Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the possible neuroprotective effects of the free radical scavenger edaravone in experimental hydrocephalus.
Methods
Seven-day-old Wistar rats were divided into three groups: control group (C), untreated hydrocephalic (H), and hydrocephalic treated with edaravone (EH). The H and EH groups were subjected to hydrocephalus induction by 20% kaolin intracisternal injection. The edaravone (20 mg/kg) was administered daily for 14 days from the induction of hydrocephalus. All animals were daily weighed and submitted to behavioral test and assessment by magnetic resonance imaging. After 14 days, the animals were sacrificed and the brain was removed for histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical studies.
Results
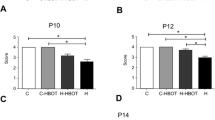
The gain weight was similar between groups from the ninth post-induction day. The open field test performance of EH group was better (p < 0.05) as compared to untreated hydrocephalic animals. Hydrocephalic animals (H and EH) showed ventricular ratio values were higher (p < 0.05), whereas magnetization transfer values were lower (p < 0.05), as compared to control animals. Astrocyte activity (glial fibrillary acidic protein) and apoptotic cells (caspase-3) of EH group were decreased on the corpus callosum (p > 0.01), germinal matrix (p > 0.05), and cerebral cortex (p > 0.05), as compared to H group.
Conclusions
We have demonstrated that administration of edaravone for 14 consecutive days after induction of hydrocephalus reduced astrocyte activity and that it has some beneficial effects over apoptotic cell death.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Del Bigio MR, Bruni JE, Fewer HD (1985) Human neonatal hydrocephalus. An electron microscopic study of the periventricular tissue. J Neurosurg 63:56–63
Yamada S, Kelly E (2016) Cerebrospinal fluid dynamics and the pathophysiology of hydrocephalus: new concepts. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 37:84–91
Socci DJ, Bjugstad KB, Jones HC, Pattisapu JV, Arendash GW (1999) Evidence that oxidative stress is associated with the pathophysiology of inherited hydrocephalus in the H-Tx rat model. Exp Neurol 155:109–117
Cosan TE, Gucuyener D, Dundar E, Arslantas A, Vural M, Uzuner K, Tel E (2001) Cerebral blood flow alterations in progressive communicating hydrocephalus: transcranial Doppler ultrasonography assessment in an experimental model. J Neurosurg 94:265–269
Higashi K, Asahisa H, Ueda N, Kobayashi K, Hara K, Noda Y (1986) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in experimental hydrocephalus. Neurol Res 8:169–176
da Silva MC, Michowicz S, Drake JM, Chumas PD, Tuor UI (1995) Reduced local cerebral blood flow in periventricular white matter in experimental neonatal hydrocephalus-restoration with CSF shunting. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:1057–1065
Shulyakov AV, Buist RJ, Del Bigio MR (2012) Intracranial biomechanics of acute experimental hydrocephalus in live rats. Neurosurgery 71:1032–1040
Caner H, Atasever A, Kilinc K, Durgun B, Peker S, Ozcan OE (1993) Lipid peroxide level increase in experimental hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir 121:68–71
Fersten E, Gordon-Krajcer W, Glowacki M, Mroziak B, Jurkiewicz J, Czernicki Z (2004) Cerebrospinal fluid free-radical peroxidation products and cognitive functioning patterns differentiate varieties of normal pressure hydrocephalus. Folia neuropathologica / Association of Polish Neuropathologists and Medical Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences 42:133–140
Thiong'o GM, Luzzio C, Albright AL (2015) Ventriculoperitoneal shunt perforations of the gastrointestinal tract. J Neurosurg Pediatr: 1–6
Jones HM, Hussain R, Leach P (2015) Patient dependant on ventriculo-atrial shunt after 49 years. Br J Neurosurg: 1–2
Boon AJ, Tans JT, Delwel EJ, Egeler-Peerdeman SM, Hanlo PW, Wurzer HA, Hermans J (1999) Dutch normal-pressure hydrocephalus study: the role of cerebrovascular disease. J Neurosurg 90:221–226
White IK, Shaikh KA, Nyarenchi OM, Kundu MG, Boaz JC, Fulkerson DH (2015) Analysis of the potential risk of central intravenous lines and/or total parenteral nutrition with ventriculoatrial shunts. Child's nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery 31:563–568
Simon TD, Hall M, Riva-Cambrin J, Albert JE, Jeffries HE, Lafleur B, Dean JM, Kestle JR (2009) Infection rates following initial cerebrospinal fluid shunt placement across pediatric hospitals in the United States. Clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:156–165
Ochieng N, Okechi H, Ferson S, Albright AL (2015) Bacteria causing ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections in a Kenyan population. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15:150–155
Catalao CH, Correa DA, Saito ST, Lopes Lda S (2014) Camellia sinensis neuroprotective role in experimentally induced hydrocephalus in Wistar rats. Childs Nerv Syst 30:591–597
