Abstract
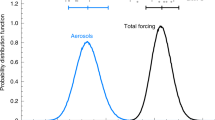
Radiative forcing is a useful concept in determining the potential influence of a particular mechanism of climate change. However, due to the increased number of forcing agents identified over the past decade, the total radiative forcing is difficult to assess. By assigning a range of probability distribution functions to the individual radiative forcings and using a Monte-Carlo approach, we estimate the total radiative forcing since pre-industrial times including all quantitative radiative forcing estimates to date. The resulting total radiative forcing has a 75–97% probability of being positive (or similarly a 3–25% probability of being negative), with mean radiative forcing ranging from +0.68 to +1.34 W m−2, and median radiative forcing ranging from +0.94 to +1.39 W m−2.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 March 2001 / Accepted: 1 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boucher, O., Haywood, J. On summing the components of radiative forcing of climate change. Climate Dynamics 18, 297–302 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820100185
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820100185