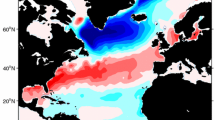
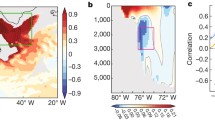
Abstract
Mediterranean Outflow Water (MOW) is thought to be a key contributor to the strength and stability of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), but the future of Mediterranean-Atlantic water exchange is uncertain. It is chiefly dependent on the difference between Mediterranean and Atlantic temperature and salinity characteristics, and as a semi-enclosed basin, the Mediterranean is particularly vulnerable to future changes in climate and water usage. Certainly, there is strong geologic evidence that the Mediterranean underwent dramatic salinity and sea-level fluctuations in the past. Here, we use a fully coupled atmosphere–ocean General Circulation Model to examine the impact of changes in Mediterranean-Atlantic exchange on global ocean circulation and climate. Our results suggest that MOW strengthens and possibly stabilises the AMOC not through any contribution towards NADW formation, but by delivering relatively warm, saline water to southbound Atlantic currents below 800 m. However, we find almost no climate signal associated with changes in Mediterranean-Atlantic flow strength. Mediterranean salinity, on the other hand, controls MOW buoyancy in the Atlantic and therefore affects its interaction with the shallow-intermediate circulation patterns that govern surface climate. Changing Mediterranean salinity by a factor of two reorganises shallow North Atlantic circulation, resulting in regional climate anomalies in the North Atlantic, Labrador and Greenland-Iceland-Norwegian Seas of ±4 °C or more. Although such major variations in salinity are believed to have occurred in the past, they are unlikely to occur in the near future. However, our work does suggest that changes in the Mediterranean’s hydrological balance can impact global-scale climate.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhammoud B, Meijer PT, Dijkstra HA (2010) Sensitivity of Mediterranean thermohaline circulation to gateway depth: A model investigation. Paleoceanography 25:20. doi:10.1029/2009PA001823
Artale V, Calmanti S, Sutera A (2002) Thermohaline circulation sensitivity to intermediate-level anomalies. Tellus A 54:159–174. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0870.2002.01284.x
Baringer MO, Price JF (1999) A review of the physical oceanography of the mediterranean outflow. Mar Geol 155:63–82. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00141-8
Bethoux JP, Gentili B (1999) Functioning of the Mediterranean Sea: past and present changes related to freshwater input and climate changes. J Mar Syst 20:33–47. doi:10.1016/S0924-7963(98)00069-4
Béthoux J-P, Pierre C (1999) Mediterranean functioning and sapropel formation: respective influences of climate and hydrological changes in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Mar Geol 153:29–39. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00091-7
Bethoux J, Gentili B, Morin P, Nicolas E, Pierre C, Ruiz-Pino D (1999) The mediterranean sea: a miniature ocean for climatic and environmental studies and a key for the climatic functioning of the North Atlantic. Prog Oceanogr 44:131–146. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(99)00023-3
Bigg GR, Wadley MR (2001) Millennial-scale variability in the oceans: an ocean modelling view. J Quat Sci 16:309–319. doi:10.1002/jqs.599
Bower AS, Le Cann B, Rossby T et al (2002a) Directly measured mid-depth circulation in the north eastern North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 419:603–607. doi:10.1038/nature01078
Bower AS, Serra N, Ambar I (2002b) Structure of the Mediterranean Undercurrent and Mediterranean Water spreading around the southwestern Iberian Peninsula. J Geophys Res 107: 19 pp. doi:10.1029/2001JC001007
Boyer TP, Antonov JI, Baranova OK et al. (2009) World Ocean Database 2009. In: S. Levitus (Ed.) NOAA Atlas NESDIS 66. US Gov. Printing Office: Washington DC, 216 pp. DVDs
Broecker WS, Bond G, Klas M, Bonani G, Wolfli W (1990) A salt oscillator in the glacial Atlantic? 1. The concept. Paleoceanography 5: p. 469. doi:10.1029/PA005i004p00469
