Abstract
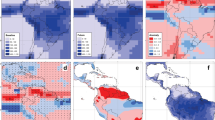
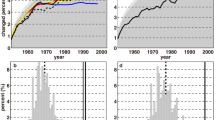
Changes in land surface driving variables, predicted by GCM transient climate change experiments, are confirmed to exhibit linearity in the global mean land temperature anomaly, ΔT l . The associated constants of proportionality retain spatial and seasonal characteristics of the GCM output, whilst ΔT l is related to radiative forcing anomalies. The resultant analogue model is shown to be robust between GCM runs and as such provides a computationally efficient technique of extending existing GCM experiments to a large range of climate change scenarios. As an example impacts study, the analogue model is used to drive a terrestrial ecosystem model, and predicted changes in terrestrial carbon are found to be similar to those when using GCM anomalies directly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 January 1999 / Accepted: 11 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huntingford, C., Cox, P. An analogue model to derive additional climate change scenarios from existing GCM simulations. Climate Dynamics 16, 575–586 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820000067
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820000067