Abstract
Background
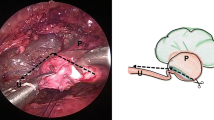
Common causes of complications of laparoscopic pyeloplasty in children include anastomotic stricture, poor drainage due to high ureteropelvic anastomosis, and torsion of ureter. Herewith, we described our modified technique of paraumbilical three-port laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty (PTLDP) to minimize these complications.
Patients and methods
Data from 62 patients (age: 1–180 months, median: 12 months) with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) who underwent pyeloplasty using our modified technique of PTLDP between February 2014 and September 2014 at our institution were reviewed. The key steps of our modified method involve identifying the lowest point of the renal pelvis and the lateral aspect of the ureter to guarantee a low pelviureteric and correct orientation anastomosis, and using a 4-0 silk for assistant suturing to avoid crushing of the anastomotic tissue.
Results
All surgeries were successfully completed without conversion. Three patients required an accessory port for the anastomosis. All the patients achieved complete clinical or radiologic resolution after the operation. The mean operative time was 103.4 min, and mean estimated blood loss was 14.4 mL. Mean postoperative differential function of affected kidney was 43.0 ± 16.3 % (range 24–100 %), increased from 39.7 ± 18.0 % (range 18–100 %), preoperatively (p < 0.001). The success rate was 100 % at a mean follow-up of 18.3 ± 2.9 (range 13–25) months.
Conclusions
Our modified technique of PTLDP is safe and feasible and to allow high success rate for the treatment of pelviureteric junction obstruction in children.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingler HC, Remzi M, Janetschek G et al (2003) Comparison of open versus laparoscopic pyeloplasty techniques in treatment of uretero-pelvic junction obstruction. Eur Urol 44(3):340–345
Piaggio LA, Franc-Guimond J, Noh PH et al (2007) Transperitoneal laparoscopic pyeloplasty for primary repair of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in infants and children: comparison with open surgery. J Urol 178(4 Pt 2):1579–1583
Peters CA, Schlussel RN, Retik AB (1995) Pediatric laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty. J Urol 153(6):1962–1965
Yang K, Yao L, Li X et al (2015) A modified suture technique for transperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty of pelviureteric junction obstruction. Urology 85(1):263–267
Chandrasekharam VV (2013) A simple technique of ureteric spatulation and handling during laparoscopic pyeloplasty in infants and children. J Pediatr Urol 9(3):384–387
Zhou H, Liu X, Xie H (2014) Early experience of using transumbilical multi-stab laparoscopic pyeloplasty for infants younger than 3 months. J Pediatr Urol 10(5):854–858
Zhou H, Sun N, Zhang X et al (2012) Transumbilical laparoendoscopic single-site pyeloplasty in infants and children: initial experience and short-term outcome. Pediatr Surg Int 28(3):321–325
Yiee J, Wilcox D (2008) Management of fetal hydronephrosis. Pediatr Nephrol 23(3):347–353
Buffi NM, Lughezzani G, Fossati N et al (2015) Robot-assisted, single-site, dismembered pyeloplasty for ureteropelvic junction obstruction with the new da Vinci platform: a stage 2a study. Eur Urol 67(1):151–156
Draaijers LJ, Tempelman FRH, Botman YAM et al (2004) The patient and observer scar assessment scale: a reliable and feasible tool for scar evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:1960
Nishi M, Tsuchida M, Ikeda M et al (2015) Laparoscopic pyeloplasty for secondary ureteropelvic junction obstruction: long-term results. Int J Urol Off J Japn Urol Assoc 22(4):368–371
Moon DA, El-Shazly MA, Chang CM et al (2006) Laparoscopic pyeloplasty: evolution of a new gold standard. Urology 67(5):932–936
Haga N, Sato Y, Ogawa S et al (2015) Laparoscopic modified bypass pyeloplasty: a simple procedure for straightforward ureteral spatulation and intracorporeal suturing. Int Urol Nephrol 47(12):1933–1938
Singh O, Gupta SS, Arvind NK (2011) Laparoscopic pyeloplasty: an analysis of first 100 cases and important lessons learned. Int Urol Nephrol 43(1):85–90
Rizkala ER, Franco I (2010) Ex-vivo ureteral spatulation during laparoscopic pyeloplasty: a novel approach to a difficult problem. J Endourol Endourol Soc 24(12):2029–2031
Jc A, Hynes W (1949) Retrocaval ureter; a case diagnosed pre-operatively and treated successfully by a plastic operation. Br J Urol 21(3):209–214
Cascio S, Tien A, Chee W et al (2007) Laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty in children younger than 2 years. J Urol 177(1):335–338
Tasian GE, Wiebe DJ, Casale P (2013) Learning curve of robotic assisted pyeloplasty for pediatric urology fellows. J Urol 190(4 Suppl):1622–1626
Dangle PP, Kearns J, Anderson B et al (2013) Outcomes of infants undergoing robot-assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty compared to open repair. J Urol 190(6):2221–2226
Salo M, Sjoberg Altemani T, Anderberg M (2016) Pyeloplasty in children: perioperative results and long-term outcomes of robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery compared to open surgery. Pediatr Surg Int 32(6):599–607
Buffi N, Cestari A, Lughezzani G et al (2011) Robot-assisted uretero-ureterostomy for iatrogenic lumbar and iliac ureteral stricture: technical details and preliminary clinical results. Eur Urol 60(6):1221–1225
Lee Z, Simhan J, Parker DC et al (2013) Novel use of indocyanine green for intraoperative, real-time localization of ureteral stenosis during robot-assisted ureteroureterostomy. Urology 82(3):729–733
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Long Li, Xu Zhang, and all the colleagues who helped in the preparation of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was funded by the national public welfare industry research projects (No. 201402007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
H. Cao, H. Zhou and K. Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 185687 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Zhou, H., Liu, K. et al. A modified technique of paraumbilical three-port laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty for infants and children. Pediatr Surg Int 32, 1037–1045 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3958-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3958-2