Abstract
Introduction
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) is a brain disease that is caused by perinatal asphyxia. Icariin (ICA), which is an active component of Epimedii (a Chinese medicinal herb), has been verified to demonstrate a wide range of therapeutic effects, such as alleviating various kinds of brain injury.
Objective
The current study aims to examine the neuroprotective effects of ICA on neonatal HIBD in mice.
Materials and methods
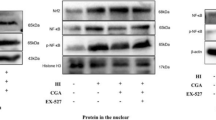
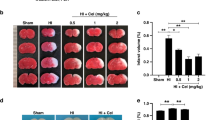
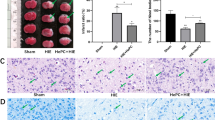
A modified version of the Rice-Vannucci method was performed to establish neonatal HIBD in 7-day-old mouse pups that were pretreated with ICA or vehicle. The infarct volume was measured, and behavioral tests were conducted to assess the protective effects of ICA on the neonatal brain and to evaluate functional recovery after injury. TUNEL staining was used to detect cell apoptosis, and the levels of cleaved caspase-3 and phosphorylated protein kinase B (Akt) were determined by using Western blot.
Results
We showed that pretreatment with ICA could significantly reduce brain damage, improve neurobehavioral outcomes, and suppress apoptotic cell death following HI injury. ICA reversed the HI-induced reduction in phosphorylated Akt and activation of cleaved caspase-3.
Conclusion
The results demonstrate that ICA exerts potential neuroprotective effects on neonatal HIBD, which may be mediated by its anti-apoptotic activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair J, Kumar VHS (2018) Current and emerging therapies in the management of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in neonates. Children (Basel) 5(7):E99
Pappas A, Korzeniewski SJ (2016) Long-term cognitive outcomes of birth asphyxia and the contribution of identified perinatal asphyxia to cerebral palsy. Clin Perinatol 43(3):559–572
Shah GS, Singh R, Das BK (2005) Outcome of newborns with birth asphyxia. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc 44:44–46
McAdams RM, Juul SE (2016) Neonatal encephalopathy: update on therapeutic hypothermia and other novel therapeutics. Clin Perinatol 43(3):485–500
Wei Z, Wang M, Hong M, Diao S, Liu A, Huang Y, Yu Q, Peng Z (2016) Icariin exerts estrogen-like activity in ameliorating EAE via mediating estrogen receptor β, modulating HPA function and glucocorticoid receptor expression. Am J Transl Res 8(4):1910–1918
Xiong D, Deng Y, Huang B, Yin C, Liu B, Shi J, Gong Q (2016) Icariin attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of inflammatory response mediated by NF-κB, PPARα and PPARγ in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 30:157–162
Mo ZT, Li WN, Zhai YR, Gong QH (2016) Icariin attenuates OGD/R-induced autophagy via Bcl-2-dependent cross talk between apoptosis and autophagy in PC12 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:4343084
Wei Z, Deng X, Hong M, Su Q, Liu A, Huang Y, Yu Q, Peng Z (2015) Icariin has synergistic effects with methylprednisolone to ameliorate EAE via modulating HPA function, promoting anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(11):20188–20197
Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9(2):131–141
Manabat C, Han BH, Wendland M, Derugin N, Fox CK, Choi J, Holtzman DM, Ferriero DM (2003) Reperfusion differentially induces caspase-3 activation in ischemic core and penumbra after stroke in immature brain. Stroke 34(1):207–213
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM (2006) Steinberg GK. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/akt survival signal pathways are implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol 34(3):249–270
Xu CQ, Liu BJ, Wu JF, Xu YC, Duan XH, Cao YX, Dong JC (2010) Icariin attenuates LPS-induced acute inflammatory responses: involvement of PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 642(1–3):146–153
Jin J, Wang H, Hua X, Chen D, Huang C, Chen Z (2019) An outline for thepharmacological effect of icariin in the nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol 842:20–32
Li L, Zhou QX, Shi JS (2005) Protective effects of icariin on neurons injured by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Chin Med J 118(19):1637–1643
Zheng M, Qu L, Lou Y (2008) Effects of icariin combined with Panax notoginseng saponins on ischemia reperfusion-induced cognitive impairments related with oxidative stress and CA1 of hippocampal neurons in rat. Phytother Res 22(5):597–604