Bryden HL, Kinder TH (1991) Steady 2-layer exchange through the strait of gibraltar. Deep Sea Res Part 1 Oceanogr Res Pap 38:S445–S463
Bryden HL, Candela J, Kinder TH (1994) Exchange through the strait of Gibraltar. Prog Oceanogr 33:201–248
Cacho I, Grimalt JO, Sierro FJ, Shackleton N, Canals M (2000) Evidence for enhanced Mediterranean thermohaline circulation during rapid climatic coolings. Earth Planet Sci Lett 183:417–429. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00296-X
Cacho I, Grimalt JO, Canals M (2002) Response of the Western Mediterranean Sea to rapid climatic variability during the last 50,000 years: a molecular biomarker approach. J Mar Syst 33–34:253–272. doi:10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00061-1
Candela J (1991) The Gibraltar strait and its role in the dynamics of the Mediterranean-Sea. Dyn Atmospheres Ocean 15:267–299
Cattle H, Crossley J, Drewry DJ (1995) Modelling arctic climate change [and discussion]. Philos Transact A Math Phys Eng Sci 352:201–213
Chan W-L, Motoi T (2003) Effects of stopping the Mediterranean outflow on the southern polar region. Polar Meteorol Glaciol (Nat Inst Polar Res) 25–35
Christensen JH, Christensen OB (2007) A summary of the PRUDENCE model projections of changes in European climate by the end of this century. Climatic Change 81:7–30. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9210-7
Clauzon G, Suc J-P, Gautier F, Berger A, Loutre M-F (1996) Alternate interpretation of the Messinian salinity crisis: controversy resolved? Geology 24:363–366. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0363:AIOTMS>2.3.CO;2
Cox PM, Betts RA, Bunton CB, Essery RLH, Rowntree PR, Smith J (1999) The impact of new land surface physics on the GCM simulation of climate and climate sensitivity. Clim Dyn 15:183–203. doi:10.1007/s003820050276
Cunningham SA, Kanzow T, Rayner D et al (2007) Temporal variability of the Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation at 26.5°N. Science 317:935–938. doi:10.1126/science.1141304
de Lange GJ, Krijgsman W (2010) Messinian salinity crisis: a novel unifying shallow gypsum/deep dolomite formation mechanism. Mar Geol 275:273–277. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2010.05.003
Dietrich DE, Tseng Y-H, Medina R et al. (2008) Mediterranean Overflow Water (MOW) simulation using a coupled multiple-grid Mediterranean Sea/North Atlantic Ocean model. J Geophys Res 113: 14 pp. doi:10.1029/2006JC003914
Dijkstra HA (2007) Characterization of the multiple equilibria regime in a global ocean model. Tellus A 59. Available at: http://tellusa.net/index.php/tellusa/article/view/15173. doi:10.3402/tellusa.v59i5.15173
Dubois C, Somot S, Calmanti S et al. (2011) Future projections of the surface heat and water budgets of the Mediterranean Sea in an ensemble of coupled atmosphere–ocean regional climate models. Clim Dyn. Available at: http://www.springerlink.com/index/10.1007/s00382-011-1261-4. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1261-4
Edwards JM, Slingo A (1996) Studies with a flexible new radiation code. I: choosing a configuration for a large-scale model. Q J R Meteorol Soc 122:689–719. doi:10.1002/qj.49712253107
Flecker R, Ellam RM (2006) Identifying Late Miocene episodes of connection and isolation in the Mediterranean-Paratethyan realm using Sr isotopes. Sediment Geol 188–189:189–203. doi:16/j.sedgeo.2006.03.005
Fleming K, Johnston P, Zwartz D, Yokoyama Y, Lambeck K, Chappell J (1998) Refining the eustatic sea-level curve since the last glacial maximum using far- and intermediate-field sites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 163:327–342. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00198-8
Gao X, Giorgi F (2008) Increased aridity in the Mediterranean region under greenhouse gas forcing estimated from high resolution simulations with a regional climate model. Glob Planet Change 62:195–209. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2008.02.002
García-Lafuente J, Sánchez-Román A, Naranjo C, Sánchez-Garrido JC (2011) The very first transformation of the Mediterranean outflow in the Strait of Gibraltar. J Geophys Res 116: 7 PP. doi:10.1029/2011JC006967
