Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of modified pedicle subtraction osteotomy (mPSO) for thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis in pediatric patients.
Methods
From January 2008 to August 2012, 26 consecutive pediatric patients with thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis underwent modified pedicle subtraction osteotomy (mPSO). The clinical and radiologic outcomes were analyzed preoperatively, postoperatively, and at the last follow-up.
Results
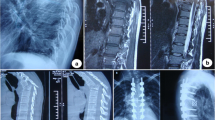
Twenty-six patients with thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis underwent mPSO. The average operation time was 256 min (188~314 min). The mean follow-up was 41 months (18~56 months). The mean estimated blood loss was 870 ml (620 ~ 1020 ml). The thoracolumbar kyphotic angle ranged from 51° to 79° before operation, 60.6° in average. The mean thoracolumbar kyphotic Cobb angle was 19.7° after operation, with a mean correction of 40.9°. The C7 sagittal plumb line was 3.8 cm after operation, comparing to the 10.5 cm preoperative. The mean preoperative angle of thoracic kyphosis (TK) was 9.9° ± 1.2° and increased to 11.8° ± 1.4°, postoperatively. Lumbar lordosis (LL) improved from −22.8° ± 4.9° preoperative to −17.8° ± 2.1° postoperative. Visual analogue scale (VAS) was 8.7 ± 1.1 preoperative and 1.2 ± 0.4 postoperative, respectively. The mean Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) improved from 49.2 ± 5.3 before surgery to 10.8 ± 3.3 postoperative (P < 0.01). All patients received good bone healing, no significant loss of correction angle. Most patients (24/26) considered pain and exterior was significantly improved.
Conclusion
Modified pedicle subtraction osteotomy (mPSO) is effective and reliable for thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis in pediatric patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moon M-S (1997) Tuberculosis of the spine: controversies and a new challenge. Spine 22:1791–1797
Tuli SM (1995) Severe kyphotic deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. Int Orthop 19:327–331
Moon MS, Kim I, Woo YK, Park YO (1987) Conservative treatment of tuberculosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine in adults and children. Int Orthop 11:315–322
Rajasekaran S (2001) The natural history of post-tubercular kyphosis in children. Radiological signs which predict late increase in deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:954–962
Rajasekaran S (2012) Kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis and its management. Int Orthop 36:359–365
Cho K-J, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Berra A, Baldus C (2005) Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine 30:2030–2037
Kim K-T, Lee S-H, Suk K-S, Lee J-H, Jeong B-O (2012) Outcome of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance of multiple etiologies: a retrospective review of 140 patients. Spine 37:1667–1675
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Edwards C, Lenke LG, Iffrig TM, Berra A, Baldus C, Blanke K (2003) Complications and outcomes of pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine 28:2093–2101
Lenke LG, O’Leary PT, Bridwell KH, Sides BA, Koester LA, Blanke KM (2009) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity: minimum two-year follow-up of thirty-five consecutive patients. Spine 34:2213–2221
Suk S-I, Kim J-H, Kim W-J, Lee S-M, Chung E-R, Nah K-H (2002) Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine 27:2374–2382
Smith-Petersen M, Larson CB, Aufranc OE (1945) Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 27:1–11
Thomasen E (1985) Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 194:142–152
Shimode M, Kojima T, Sowa K (2002) Spinal wedge osteotomy by a single posterior approach for correction of severe and rigid kyphosis or kyphoscoliosis. Spine 27:2260–2267
Kawahara N, Tomita K, Baba H, Kobayashi T, Fujita T, Murakami H (2001) Closing-opening wedge osteotomy to correct angular kyphotic deformity by a single posterior approach. Spine 26:391–402
Chunguang Z, Limin L, Rigao C, Yueming S, Hao L, Qingquan K, Quan G, Tao L, Jiancheng Z (2010) Surgical treatment of kyphosis in children in healed stages of spinal tuberculosis. J Pediatr Orthop 30:271–276
Moon M-S, Woo Y-K, Lee K-S, Ha K-Y, Kim S-S, Sun D-H (1995) Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine 20:1910–1916
Bezer M, Kucukdurmaz F, Guven O (2007) Transpedicular decancellation osteotomy in the treatment of posttuberculous kyphosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 20:209–215
Kalra K, Dhar S, Shetty G, Dhariwal Q (2006) Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for rigid post-tuberculous kyphosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:925–927
Rajasekaran S, Vijay K, Shetty AP (2010) Single-stage closing? Opening wedge osteotomy of spine to correct severe post-tubercular kyphotic deformities of the spine: a 3-year follow-up of 17 patients. Eur Spine J 19:583–592
Hamzaoglu A, Alanay A, Ozturk C, Sarier M, Karadereler S, Ganiyusufoglu K (2011) Posterior vertebral column resection in severe spinal deformities: a total of 102 cases. Spine 36:E340–E344
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K (2004) Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Essent Surg Tech 86:44–49
Kim K-T, Suk K-S, Cho Y-J, Hong G-P, Park B-J (2002) Clinical outcome results of pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with kyphotic deformity. Spine 27:612–618
Heary RF, Bono CM (2006) Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in the treatment of chronic, posttraumatic kyphotic deformity. J Neurosurg Spine 5:1–8
Acknowledgments
The study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO 81271940) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (NO 12JJ2043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong-Qi, Z., Yong, C., Jia, H. et al. Modified pedicle subtraction osteotomies (mPSO) for thoracolumbar post-tubercular kyphosis in pediatric patients: retrospective clinical cases and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 1347–1354 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2738-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2738-y