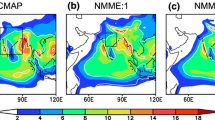
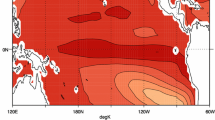
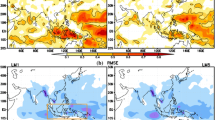
Abstract
The variability of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) is studied using a partially coupled climate model (PCCM) in which the ocean component is driven by observed monthly mean wind stress anomalies added to the monthly mean wind stress climatology from a fully coupled control run. The thermodynamic coupling between the atmospheric and oceanic components is the same as in the fully coupled model and, in particular, sea surface temperature (SST) is a fully prognostic variable. The results show that the PCCM simulates the observed SST variability remarkably well in the tropical and North Pacific and Indian Oceans. Analysis of the rainfall-SST and rainfall-SST tendency correlation shows that the PCCM exhibits local air-sea coupling as in the fully coupled model and closer to what is seen in observations than is found in an atmospheric model driven by observed SST. An ensemble of experiments using the PCCM is analysed using a multivariate EOF analysis to identify the two major modes of variability of the EASM. The PCCM simulates the spatial pattern of the first two modes seen in the ERA40 reanalysis as well as part of the variability of the first principal component (correlation up to 0.5 for the model ensemble mean). Different from previous studies, the link between the first principal component and ENSO in the previous winter is found to be robust for the ensemble mean throughout the whole period of 1958–2001. Individual ensemble members nevertheless show the breakdown in the relationship before the 1980’s as seen in the observations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M (1992) Midlatitude atmosphere–ocean interaction during El Niño. Part I: the North Pacific ocean. J Clim 5(9):944–958. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1992)005<0959:MAIDEN>2.0.CO;2
Chen T, Chang C (1980) The structure and vorticity budget of an early summer monsoon trough (Mei-Yu) over southeastern China and Japan. Mon Wea Rev 108(7):942–953. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<0942:TSAVBO>2.0.CO;2
DelSole T, Shukla J (2012) Climate models produce skillful predictions of Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 39(9):L09,703. doi:10.1029/2012GL051279
Ding H, Keenlyside N, Latif M (2011) Impact of the equatorial Atlantic on the El Niño southern oscillation. Clim Dyn 38(9-10):152. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1097-y
Ding Y, Chan J (2005) The Aast Asian summer monsoon: an overview. Meteorol Atmos Phys 89(1):117–142. doi:10.1007/s00703-005-0125-z
Enfield D, Mayer D (1997) Tropical Atlantic sea surface temperature variability and its relation to El Niño-southern oscillation. J Geophys Res 102(C1):929–945. doi:10.1029/96JC03296
Fu X, Wang B, Li T (2002) Impacts of air-sea coupling on the simulation of mean Asian summer monsoon in the ECHAM4 model. Mon Wea Rev 130(12):2889–2904. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2002)130<2889:IOASCO>2.0.CO;2
Gill A (1980) Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Quart J R Meteor Soc 106(449):447–462. doi:10.1002/qj.49710644905
Greatbatch R, Sun X, Yang XQ (2012) Impact of variability in the Indian summer monsoon on the East Asian summer monsoon. Atmospheric Science Letters (in press)
Hu Y, Zhong Z, Liu X, Zhu Y (2012) Influence of air–sea interaction on the simulation of East Asian summer monsoon: a case study. Dyn Atmos Oceans 53(54):1–16
Jin F (1997) An equatorial ocean recharge paradigm for ENSO. Part I: conceptual model. J Atmos Sci 54(7):811–829. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1997)054<0811:AEORPF>2.0.CO;2
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77(3):437–471. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
Kosaka Y, Nakamura H (2006) Structure and dynamics of the summertime Pacific-Japan teleconnection pattern. Quart J R Meteor Soc 132(619):2009–2030. doi:10.1256/qj.05.204
Kumar K, Rajagopalan B, Cane M (1999) On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO. Science 284(5423):2156–2159. doi:10.1126/science.284.5423.2156