Ishibashi A, Yoshitake Y, Adachi H (2013) Investigation of effect of edaravone on ischemic stroke. The Kurume medical journal 60:53–57
Dohare P, Hyzinski-Garcia MC, Vipani A, Bowens NH, Nalwalk JW, Feustel PJ, Keller RW, Jr., Jourd'heuil D, Mongin AA (2014) The neuroprotective properties of the superoxide dismutase mimetic tempol correlate with its ability to reduce pathological glutamate release in a rodent model of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med
Kikuchi K, Miura N, Kawahara KI, Murai Y, Morioka M, Lapchak PA, Tanaka E (2013) Edaravone (Radicut), a free radical scavenger, is a potentially useful addition to thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Biomedical reports 1:7–12
Nakamura T, Kuroda Y, Yamashita S, Zhang X, Miyamoto O, Tamiya T, Nagao S, Xi G, Keep RF, Itano T (2008) Edaravone attenuates brain edema and neurologic deficits in a rat model of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 39:463–469
Noor JI, Ikeda T, Mishima K, Aoo N, Ohta S, Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M, Ikenoue T (2005) Short-term administration of a new free radical scavenger, edaravone, is more effective than its long-term administration for the treatment of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Stroke 36:2468–2474
Yagi K, Kitazato KT, Uno M, Tada Y, Kinouchi T, Shimada K, Nagahiro S (2009) Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, inhibits MMP-9-related brain hemorrhage in rats treated with tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 40:626–631
Munakata A, Ohkuma H, Nakano T, Shimamura N, Asano K, Naraoka M (2009) Effect of a free radical scavenger, edaravone, in the treatment of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 64:423–428 discussion 428-429
Ito H, Wate R, Zhang J, Ohnishi S, Kaneko S, Nakano S, Kusaka H (2008) Treatment with edaravone, initiated at symptom onset, slows motor decline and decreases SOD1 deposition in ALS mice. Exp Neurol 213:448–455
Itoh T, Satou T, Nishida S, Tsubaki M, Hashimoto S, Ito H (2009) The novel free radical scavenger, edaravone, increases neural stem cell number around the area of damage following rat traumatic brain injury. Neurotox Res 16:378–389
Wang J, Guo G, Wang W, Tang Y, Shun J, Zhou X, Zhang P (2013) Effect of methylprednisolone and edaravone administration on spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:2766–2772
Kamida T, Fujiki M, Ooba H, Anan M, Abe T, Kobayashi H (2009) Neuroprotective effects of edaravone, a free radical scavenger, on the rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Seizure 18:71–75
Lopes Lda S, Slobodian I, Del Bigio MR (2009) Characterization of juvenile and young adult mice following induction of hydrocephalus with kaolin. Exp Neurol 219:187–196
Kamida T, Abe E, Abe T, Ooba H, Fujiki M, Kobayashi H (2009) Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, retards the development of amygdala kindling in rats. Neurosci Lett 461:298–301
Rocha Catalao CH, Leme Correa DA, Bernardino Garcia CA, Dos Santos AC, Garrido Salmon CE, Alves Rocha MJ, da Silva Lopes L (2014) Pre- and postshunting magnetization transfer ratios are in accordance with neurological and behavioral changes in hydrocephalic immature rats. Dev Neurosci 36:520–531
Fox WM (1965) Reflex-ontogeny and behavioural development of the mouse. Anim Behav 13:234–241
Khan OH, Enno TL, Del Bigio MR (2006) Brain damage in neonatal rats following kaolin induction of hydrocephalus. Exp Neurol 200:311–320
Tatem KS, Quinn JL, Phadke A, Yu Q, Gordish-Dressman H, Nagaraju K (2014) Behavioral and locomotor measurements using an open field activity monitoring system for skeletal muscle diseases. J Vis Exp: JoVE
Williams MT, Braun AA, Amos-Kroohs RM, McAllister JP, Lindquist DM, Mangano FT, Vorhees CV, Yuan W (2014) Kaolin-induced ventriculomegaly at weaning produces long-term learning, memory, and motor deficits in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 35:7–15
Braun KP, Dijkhuizen RM, de Graaf RA, Nicolay K, Vandertop WP, Gooskens RH, Tulleken KA (1997) Cerebral ischemia and white matter edema in experimental hydrocephalus: a combined in vivo MRI and MRS study. Brain Res 757:295–298
Castro SC, Machado HR, Catalao CH, Siqueira BA, Simoes AL, Lachat JJ, Lopes Lda S (2012) 0.1 T magnetic resonance image in the study of experimental hydrocephalus in rats. Accuracy of the method in the measurements of the ventricular size. Acta Cir Bras 27:768–772
Corkill RG, Garnett MR, Blamire AM, Rajagopalan B, Cadoux-Hudson TA, Styles P (2003) Multi-modal MRI in normal pressure hydrocephalus identifies pre-operative haemodynamic and diffusion coefficient changes in normal appearing white matter correlating with surgical outcome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 105:193–202
Yamada H, Yokota A, Furuta A, Horie A (1992) Reconstitution of shunted mantle in experimental hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 76:856–862
Yuan W, Mangano FT, Air EL, Holland SK, Jones BV, Altaye M, Bierbrauer K (2009) Anisotropic diffusion properties in infants with hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1792–1798
