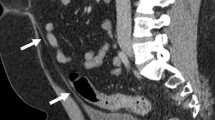
Abstract
The malrotation and no well fixation anomalies of the digestive tract is also frequent in older child, young and adult, with characteristic and specific clinical presentation. Actually, the diagnostic and treatment seem to be late, after suffering prolonged symptoms and/or in emergency. We present nine cases of anomalies in the embryonic development of the digestive tract which were diagnosed and treated in infants or young, all above 2 years old. Eight cases were of more or less complete intestinal malrotation; one of them was a complete malrotation with an intrinsic duodenal stenosis associated (no bands of Ladd) and another one was a right paramesocolic hernia, always accompanied by malrotation. The association with other extra-digestive anomalies, especially urological, was 70%. The predominant symptom was intermittent abdominal pain (IAP)—80%—sometimes accompanied by vomiting (35%) and episodes of diarrhoea (25%). In all the cases, while the clinical background was early, diagnosis was late. Indeed, in 60% of the cases diagnosis was made intra-operatively in emergency surgical interventions. The imaging procedures employed were scanning and Doppler ultrasound, CT scan, and contrast gastrointestinal series (GIS). Up to 30% of errors in interpretation occurred, although they were eventually corrected with other tests. The most reliable diagnostic procedures were GIS and CT scan with contrast, although partial interpretation errors occurred with the latter procedure. Surgery was essential in 80% of the pre-operative cases, and in another two it was required as a preventative measure. Post-operatively, there was notable persistence of SBS in the cases of intestinal necrosis, and of other lesser symptoms in the rest. We conclude that: intestinal malrotations and malfixations are still being diagnosed very late, with serious systemic consequences such as intestinal obstructions or necroses, and prolonged clinical suffering. This could all be avoided if more attention were paid to the digestive symptoms associated with IAP, and to subocclusion or other abdominal phenomena (distension,...), together with, in the case of doubt about the findings with the previous procedures, the opportune imaging tests (e.g., abdominal Doppler ultrasound, CT scan with contrast, and barium GIS). Unlike other authors, we consider that the morbidity/mortality associated with cases of late diagnosis of these anomalies is high, and calls for earlier surgical treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dott NM (1923) Anomalies of intestinal rotation. Their embryology and surgical aspects, with report of five cases. Br J Surg 11:251
Snyder WH, Chaffin L (1954) Embryology and pathology of the intestinal tract: presentation of 48 cases of malrotation. Ann Surg 140:368–377
Kantor JL (1934) Anomalies of the colon: their Roentgen diagnosis and clinical significance. Resume of ten years study. Radiology 23:651–662
Gardner CE, Hart D (1934) Anomalies of intestinal rotation as a cause of intestinal obstruction. Arch Surg 29:942–946
Collins DC (1963) 71 000 human appendix specimens: a final report, summarizing forty years’ study. Am J Proctol 14:365–380
Estrada RL (1958) Anomalies of intestinal rotation and fixation. Charles C. Thomas. Springfield
Warner BW (1997) Malrotation. In: Oldham KT, Colombani PM, Foglia RP (eds) Surgery of infants and children: scientific principles and practice. lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 1229–1240
Ford EG, Senac MO Jr, Srikanth MS, Weitzman JJ (1992) Malrotation of the intestine in children. Ann Surg 215:172–178
Forrester MB, Merz RD (2003) Epidemiology of intestinal malrotation, Hawaii, 1986–99. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 17:195–200
Ameh EA, Nmadu PT (2000) Intestinal volvulus: aetiology, morbidity and mortality in Nigerian children. Pediatr Surg Int 16:50–56
Gurleyik E, Gurleyik G (1998) Small bowel volvulus: a common cause of mechanical intestinal obstruction in our region. Eur J Surg 164:51–55
Nair R, Hadley GP (1996) Intestinal malrotation–experience with 56 patients. S Afr J Surg 34:73–75
Moran JM, Salas J, Sanjuán S, Amaya JL, Rincón P, Serrano A, Tallo E (2004) Paramesocolic hernias: consequences of delayed diagnosis. J Pediat Surg 39:112–116
Mordehai J, Cohen Z, Kurzbart E, Mares AJ (2002) Preduodenal portal vein causing duodenal obstruction associated with situs inversus, intestinal malrotation, and polysplenia: a case report. J Pediatr Surg 37(4):E5