Latif M, Sperber K, Arblaster J, Braconnot P, Chen D, Colman A, Cubasch U, Cooper C, Delecluse P, DeWitt D et al (2001) Ensip: the El Niño simulation intercomparison project. Clim Dyn 18(3):255–276. doi:10.1007/s003820100174
Latif M, Park W, Ding H, Keenlyside N (2009) Internal and external North Atlantic sector variability in the Kiel climate model. Meteorologische Zeitschrift 18(4):433–443. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0395
Lau K, Yang G, Shen S (1988) Seasonal and intraseasonal climatology of summer monsoon rainfall over East Asia. Mon Wea Rev 116(1):18–37. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1988)116<0018:SAICOS>2.0.CO;2
Li C, Lu R, Dong B (2012) Predictability of the western North Pacific summer climate demonstrated by the coupled models of ENSEMBLES. Clim Dyn 39(1–2):2. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1274-z
Li Y, Lu R, Dong B (2007) The ENSO-Asian monsoon interaction in a coupled ocean-atmosphere GCM. J Clim 20(20):5164–5177. doi:10.1175/JCLI4289.1
Lin H (2009) Global extratropical response to diabatic heating variability of the Asian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 66(9):2697–2713. doi:10.1175/2009JAS3008.1
Lin H, Wu Z (2012) Indian summer monsoon influence on the climate in the North Atlantic–European region. Clim Dyn 39:303–311. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1286-8
Lu R, Li Y, Dong B (2006) External and internal summer atmospheric variability in the western North Pacific and East Asia. J Meteor Soc Japan 84(3):447–462
Madec G (2008) NEMO ocean engine. Note du Pole de modelisation. 27, Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace (IPSL)
Mantua N, Hare S, Zhang Y, Wallace J, Francis R, et al (1997) A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(6):1069–1080. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<1069:APICOW>2.0.CO;2
Nitta T (1987) Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the northern hemisphere summer circulation. J Meteor Soc Japan 65(3):373–390
Park W, Latif M (2008) Multidecadal and multicentennial variability of the meridional overturning circulation. Geophys Res Lett 35(22):L22,703. doi:10.1029/2008GL035779
Park W, Latif M (2011) Atlantic meridional overturning circulation response to idealized external forcing. Clim Dyn 1:1–18. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1212-0
Park W, Keenlyside N, Latif M, Ströh A, Redler R, Roeckner E, Madec G (2009) Tropical Pacific climate and its response to global warming in the Kiel climate model. J Clim 22(1):71–92. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2261.1
Philander S (1990) El Niño, La Niña, and the southern oscillation. Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Rayner N, Parker D, Horton E, Folland C, Alexander L, Rowell D, Kent E, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108(D14):4407–4453. doi:10.1029/2002JD002670
Richter I, Xie S (2008) On the origin of equatorial Atlantic biases in coupled general circulation models. Clim Dyn 31(5):587–598. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0364-z
Rodwell M, Hoskins B (2001) Subtropical anticyclones and summer monsoons. J Clim 14(15):3192–3211. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<3192:SAASM>2.0.CO;2
Roeckner E, Bäuml G, Bonaventura L, Brokopf R, Esch M, Girogetta M, Hagemann S, Kirchner I, Kornblueh L, Manzini E, Rhodin A, Schlese U, Schulzweida U, Tompkins A (2003) The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM 5, part I, MPI Report 349:137p. Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie, Hamburg
Sun X, Greatbatch R, Park W, Latif M (2010) Two major modes of variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Quart J R Meteor Soc 136(649):829–841. doi:10.1002/qj.635
Tao S, Chen L (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. Monsoon Meteorol 60:92
Trenberth K, Hurrell J (1994) Decadal atmosphere-ocean variations in the Pacific. Clim Dyn 9(6):303–319. doi:10.1007/BF00204745
Trenberth K, Branstator G, Karoly D (1998) Progress during TOGA in understanding and modeling global teleconnections associated with tropical sea surface temperatures. J Geophys Res 103(C7):14–291. doi:10.1029/97JC01444
Uppala S, Kållberg P, Simmons A, Andrae U, Bechtold V, Fiorino M, Gibson J, Haseler J, Hernandez A, Kelly G et al (2005) The ERA-40 re-analysis. Quart J R Meteor Soc 131(612):2961–3012. doi:10.1256/qj.04.176