Newbould RD, Nicholas R, Thomas CL, Quest R, Lee JS, Honeyfield L, Colasanti A, Malik O, Mattoscio M, Matthews PM, Sormani MP, Waldman AD, Muraro PA (2014) Age independently affects myelin integrity as detected by magnetization transfer magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clinical 4:641–648
Schmierer K, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Tozer DJ, Boulby PA, Parkes HG, Yousry TA, Scaravilli F, Barker GJ, Tofts PS, Miller DH (2008) Quantitative magnetic resonance of postmortem multiple sclerosis brain before and after fixation. Magn Reson Med 59:268–277
Levesque I, Sled JG, Narayanan S, Santos AC, Brass SD, Francis SJ, Arnold DL, Pike GB (2005) The role of edema and demyelination in chronic T1 black holes: a quantitative magnetization transfer study. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:103–110
Giacomini PS, Levesque IR, Ribeiro L, Narayanan S, Francis SJ, Pike GB, Arnold DL (2009) Measuring demyelination and remyelination in acute multiple sclerosis lesion voxels. Arch Neurol 66:375–381
Silver NC, Barker GJ, MacManus DG, Tofts PS, Miller DH (1997) Magnetisation transfer ratio of normal brain white matter: a normative database spanning four decades of life. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 62:223–228
Sled JG, Levesque I, Santos AC, Francis SJ, Narayanan S, Brass SD, Arnold DL, Pike GB (2004) Regional variations in normal brain shown by quantitative magnetization transfer imaging. Magn Reson Med 51:299–303
Wang GH, Jiang ZL, Li YC, Li X, Shi H, Gao YQ, Vosler PS, Chen J (2011) Free-radical scavenger edaravone treatment confers neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 28:2123–2134
Ishikawa A, Yoshida H, Metoki N, Toki T, Imaizumi T, Matsumiya T, Yamashita K, Taima K, Satoh K (2007) Edaravone inhibits the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human astrocytes exposed to hypoxia. Neurosci Res 59:406–412
Botfield H, Gonzalez AM, Abdullah O, Skjolding AD, Berry M, McAllister JP, Logan A (2013) Decorin prevents the development of juvenile communicating hydrocephalus. Brain 136:2842–2858
Xu H, Tan G, Zhang S, Zhu H, Liu F, Huang C, Zhang F, Wang Z (2012) Minocycline reduces reactive gliosis in the rat model of hydrocephalus. BMC Neurosci 13:148
Di Curzio DL, Turner-Brannen E, Mao X, Del Bigio MR (2016) Magnesium sulfate treatment for juvenile ferrets following induction of hydrocephalus with kaolin. Fluids Barriers CNS 13:7
Li X, Li L, Li J, Sipple J, Schick J, Mehta PA, Davies SM, Dasgupta B, Waclaw RR, Pang Q (2014) Concomitant inactivation of foxo3a and fancc or fancd2 reveals a two-tier protection from oxidative stress-induced hydrocephalus. Antioxid Redox Signal
Di Curzio DL, Turner-Brannen E, Del Bigio MR (2014) Oral antioxidant therapy for juvenile rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 11:23
Yoshida H, Yanai H, Namiki Y, Fukatsu-Sasaki K, Furutani N, Tada N (2006) Neuroprotective effects of edaravone: a novel free radical scavenger in cerebrovascular injury. CNS Drug Rev 12:9–20
Li Q, Bi MJ, Bi WK, Kang H, Yan LJ, Guo YL (2014) Edaravone attenuates brain damage in rats after acute CO poisoning through inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol
Tsuruoka A, Atsumi C, Mizukami H, Imai T, Hagiwara Y, Hasegawa Y (2014) Effects of edaravone, a free radical scavenger, on circulating levels of MMP-9 and hemorrhagic transformation in patients with intravenous thrombolysis using low-dose alteplase. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis
Shokrzadeh M, Shaki F, Mohammadi E, Rezagholizadeh N, Ebrahimi F (2014) Edaravone decreases paraquat toxicity in a549 cells and lung isolated mitochondria. Iran J Pharm Res 13:675–681
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a grant and regulates assistance from FAPESP—Foundation of São Paulo Research. Camila A B Garcia was a recipient of FAPESP scholarship (grant number 2013/04130-6). The authors are grateful to Antonio Renato Meirelles e Silva for his assistance with the microscope photographs and to Prof Dr. João Pereira Leite for his assistance with the immunofluorescence analysis (Department of Neuroscience and Behavioral Sciences, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was designed according to the ethical guidelines published by the Brazilian College of Animal Experimentation (COBEA), protocol number 114/2012, and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Experimentation of Ribeirao Preto Medical School, University of Sao Paulo (CETEA/FMRP-USP).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the reported research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, C.A.B., Catalão, C.H.R., Machado, H.R. et al. Edaravone reduces astrogliosis and apoptosis in young rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 419–428 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3313-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3313-x