Erez I, Reish O, Kovalivker M, Lazar L, Raz A, Katz S (2001) Congenital short-bowel and malrotation: clinical presentation and outcome of six affected offspring in three related families. Eur J Pediatr Surg 11:331–334
Bao Quan Q, Diez-Pardo JA, Tovar JA (1995) Intestinal rotation in experimental congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 30:1457–1462
Bates MD, Deutsch GH (2003) Molecular insights into congenital disorders of the digestive system. Pediatr Dev Pathol Jun 13 (Epub ahead of print)
Ramalho-Santos M, Melton DA, McMahon AP (2000) Hedgehog signals regulate multiple aspects of gastrointestinal development. Development 127:2763–2772
Janik JS, Ein SH (1979) Normal intestinal rotation with non-fixation: a cause of chronic abdominal pain. J Pediatr Surg 14:670–674
El-Gohari MA, Cook RCZ (1984) Intestinal malrotation beyond the neonatal period. Kinderchir 39:237–241
Rescorla FJ, Shedd FJ, Grosfeld JL, Vane DW, West KW (1990) Anomalies of intestinal rotation in childhood: analysis of 447 cases. Surgery 108:710–715 (discussion 715)
Spigland N, Brandt ML, Yazbeck S (1990) Malrotation presenting beyond the neonatal period. J Pediatr Surg 25:1139–1142
Fernandez Sanchez A, Lopez Pereira P, Diez Pardo JA, Utrilla J (1987) Intestinal malrotation in children. An Esp Pediatr 27:375–378
Stewart DR, Colodny AL, Daggett WC (1976) Malrotation of the bowel in infants and children: a 15 year review. Surgery 79:716–720
Andrassy RJ, Mahour GH (1981) Malrotation of the midgut in infants and children: a 25-year review. Arch Surg 116:158–160
Iida F, Wada R, Sato A, Yamada T (1980) Clinicopathologic consideration of protein-losing enteropathy due to lymphangiectasia of the intestine. Surg Gynecol Obstet 151:391–395
Yanez R, Spitz L (1986) Intestinal malrotation presenting outside the neonatal period. Arch Dis Child 61:682–685
Steffani KD, Eisenberger CF, Gocht A, Izbicki JR, Yekebas EF (2003) Recurrent intestinal bleeding in a patient with arterio-venous fistulas in the small bowel, limited mesenteric varicosis without portal hypertension and malrotation type I. Z Gastroenterol 41:587–590
Roseau G, Perniceni T, Ponsot P, Palazzo L, Amouyal P, Paolaggi JA (1988) Left paraduodenal hernia disclosed by digestive hemorrhage. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 12:971–972
Walsh DS, Cromblehome TM (2000) Superior mesenteric venous thrombosis in malrotation with chronic volvulus. J Pediatr Surg 35:753–755
Kumar D, Brereton RJ, Spitz L, Hall CM (1988) Gastro-oesophageal reflux and intestinal malrotation in children. Br J Surg 75:533–535
Kullendorff CM, Mikaelsson C, Ivancev K (1985) Malrotation in children with symptoms of gastrointestinal allergy and psychosomatic abdominal pain. Acta Paediatr Scand 74:296–299
Jackson A, Bisset R, Dickson AP (1989) Malrotation and midgut volvulus presenting as malabsorption. Clin Radiol 40:536–537
Jolley SG, Tunell WP, Thomas S, Young J, Smith EI (1985) The significance of gastric emptying in children with intestinal malrotation. J Pediatr Surg 20:627–631
Upadhyay V, Hea CM, Matthews RD (2001) Oesophageal atresia: a handshake with malrotation. Eur J Pediatr Surg 11:368–370
Luo CC, Wang CR, Chiu CH (2003) Intussusception and intestinal malrotation in an infant: a case report. Pediatr Surg Int 19:413–414
Bruyn R, Hall CM, Spitz L (1982) Hirschsprung’s disease and malrotation of the mid-gut. An uncommon association. Br J Radiol 55:554–557
Jolley SG, Lorenz ML, Hendrickson M, Kurlinski JP (1999) Esophageal pH monitoring abnormalities and gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants with intestinal malrotation. Arch Surg 134:747–752 (discussion 752)
Dietz DW, Walsh RM, Grundfest-Broniatowski S, Lavery IC, Fazio VW, Vogt DP (2002) Intestinal malrotation: a rare but important cause of bowel obstruction in adults. Dis Colon Rectum 45:1381–1386
Mehall JR, Chandler JC, Mehall RL, Jackson RJ, Wagner CW, Smith SD (2002) Management of typical and atypical intestinal malrotation. J Pediatr Surg 37:1169–1172
Fukuya T, Brown BP, Lu CC (1993) Midgut volvulus as a complication of intestinal malrotation in adults. Dig Dis Sci 38:438–444
Flue M, Herzog U, Ackermann C, Tondelli P, Harder F (1994) Acute and chronic presentation of intestinal nonrotation in adults. Dis Colon Rectum 37:192–198
Weinberger E, Winters WD, Liddell RM, Rosenbaum DM, Krauter D (1992) Sonographic diagnosis of intestinal malrotation in infants: importance of the relative positions of the superior mesenteric vein and artery. AJR 159:825–828
