory tract infection was present in 39 cases, including 10 extralobar and 29 intralobar cases. Operations were completed successfully, and diagnoses were confirmed pathologically. Thirty-seven cases were associated with congenital bronchopulmonary malformation changes, of which 4 were extralobar, 31 were intralobar, and 2 were within the diaphragm.
Conclusions
The intralobar type was relatively uncommon among bronchopulmonary sequestrations. However, due to communication with normal lung tissue, infection is common in the intralobar type. Computed tomography examinations are very important immediately after birth. It is necessary to resect the mass in early childhood.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pryce DM (1946) Lower accessory pulmonary artery with intralobar sequestration of the lung: report of cases. J Pathol 58:457–467 (PMID:20283082)
Moore KL, Persaud TVN, Torchia MG (2015) The Developing Human. In: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 10th edn. Elsevier
Carter R (1969) Pulmonary sequestration. Ann Thorac Surg 7(1):68–88 (PMID:4883836)
Doski JJ, Lou D, Hicks BA et al (2000) Management of parapneumonic collections in infants and children. J pediatr Sura 35:265 (PMID:10693678)
Okubo Y, Hamakawa H, Ueda H et al (2016) Extralobar sequestration presenting as sudden chest pain due to hemothorax. Ann Thorac Surg 101(1):e27. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.10.025
Hussain S, Ahmed S, Awais U, Hassan Shah S et al (2017) A rare cause of recurrent chest infection in children-bronchopulmonary sequestration. J Pak Med Asso. 67(2):311–313
Kim CW, Kim DH (2016) Single-incision video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy in the treatment of adult communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation with large aberrant artery. J Thorac Dis 8(1):E148–E151. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2016.01.36
Davoli F, Turello D, Valente G et al (2016) Extralobar pulmonary sequestration presenting with recurring massive pleural effusion in a young woman: a challenging case. Heart Lung Circ 25(1):e13–e15. doi:10.1016/j.hlc.2015.09.006 (Epub 2015 Oct 9PMID:2654609)
Laurin S, Hägerstrand I (1999) Intralobar bronchopulmonary sequestration in the newborn: a congenital malformation. Pediatr Radiol 29(3):174–178 (PMID:10201034)
Parikh PP, Tashiro J, Chahwala V et al (2014) Infant with bilateral pulmonary sequestrations with portal venous drainage excised by video-assisted thoracic surgery. J Pediatr Surg 49(8):1332–1334 (PMID:25092101)
Simoglou C, Lawal LA (2015) Adenocarcinoma in pulmonary sequestration: a case report and literature review. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 23(9):1119–1120 (PMID:26048591)
Chen JSC, Walford N, Yan YL et al (2003) Foetal intralobar lung sequestration: antenatal diagnosis and management. Singapore Med J 44(12):630–634 (PMID:14770257)
Laberge JM, Puligandia P, Flageole H (2005) Asymptomatic congenital lung malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg 14(1):16–33 (PMID:15770585)
Nakano T, Tetsuka K, Yamamoto S et al (2014) Strangulation of aberrant artery in extralobar pulmonary sequestration on video imaging. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 19(2):324–325 (PMID:24729200)
Choe J, Goo HW (2015) Extralobar pulmonary sequestration with hemorrhagic infarction in a child: preoperative imaging diagnosis and pathological correlation. Korean J Radiol 16(3):662–667 (PMID:25995698)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript. The work described is original research that has not been published previously, and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Additional information
Chun Hong and Gang Yu: Co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, C., Yu, G., Tang, J. et al. Risk analysis and outcomes of bronchopulmonary sequestrations. Pediatr Surg Int 33, 971–975 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4097-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4097-0