García-Ruiz JM, López-Moreno JI, Vicente-Serrano SM, Lasanta–Martínez T, Beguería S (2011) Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth Sci Rev 105:121–139
Gent PR, Mcwilliams JC (1990) Isopycnal mixing in ocean circulation models. J Phys Oceanogr 20:150–155. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1990)020<0150:IMIOCM>2.0.CO;2
Giorgi F, Lionello P (2008) Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob Planet Change 63:90–104. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.09.005
Gómez F (2003) The role of the exchanges through the Strait of Gibraltar on the budget of elements in the Western Mediterranean Sea: consequences of human-induced modifications. Mar Pollution Bull 46:685–694. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00123-1
Gordon C, Cooper C, Senior CA et al (2000) The simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments. Clim Dyn 16:147–168. doi:10.1007/s003820050010
Govers R, Meijer P, Krijgsman W (2009) Regional isostatic response to Messinian Salinity Crisis events. Tectonophysics 463:109–129. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2008.09.026
Gregory D, Kershaw R, Inness PM (1997) Parametrization of momentum transport by convection. II: tests in single-column and general circulation models. Q J R Meteorol Soc 123:1153–1183. doi:10.1002/qj.49712354103
Griffies SM, Böning C, Bryan FO et al (2000) Developments in ocean climate modelling. Ocean Model 2:123–192. doi:10.1016/S1463-5003(00)00014-7
Hawkins E, Smith RS, Allison LC et al. (2011) Bistability of the Atlantic overturning circulation in a global climate model and links to ocean freshwater transport. Geophys Res Lett 38: 6 pp. doi:10.1029/2011GL047208
Hibler WD (1979) A dynamic thermodynamic sea ice model. J Phys Oceanogr 9:815–846. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1979)009<0815:ADTSIM>2.0.CO;2
Huisman SE, den Toom M, Dijkstra HA, Drijfhout S (2010) An Indicator of the multiple equilibria regime of the Atlantic Meridional overturning circulation. J Phys Oceanogr 40:551–567. doi:10.1175/2009JPO4215.1
Ivanovic RF, Valdes PJ, Flecker R, Gregoire LJ, Gutjahr M (2013) The parameterisation of Mediterranean–Atlantic water exchange in the Hadley Centre model HadCM3, and its effect on modelled North Atlantic climate. Ocean Model 62:11–16. doi:10.1016/j.ocemod.2012.11.002
Johns TC, Carnell RE, Crossley JF et al (1997) The second Hadley Centre coupled ocean-atmosphere GCM: model description, spinup and validation. Clim Dyn 13:103–134. doi:10.1007/s003820050155
Johnson RG (1997) Climate control required a dam at the Strait of Gibraltar Eos Trans AGU 78: PAGE 277. doi:10.1029/97EO00180
Johnson J, Ambar I, Serra N, Stevens I (2002) Comparative studies of the spreading of Mediterranean water through the Gulf of Cadiz. Deep Sea Res Part 2 Top Stud Oceanogr 49:4179–4193
Jungclaus JH, Mellor GL (2000) A three-dimensional model study of the Mediterranean outflow. J Mar Syst 24:41–66. doi:10.1016/S0924-7963(99)00078-0
Kahana R (2005) Modelling the interactions between the Mediterranean and the Global Thermohaline Circulations. PhD thesis, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK
Krijgsman W, Hilgen FJ, Raffi I, Sierro FJ, Wilson DS (1999) Chronology, causes and progression of the Messinian salinity crisis. Nature 400:652–655. doi:10.1038/23231
Loget N, Vandendriessche J (2006) On the origin of the Strait of Gibraltar. Sediment Geol 188–189:341–356. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.03.012
Marino G, Rohling EJ, Rijpstra WIC, Sangiorgi F, Schouten S, Damsté JSS (2007) Aegean Sea as driver of hydrographic and ecological changes in the Eastern Mediterranean. Geology 35:675–678. doi:10.1130/G23831A.1
Mariotti A (2010) Recent changes in the Mediterranean Water cycle: a Pathway toward long-term regional hydroclimatic change? J Clim 23:1513–1525. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI3251.1
Mariotti A, Struglia MV, Zeng N, Lau K-M (2002) The hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean region and implications for the water budget of the Mediterranean Sea. J Clim 15:1674–1690. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<1674:THCITM>2.0.CO;2
