Abstract
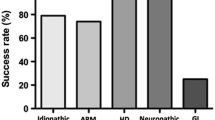
The purpose of this study was to assess current status of antegrade continence enema (ACE) procedure taking into account the recent improvement in the technique and outcome. Reviewing our record of 48 patients with ACE procedure performed between January 2002 and May 2007, we found that the underlying diagnoses were idiopathic constipation in 56%, anorectal malformation in 31%, spina bifida in 8% and Hirschsprung’s disease in 4%. Mean age of operation was 10.7 years. Appendix was used as stoma in 73% of cases. Stomal stenosis requiring revision was seen in 6% of cases and continence was achieved in 92% of cases. A systematic search of database was performed for the same period. Twenty-four studies describing 676 patients were found. The mean age was 10 years and various sites used for ACE were, right side of abdomen in 71%, umbilicus in 15% and left side of abdomen in 14%. The incidence of open and laparoscopic procedures were 87 and 13%, respectively. Appendix was used for stoma in 76% procedures. Other operative modalities were retubularised colon, retubularised ileum, caecal button and caecostomy tube, etc. The mean volume of enema fluid used was 516 ml. The mean evacuation time was 42 min. Stomal stenosis requiring revision was seen in 13% of cases. Continence was achieved in 93% of cases. There has been significant improvement in the outcome during last 5 years in comparison to the outcome published in late 1990s. Advancements in techniques, better-trained stoma care nurses and better stoma appliances could have played major role in this success.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cataldo PA (1993) History of stomas. In: Mackeigan JM, Kataldo PA (eds) Intestinal stomas: principles, techniques and management. Quality Medical Publishing, St Louis, pp 3–37
Malone PS, Ransley PG, Keily EM et al (1990) Preliminary report: the antegrade colonic enema. Lancet 336:1217–1218
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13 doi:10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Keshtgar AS, Ward HC, Clayden GS (2004) Diagnosis and management of children with intractable constipation. Semin Pediatr Surg 13:300–309
Graf JL, Strear C, Bratton B et al (1998) The antegrade continence enema procedure: a review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg 33:1294–1296
Curry JJ, Osborne A, Malone PSJ (1999) The MACE procedure: experience in the United Kindom. J Pediatr Surg 34:338–340
Griffiths DM, Malone PS (1995) The Malone antegrade continence enema. J Pediatr Surg 30:68–71
Squire R, Kiely EM, Carr B et al (1993) The clinical application of the Malone antegrade colonic enema. J Pediatr Surg 28:1012–1015
Levitt MA, Soffer SZ, Pena A (1997) Continent appendicostomy in the bowel management of fecally incontinent children. J Pediatr Surg 32:1630–1633
Koivusalo A, Pakarinen M, Rintala RJ (2006) Are cecal wrap and fixation necessary for antegrade colonic enema appendicostomy? J Pediatr Surg 41:323–326
Koyle MA, Kaji DM, Duque M et al (1995) The Malone antegrade continence enema for neurogenic and structural fecal incontinence and constipation. J Urol 154:759–761
Kim SM, Han SW, Choi SH (2006) Left colonic antegrade continence enema: experience gained from 19 cases. J Pediatr Surg 41:1750–1754
Rawat DJ, Haddad M, Geoghegan N et al (2004) Percutaneous endoscopic colostomy of the left colon: a new technique for management of intractable constipation in children. Gastrointest Endosc 60:39–43
Liloku RB, Mure PY, Braga L et al (2002) The left Monti–Malone procedure: preliminary results in seven cases. J Pediatr Surg 37:228–231
Lee SL, Rowell S, Greenholz SK (2002) Therapeutic cecostomy tubes in infants with imperforate anus and caudal agenesis. J Pediatr Surg 37:345–347
Yerkes EB, Rink RC, Cain MP et al (2002) Use of a Monti channel for administration of antegrade continence enemas. J Urol 168:1883–1885
Casio S, Flett ME, Hunt D et al (2004) MACE or caecostomy button for idiopathic constipation in children: a comparison of complication and outcomes. Pediatr Surg Int 20:484–487
Surfield GA, Andrewa D (2005) Tapered terminal ileum conduit for antegrade continence enemas. Pediatr Surg Int 21:989–990
Herndon CDA, Cain MP, Casale AJ et al (2005) The colon flap/extension malone antegrade continence enema: an alternative to the Monti–Malone antegrade continence enema. J Urol 174:299–302
Casale P, Grady RW, Feng WC et al (2004) A novel approach to the laparoscopic antegrade continence enema procedure: intracorporeal and extracorporeal techniques. J Urol 171:817–819
Yagmurlu A, Harmon CM, Georgeson KE (2006) Laparoscopic cecostomy button placement for the management of fecal incontinence in children with Hirschsprung’s disease and anorectal anomalies. Surg Endosc 20:624–627
Antao B, Ng J, Robert J (2006) Laparoscpic antegrade continence enema using a two-port technique. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 16:168–173
Kim J, Beasley SW, Maoate K (2006) Appendicostomy stoma and antegrade colonic irrigation after laparoscopic antegrade continence enema. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 16:400–403
Biryani D, Barrow E, Hodson P et al (2007) Endoscopically placed caecostomy buttons: a trial ACE procedure. Colorectal Dis 9:373–376
Chait PG, Shandling B, Richards HM et al (1997) Fecal incontinence in children: treatment with percutaneous cecostomy tube placement: a prospective study. Radiology 203(3):621–624
Lopez PJ, Ashrafian H, Clarke S et al (2007) Early experience with the antegrade colonic enema stopper to reduce stomal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg 42:522–524
Farrugia MK, Melville D, Boddy SA (2007) Coming face to face with the stenotic MACE—combined Maceoscopy and colonoscopy (the rendez-vous procedure): a preliminary report. J Pediatr Surg 42:685–687
Koivusalo A, Pakarinen MP, Rintal RJ (2006) Treatment of a leaking ACE conduit with deflux injection. Pediatr Surg Int 22:1003–1006
Yerkes EB, Cain MP, King S et al (2003) The Malone antegrade continence enema procedure: quality of life and family perspective. J Urol 169:320–323
Aksnes G, Diseth TH, Helseth A et al (2006) Appendicostomy for antegrade enema: effect on somatic and psychsocial functioning in children with myelomeningocele. Pediatrics 109:484–488
Matrix KD, Novotny NM, Shelley AA, et al (2007) Malone antegrade continence enema (MACE) for fecal incontinence in imperforate anu improves quality of life. Pediatr Surg Int 23(12):1175–1177 (Epub ahead of print)
Dinning PG, Fuentealbas SE, Kennedy ML et al (2005) Sacral nerve stimulation initiates propagating pressure waves throughout the colon in patients with slow transit constipation. Neurohastroenterol Motil 17:A76
Wong SW, Lubowski DZ (2007) Slow transit constipation: evaluation and treatment. Anz J Surg 77:320–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, C.K., Grewal, A. & Ward, H.C. Antegrade continence enema (ACE): current practice. Pediatr Surg Int 24, 685–688 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-008-2130-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-008-2130-z