Jia JM, Peng C, Wang Y, Zheng J, Ge WP (2018) Control of occlusion of middle cerebral artery in perinatal and neonatal mice with magnetic force. Mol Brain 11(1):47
Xu B, Xiao AJ, Chen W, Turlova E, Liu R, Barszczyk A, Sun CLF, Liu L, Tymianski M, Feng ZP (2016) Neuroprotective effects of a PSD-95 inhibitor in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 53(9):5962–5970
Xiao AJ, Chen W, Xu B, Liu R, Turlova E, Barszczyk A, Sun CL, Liu L, Deurloo M, Wang GL (2014) Marine compound xyloketal B reduces neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Mar Drugs 13(1):29–47
Hagberg H, Mallard C, Rousset CI (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms in the immature brain: involvement of mitochondria. J Child Neurol 24(9):1141–1146
Song YH, Cai H, Gu N, Qian CF, Cao SP, Zhao ZM (2011) Icariin attenuates cardiac remodelling through down-regulating myocardial apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinase activity in rats with congestive heart failure. J Pharm Pharmacol 63(4):541–549
Li L, Wang XM (2008) Progress of pharmacological research on icariin. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 33(23):2727–2732
Pruitt DG, Bullock KM, Banks WA, Jelliss PA (2017) Development of rhenacarborane complexes as central nervous system (CNS) drug delivery agents. Inorg Chim Acta 466:139–144
Zhao YJ, Nai Y, Li SY, Zheng YH (2018) Retigabine protects the blood-brain barrier by regulating tight junctions between cerebral vascular endothelial cells in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(23):8509–8518
Yang H, Xu Z, Liu W, Wei Y, Deng Y, Xu B (2012) Efect of grape seed pranthocyanidin extracts on methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 147(1–3):156–164
Liu B, Xu C, Wu X, Liu F, Du Y, Sun J, Tao J, Dong J (2015) Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation. Neuroscience 294:193–205
Liu XM, Feng Y, Li AM (2015) Efect of G-CSF and TPO on HIBD in neonatal rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 8:132–136
Jin F, Gong QH, Xu YS, Wang LN, Jin H, Li F, Li LS, Ma YM, Shi JS (2014) Icariin, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, improves learning and memory in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by stimulation of NO/cGMP signalling. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17(6):871–881
Chen WF, Wu L, Du ZR, Chen L, Xu AL, Chen XH, Teng JJ, Wong MS (2017) Neuroprotective properties of icariin in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease: involvement of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 25:93–99
Zhu HR, Wang ZY, Zhu XL, Wu XX, Li EG, Xu Y (2010) Icariin protects against brain injury by enhancing SIRT1-dependent PGC-1alpha expression in experimental stroke. Neuropharmacology 59(1–2):70–76
Wang L, Zhang L, Chen ZB, Wu JY, Zhang X, Xu Y (2009) Icariin enhances neuronal survival after oxygen and glucose deprivation by increasing SIRT1. Eur J Pharmacol 609(1–3):40–44
Chen W, Xu B, Xiao A, Liu L, Fang X, Liu R, Turlova E, Barszczyk A, Zhong X, Sun CL, Britto LR, Feng ZP, Sun HS (2015) TRPM7 inhibitor carvacrol protects brain from neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Mol Brain 8:11
Kilicdag H, Daglioglu YK, Erdogan S, Zorludemir S (2014) Effects of caffeine on neuronal apoptosis in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 27(14):1470–1475
Sidhu RS, Tuor UI, Del Bigio MR (1997) Nuclear condensation and fragmentation following cerebral hypoxia-ischemia occurs more frequently in immature than older rats. Neurosci Lett 223(2):129–132
Funding
This project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Youth (grant no. 81901524), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2018A030313579), the Science Foundation of Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine(20191015), the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (grant no. A2020252), and the Science Foundation of Guangdong No. 2 Provincial People’s Hospital for Youth (grant no. YQ2017-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Rong, Y. & Luo, L. Neuroprotective effects of icariin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemic brain damage via its anti-apoptotic property. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 39–46 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04690-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04690-8