Mariotti A, Zeng N, Yoon J-H et al (2008) Mediterranean water cycle changes: transition to drier 21st century conditions in observations and CMIP3 simulations. Environ Res Lett 3:044001. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/3/4/044001
Mauritzen C, Morel Y, Paillet J (2001) On the influence of Mediterranean water on the central waters of the North Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res Part 2 Top Stud Oceanogr 48:347–381. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(00)00043-1
McCartney MS, Mauritzen C (2001) On the origin of the warm inflow to the Nordic Seas. Prog Oceanogr 51:125–214. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(01)00084-2
Milne GA, Long AJ, Bassett SE (2005) Modelling Holocene relative sea-level observations from the Caribbean and South America. Quat Sci Rev 24:1183–1202. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2004.10.005
New A, Barnard S, Herrmann P, Molines J-M (2001) On the origin and pathway of the saline inflow to the Nordic Seas: insights from models. Progr Oceanogr 48:255–287. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(01)00007-6
Osborne AH, Marino G, Vance D, Rohling EJ (2010) Eastern Mediterranean surface water Nd during Eemian sapropel S5: monitoring northerly (mid-latitude) versus southerly (sub-tropical) freshwater contributions. Quat Sci Rev 29:2473–2483. doi:16/j.quascirev.2010.05.015
Papadakis MP, Chassignet EP, Hallberg RW (2003) Numerical simulations of the Mediterranean sea outflow: impact of the entrainment parameterization in an isopycnic coordinate ocean model. Ocean Model 5:325–356. doi:10.1016/S1463-5003(02)00042-2
Penaud A, Eynaud F, Sánchez-Goñi M, Malaizé B, Turon JL, Rossignol L (2011) Contrasting sea-surface responses between the western Mediterranean Sea and eastern subtropical latitudes of the North Atlantic during abrupt climatic events of MIS 3. Mar Micropaleontol 80:1–17. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2011.03.002
Pope VD, Gallani ML, Rowntree PR, Stratton RA (2000) The impact of new physical parametrizations in the Hadley Centre climate model: hadAM3. Clim Dyn 16:123–146. doi:10.1007/s003820050009
Rahmstorf S (1996) On the freshwater forcing and transport of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation. Clim Dyn 12:799–811. doi:10.1007/s003820050144
Rahmstorf S (1998) Influence of mediterranean outflow on climate. Eos Trans AGU 79:281. doi:199810.1029/98EO00208
Reid JL (1978) On the middepth circulation and salinity Field in the North Atlantic Ocean. J Geophys Res 83:5063–5067. doi:197810.1029/JC083iC10p05063
Reid JL (1979) On the contribution of the Mediterranean Sea outflow to the Norwegian-Greenland Sea. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanogra Res Pap 26:1199–1223. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(79)90064-5
Rogerson M, Rohling EJ, Weaver PPE (2006) Promotion of meridional overturning by Mediterranean-derived salt during the last deglaciation. Paleoceanography 21: 8 pp. doi:10.1029/2006PA001306
Rogerson M, Colmenero-Hidalgo E, Levine RC et al. (2010) Enhanced Mediterranean-Atlantic exchange during Atlantic freshening phases. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 11: 22 PP. doi:10.1029/2009GC002931
Rogerson M, Bigg GR, Rohling EJ, Ramirez J (2011) Vertical density gradient in the eastern North Atlantic during the last 30,000 years. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1148-4
Rogerson M, Rohling EJ, Bigg GR, Ramirez J (2012) Paleoceanography of the Atlantic-Mediterranean exchange: Overview and first quantitative assessment of climatic forcing. Rev Geophys 50: 32 pp. doi:10.1029/2011RG000376
Rohling EJ, Schiebel R, Siddall M (2008) Controls on Messinian Lower Evaporite cycles in the Mediterranean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 275:165–171. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.08.022
