Abstract
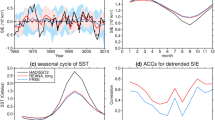
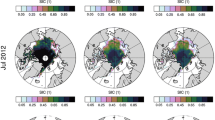
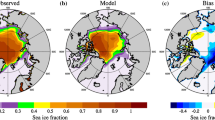
Dynamical model forecasts in the Sea Ice Outlook (SIO) of September Arctic sea-ice extent over the last decade have shown lower skill than that found in both idealized model experiments and hindcasts of previous decades. Additionally, it is unclear how different model physics, initial conditions or forecast post-processing (bias correction) techniques contribute to SIO forecast uncertainty. In this work, we have produced a seasonal forecast of 2015 Arctic summer sea ice using SIO dynamical models initialized with identical sea-ice thickness in the central Arctic. Our goals are to calculate the relative contribution of model uncertainty and irreducible error growth to forecast uncertainty and assess the importance of post-processing, and to contrast pan-Arctic forecast uncertainty with regional forecast uncertainty. We find that prior to forecast post-processing, model uncertainty is the main contributor to forecast uncertainty, whereas after forecast post-processing forecast uncertainty is reduced overall, model uncertainty is reduced by an order of magnitude, and irreducible error growth becomes the main contributor to forecast uncertainty. While all models generally agree in their post-processed forecasts of September sea-ice volume and extent, this is not the case for sea-ice concentration. Additionally, forecast uncertainty of sea-ice thickness grows at a much higher rate along Arctic coastlines relative to the central Arctic ocean. Potential ways of offering spatial forecast information based on the timescale over which the forecast signal beats the noise are also explored.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E, Bitz CM (2014) Characteristics of Arctic sea-ice thickness variability in GCMs. J Clim 27(21):8244–8258
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E, Bitz CM, Holland MH (2011) Influence of initial conditions and climate forcing on predicting Arctic sea ice. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2011GL048807
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E, Cullather R, Wang W, Zhang J, Bitz C (2015) Model forecast skill and sensitivity to initial conditions in the seasonal Sea Ice Outlook. Geophys Res Lett 42(19):8042–8048
Branstator G, Teng H (2010) Two limits of initial-value decadal predictability in a CGCM. J Clim. doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3678.1
Chevallier M, Smith GC, Dupont F, Lemieux JF, Forget G, Fujii Y, Hernandez F, Msadek R, Peterson KA, Storto A, Toyoda T et al (2016) Intercomparison of the Arctic sea ice cover in global ocean–sea ice reanalyses from the ORA-IP project. Clim Dyn 1–30. doi:10.1007/s00382-016-2985-y
Collow TW, Wang W, Kumar A, Zhang J (2015) Improving Arctic sea ice prediction using PIOMAS initial sea ice thickness in a coupled ocean–atmosphere model. Mon Weather Rev 143(11):4618–4630
Comiso J (2000, updated 2015) Bootstrap sea ice concentrations for nimbus-7 smmr and dmsp ssm/i, version 2. Digital Media, National Snow and Ice Data Center
Day J, Hawkins E, Tietsche S (2014a) Will Arctic sea ice thickness initialization improve seasonal forecast skill? Geophys Res Lett 41(21):7566–7575
Day J, Tietsche S, Hawkins E (2014b) Pan-Arctic and regional sea ice predictability: initialisation month dependence. J Clim 27(12):4371–4390
Deser C, Walsh JE, Timlin MS (2000) Arctic sea ice variability in the context of recent atmospheric circulation trends. J Clim 13(3):617–633
Fetterer F, Knowles K, Meier W, Savoie M (2002, updated 2015) Sea ice index. http://nsidc.org/data/go2135.html
Fučkar NS, Volpi D, Guemas V, Doblas-Reyes FJ (2014) A posteriori adjustment of near-term climate predictions: accounting for the drift dependence on the initial conditions. Geophys Res Lett 41(14):5200–5207
Goessling HF, Tietsche S, Day JJ, Hawkins E, Jung T (2016) Predictability of the Arctic sea ice edge. Geophys Res Lett 43:1642–1650. doi:10.1002/2015GL067232
Guemas V, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Mogensen K, Keeley S, Tang Y (2014) Ensemble of sea ice initial conditions for interannual climate predictions. Clim Dyn 43(9–10):2813–2829
Haas C (2003) Dynamics versus thermodynamics: the sea ice thickness distribution. In: Sea Ice: an Introduction to its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, p 402
Hamill TM (2001) Interpretation of rank histograms for verifying ensemble forecasts. Mon Weather Rev 129(3):550–560
Kurtz N, Farrell S, Studinger M, Galin N, Harbeck J, Lindsay R, Onana V, Panzer B, Sonntag J (2013) Sea ice thickness, freeboard, and snow depth products from Operation IceBridge airborne data. doi:10.5194/tc-7-1035-2013
Laxon SW, Giles KA, Ridout AL, Wingham DJ, Willatt R, Cullen R, Kwok R, Schweiger A, Zhang J, Haas C et al (2013) Cryosat-2 estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume. Geophys Res Lett 40(4):732–737
Lindsay RW, Zhang J, Schweiger AJ, Steele MA (2008) Seasonal predictions of ice extent in the Arctic Ocean. J Geophys Res Oceans. doi:10.1029/2007jc004259
Massonnet F, Fichefet T, Goosse H, Bitz CM, Philippon-Berthier G, Holland MM, Barriat PY (2012) Constraining projections of summer arctic sea ice. The Cryosphere 6(6):1383–1394
Schweiger A, Lindsay R, Zhang J, Steele M, Stern H, Kwok R (2011) Uncertainty in modeled Arctic sea ice volume. J Geophys Res 116:C00D06. doi:10.1029/2011JC007084
Sigmond M, Fyfe J, Flato G, Kharin V, Merryfield W (2013) Seasonal forecast skill of Arctic sea ice area in a dynamical forecast system. Geophys Res Lett 40(3):529–534
Stroeve JC, Hamilton L, Bitz CM, Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E (2014) Predicting September sea ice: ensemble skill of the SEARCH sea ice outlook 2008–2013. Geophys Res Lett 41(7):2411–2418
Tietsche S, Day JJ, Guemas V, Hurlin WJ, Keeley SPE, Matei D, Msadek R, Collins M, Hawkins E (2014) Seasonal to interannual Arctic sea ice predictability in current global climate models. Geophys Res Lett 41(3):1035–1043
Tietsche S, Hawkins E, Day JJ (2016) Atmospheric and oceanic contributions to irreducible forecast uncertainty of arctic surface climate. J Clim 29(1):331–346
Tilling RL, Ridout A, Shepherd A (2016) Near real time Arctic sea ice thickness and volume from CryoSat-2. The Cryosphere (in review). doi:10.5194/tc-2016-21
Zhang J, Rothrock D (2003) Modeling global sea ice with a thickness and enthalpy distribution model in generalized curvilinear coordinates. Mon Weather Rev 131(5):845–861
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Sea Ice Prediction Network, at whose annual workshop the model experiment was originally discussed. EBW, CMB and MW were supported by ONR Grant N0014-13-1-0793. JZ was supported by ONR Grant N00014-12-1-0112. This publication is partially funded by the Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere and Ocean (JISAO) under NOAA Cooperative Agreement No. NA10OAR4320148, Contribution No. 2016-01-17, and Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Contribution Number 4515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E., Barthélemy, A., Chevallier, M. et al. Multi-model seasonal forecast of Arctic sea-ice: forecast uncertainty at pan-Arctic and regional scales. Clim Dyn 49, 1399–1410 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3388-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3388-9