Yeh WC, Wang HP, Chen C, Wang HH, Wu MS, Lin JT (1999) Preoperative sonographic diagnosis of midgut malrotation with volvulus in adults: the “whirlpool” sign. J Clin Ultrasound 27:279–283
Chao HC, Kong MS, Chen JY, Lin SJ, Lin JN (2000) Sonographic features related to volvulus in neonatal intestinal malrotation. J Ultrasound Med 19:371–376
Torres AM, Ziegler M (1993) Malrotation of the intestine. World J Surg 17:326–331
Prasil P, Flageole H, Shaw KS, Nguyen LT, Youssef S, Laberge JM (2000) Should malrotation in children be treated differently according to age? J Pediatr Surg 35:756–758
Powell DM, Othersen HB, Smith CD (1989) Malrotation of the intestines in children: the effect of age on presentation and therapy. J Pediatr Surg 24:777–780
Fisher JK (1998) Computed tomographic diagnosis of volvulus in intestinal malrotation. Radiology 140:145–156
Ai VH, Lam WW, Cheng W, Chan FL (1999) CT appearance of midgut volvulus with malrotation in a young infant. Clin Radiol 54:687–689
Zissin R, Rathaus V, Oscadchy A, Kots E, Gayer G, Shapiro-Feinberg M (1999) Intestinal malrotation as an incidental finding on CT in adults. Abdom Imaging 24:550–555
Berdon WE (1995) The diagnosis of malrotation and volvulus in the older child and adult: a trap for radiologists. Pediatr Radiol 25:101–103
Pickhardt PJ, Bhalla S (2002) Intestinal malrotation in adolescents and adults: spectrum of clinical and imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1429–1435
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI, Taylor GE, Liacouras CA (1996) Intestinal malrotation in children: tutorial on radiographic diagnosis in difficult cases. Radiology 198:775–780
Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi EC, Adams S, Kern IB, Currie B, Henry GM (2000) The radiologist says malrotation: does the surgeon operate? Pediatr Surg Int 16:45–49
Mazziotti MV, Strasberg SM, Langer JC (1997) Intestinal rotation abnormalities without volvulus: the role of laparoscopy. J Am Coll Surg 185:172–176
Bax NM, van der Zee DC (1998) Laparoscopic treatment of intestinal malrotation in children. Surg Endosc 12:1314–1316
Bass KD, Rothenberg SS, Chang JH (1998) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure in infants with malrotation. J Pediatr Surg 33:279–281
Tsumura H, Ichikawa T, Kagawa T, Nishihara M (2003) Successful laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure and appendectomy for intestinal malrotation with appendicitis. Surg Endosc 17:657–658
Gluer S, Petersen C, Ure BM (2002) Simultaneous correction of duodenal atresia due to annular pancreas and malrotation by laparoscopy. Surg Endosc 16:1004
Wu MH, Hsu WM, Lin WH, Lai HS, Chang KJ, Chen WJ (2002) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure for intestinal malrotation: report of three cases. J Formos Med Assoc 101:152–155
Yamashita H, Kato H, Uyama S, Kanata T, Nishizawa F, Kotegawa H, Watanabe T, Kuhara T (1999) Laparoscopic repair of intestinal malrotation complicated by midgut volvulus. Surg Endosc 13:1160–1162
Cuadra SA, Khalife ME, Char DJ, Wax MR, Halpern D (2002) Intestinal obstruction from midgut volvulus after laparoscopic appendectomy. Surg Endosc 16:215
Stauffer UG, Herrmann P (1980) Comparison of late results in patients with corrected intestinal malrotation with and without fixation of the mesentery. J Pediatr Surg 15:9–12
Feitz R, Vos A (1997) Malrotation: the postoperative period. J Pediatr Surg 32:1322–1324
Devane SP, Coombes R, Smith VV, Bisset WM, Booth IW, Lake BD, Milla PJ (1992) Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms after correction of malrotation. Arch Dis Child 67:218–221
Coombs RC, Buick RG, Gornall PG, Corkery JJ, Booth IW (1991) Intestinal malrotation: the role of small intestinal dysmotility in the cause of persistent symptoms. J Pediatr Surg 26:553–556
Maxson RT, Franklin PA, Wagner CW (1995) Malrotation in the older child: surgical management, treatment, and outcome. Am Surg 61:135–138
Cuadri A, Sanjuan S, Moran JM, Santamaria JI, Ruiz A (1981) Síndrome de Apple-Peel, asociado a atresias intestinales multiples. An Esp Ped 14:148–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penco, J.M.M., Murillo, J.C., Hernández, A. et al. Anomalies of intestinal rotation and fixation: consequences of late diagnosis beyond two years of age. Pediatr Surg Int 23, 723–730 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-007-1972-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-007-1972-0