Roveri M, Lugli S, Manzi V, Schreiber BC (2008) The Messinian Sicilian stratigraphy revisited: new insights for the Messinian salinity crisis. Terra Nova 20:483–488. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3121.2008.00842.x
Sanchez-Gomez E, Somot S, Josey SA, Dubois C, Elguindi N, Déqué M (2011) Evaluation of Mediterranean Sea water and heat budgets simulated by an ensemble of high resolution regional climate models. Clim Dyn 37:2067–2086. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1012-6
Serra Ambar I, Kase R (2005) Observations and numerical modelling of the Mediterranean outflow splitting and eddy generation. Deep Sea Res Part 2 Top Stud Oceanogr 52:383–408. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2004.05.025
Simmons AJ, Burridge DM (1981) An Energy and angular-momentum conserving vertical finite-difference scheme and hybrid vertical coordinates. Mon Weather Rev 109:758–766. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1981)109<0758:AEAAMC>2.0.CO;2
Skliris N, Lascaratos A (2004) Impacts of the Nile River damming on the thermohaline circulation and water mass characteristics of the Mediterranean Sea. J Mar Syst 52:121–143. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.02.005
Somot S, Sevault F, Déqué M (2006) Transient climate change scenario simulation of the Mediterranean Sea for the twenty-first century using a high-resolution ocean circulation model. Clim Dyn 27:851–879. doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0167-z
Somot S, Sevault F, Déqué M, Crépon M (2008) 21st century climate change scenario for the Mediterranean using a coupled atmosphere–ocean regional climate model. Glob Planet Change 63:112–126. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.10.003
Stanev EV (1992) Numerical experiment on the spreading of Mediterranean water in the North Atlantic. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanogra Res Pap 39:1747–1766. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(92)90027-Q
Stommel H, Farmer H (1952) Abrupt Change in Width in 2-Layer Open Channel Flow. J Mar Res 11:205–214
Stommel H, Farmer H (1953) Control of Salinity in an Estuary by a Transition. J Mar Res 12:13–20
Thorpe RB, Bigg GR (2000) Modelling the sensitivity of Mediterranean Outflow to anthropogenically forced climate change. Clim Dyn 16:355–368. doi:10.1007/s003820050333
Tsimplis MN, Bryden HL (2000) Estimation of the transports through the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res Part 2 Top Stud Oceanogr 47:2219–2242. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(00)00024-8
Vargas-Yáñez M, Zunino P, Benali A et al (2010) How much is the western Mediterranean really warming and salting? J Geophys Res 115:04001
Visbeck M, Marshall J, Haine T, Spall M (1997) Specification of eddy transfer coefficients in coarse-resolution ocean circulation models*. J Phys Oceanogr 27:381–402. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1997)027<0381:SOETCI>2.0.CO;2
Voelker AHL, Lebreiro S, Schonfeld J, Cacho I, Erlenkeuser H, Abrantes F (2006) Mediterranean outflow strengthening during northern hemisphere coolings: a salt source for the glacial Atlantic? Earth Planet Sci Lett 245:39–55. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.03.014
Xoplaki E, Luterbacher J, Gonzalez-Rouco JF (2006) Mediterranean summer temperature and winter precipitation, large scale dynamics, trends. Il Nuovo Cimento 29:45–54. doi:10.1393/ncc/i2005-10220-4
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the University of Bristol Centenary Scholarship and was carried out using the computational facilities of the Advanced Computing Research Centre, University of Bristol, http://www.bris.ac.uk/acrc/. Full access to the data produced by these simulations is provided at http://www.bridge.bris.ac.uk/resources/simulations. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanovic, R.F., Valdes, P.J., Gregoire, L. et al. Sensitivity of modern climate to the presence, strength and salinity of Mediterranean-Atlantic exchange in a global general circulation model. Clim Dyn 42, 859–877 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1680-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1680-5