Valcke S, Caubel A, Declat D, Terray L (2003) OASIS3 ocean atmosphere sea ice soil. Users guide Prisim project report 2
Venzke S, Latif M, Villwock A (2000) The coupled GCM ECHO-2. J Clim 13(8):1371–1383. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1371:TCGE>2.0.CO;2
Wahl S, Latif M, Park W, Keenlyside N (2009) On the tropical Atlantic SST warm bias in the Kiel climate model. Clim Dyn 33(6):174. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0690-9
Wang B (1992) The vertical structure and development of the ENSO anomaly mode during 1979-1989. J Atmos Sci 49(8):698–712. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1992)049<0698:TVSADO>2.0.CO;2
Wang B (2006) The Asian monsoon. Springer, Berlin
Wang B, Wu R, Fu X (2000) Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13(9):1517–1536. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2
Wang B, Kang I, Lee J (2004) Ensemble simulations of Asian-Australian monsoon variability by 11 AGCMs. J Clim 17(4):803–818. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0803:ESOAMV>2.0.CO;2
Wang B, Ding Q, Fu X, Kang I, Jin K, Shukla J, Doblas-Reyes F (2005) Fundamental challenge in simulation and prediction of summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 32(15):L15,711. doi:10.1029/2005GL022734
Wang B, Wu Z, Li J, Liu J, Chang C, Ding Y, Wu G (2008) How to measure the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 21(17):4449–4463. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2183.1
Wu R, Kirtman B (2003) On the impacts of the Indian summer monsoon on ENSO in a coupled GCM. Quart J R Meteor Soc 129(595):3439–3468. doi:10.1256/qj.02.214
Wu R, Kirtman B (2004) Impacts of the Indian Ocean on the Indian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship. J Clim 17(15):3037–3054. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<3037:IOTIOO>2.0.CO;2
Wu R, Kirtman B (2005) Roles of Indian and Pacific ocean air–sea coupling in tropical atmospheric variability. Clim Dyn 25(2):155–170. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0003-x
Wu R, Kirtman B (2007a) Regimes of seasonal air–sea interaction and implications for performance of forced simulations. Clim Dyn 29(4):393–410. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0246-9
Wu R, Kirtman B (2007b) Roles of the Indian Ocean in the Australian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship. J Clim 20(18):4768–4788. doi:10.1175/JCLI4281.1
Wu R, Hu Z, Kirtman B (2003) Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Clim 16(22):3742–3758. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3742:EOERAI>2.0.CO;2
Wu R, Kirtman B, Pegion K (2006) Local air-sea relationship in observations and model simulations. J Clim 19(19):4914–4932. doi:10.1175/JCLI3904.1
Xie P, Arkin P (1997) Global precipitation: a 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(11):2539–2558. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2539:GPAYMA>2.0.CO;2
Xie S, Du Y, Huang G, Zheng X, Tokinaga H, Hu K, Liu Q (2010) Decadal shift in El Niño influences on Indo-western Pacific and East Asian climate in the 1970s. J Clim 23(12):3352–3368. doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3429.1
Zebiak S, Cane M (1987) A model El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Mon Wea Rev 115(10):2262–2278. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<2262:AMENO>2.0.CO;2
Zhang R, Sumi A, Kimoto M (1999) A diagnostic study of the impact of El Niño on the precipitation in China. Adv Atmos Sci 16(2):229–241. doi:10.1007/BF02973084
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the BMBF MiKlip Project MODINI and GEOMAR. We are grateful to the Rechnenzentrum of Universität Kiel for the use of computer time. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. The atmospheric model (ECHAM5) runs were performed at the Northern Germany High Performance Computing Center (HLRN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Greatbatch, R.J., Park, W. et al. The variability of the East Asian summer monsoon and its relationship to ENSO in a partially coupled climate model. Clim Dyn 42, 367–379 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1642-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1642-3