Abstract
Purpose
Achondroplasia is the most common form of dwarfism. Respiratory failure is responsible for most deaths among these children and is often related to cervicomedullary compression (CMC). We present our experience with early cervicomedullary decompression in infants with achondroplasia.
Methods
Data was retrospectively collected for infants with achondroplasia who underwent CMC decompression between 1998 and 2013. Data included presurgical and postsurgical neurological examinations, MRI scans, and sleep study results.
Results
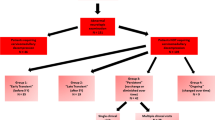
Ten infants were included. Ages at surgery were 4 to 23 months (12.5 ± 6.88 months). All infants displayed neurological findings prior to surgery, although often subtle. All infants underwent a foramen magnum opening with a wide C1 laminectomy. Following surgery, seven patients (70 %) demonstrated improved neurological status, and one displayed neurological deterioration. Seven patients demonstrated improved sleep quality 1 year after surgery. These patients had a good or improved neurological status following surgery. Preoperative radiological findings included abnormal hyperintense T2 changes in all children (improved following surgery in six children), brainstem distortion in four children (improved in all), and diminished cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) spaces at the level of the foramen magnum in eight children (improved in seven). One child with extensive preoperative T2 changes accompanied by neurological and respiratory decline, deteriorated following surgery, and remains chronically ventilated.
Conclusions
Infants with achondroplasia are prone to neurological and respiratory symptoms. We believe that early diagnosis and early surgery for decompression of the foramen magnum and C1 lamina can alleviate respiratory symptoms, improve neurological status, and perhaps prevent sudden infant death in this population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamada H, Nakamura S, Tajima M, Kageyama N (1981) Neurological manifestations of pediatric achondroplasia. J Neurosurg 54:49–57
Trotter TL, Hall JG, American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on G (2005) Health supervision for children with achondroplasia. Pediatrics 116:771–783
Morgan DF, Young RF (1980) Spinal neurological complications of achondroplasia. Results of surgical treatment. J Neurosurg 52:463–472
Hecht JT, Francomano CA, Horton WA, Annegers JF (1987) Mortality in achondroplasia. Am J Hum Genet 41:454–464
Nelson FW, Hecht JT, Horton WA, Butler IJ, Goldie WD, Miner M (1988) Neurological basis of respiratory complications in achondroplasia. Ann Neurol 24:89–93
Rimoin DL (1995) Cervicomedullary junction compression in infants with achondroplasia: when to perform neurosurgical decompression. Am J Hum Genet 56:824–827
Thomas IT, Frias JL, Williams JL, Friedman WA (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of medullary compression in achondroplasia. Am J Dis Child 142:989–992
Danielpour M, Wilcox WR, Alanay Y, Pressman BD, Rimoin DL (2007) Dynamic cervicomedullary cord compression and alterations in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in children with achondroplasia. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg 107:504–507
Afsharpaiman S, Saburi A, Waters KA (2013) Respiratory difficulties and breathing disorders in achondroplasia. Paediatr Respir Rev 14:250–255
Bagley CA, Pindrik JA, Bookland MJ, Camara-Quintana JQ, Carson BS (2006) Cervicomedullary decompression for foramen magnum stenosis in achondroplasia. J Neurosurg 104:166–172
Mukherjee D, Pressman BD, Krakow D, Rimoin DL, Danielpour M (2014) Dynamic cervicomedullary cord compression and alterations in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in children with achondroplasia: review of an 11-year surgical case series. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14:238–244
Benglis DM, Sandberg DI (2007) Acute neurological deficit after minor trauma in an infant with achondroplasia and cervicomedullary compression. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 107:152–155
(1996) Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:866–878
Uliel S, Tauman R, Greenfeld M, Sivan Y (2004) Normal polysomnographic respiratory values in children and adolescents. Chest 125:872–878
Muzumdar H, Arens R (2008) Diagnostic issues in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:263–273
Berry RB, Budhiraja R, Gottlieb DJ, Gozal D, Iber C, Kapur VK, Marcus CL, Mehra R, Parthasarathy S, Quan SF, Redline S, Strohl KP, Davidson Ward SL, Tangredi MM, American Academy of Sleep M (2012) Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med JCSM Off Publ Am Acad Sleep Med 8:597–619
(1995) Health supervision for children with achondroplasia. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Genetics. Pediatrics 95:443–451
Keiper GL Jr, Koch B, Crone KR (1999) Achondroplasia and cervicomedullary compression: prospective evaluation and surgical treatment. Pediatr Neurosurg 31:78–83
Stokes DC, Phillips JA, Leonard CO, Dorst JP, Kopits SE, Trojak JE, Brown DL (1983) Respiratory complications of achondroplasia. J Pediatr 102:534–541
Reid CS, Pyeritz RE, Kopits SE, Maria BL, Wang H, McPherson RW, Hurko O, Phillips JA 3rd, Rosenbaum AE (1987) Cervicomedullary compression in young patients with achondroplasia: value of comprehensive neurologic and respiratory evaluation. J Pediatr 110:522–530
Mogayzel PJ Jr, Carroll JL, Loughlin GM, Hurko O, Francomano CA, Marcus CL (1998) Sleep-disordered breathing in children with achondroplasia. J Pediatr 132:667–671
Waters KA, Everett F, Sillence DO, Fagan ER, Sullivan CE (1995) Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in achondroplasia: evaluation of sleep, breathing, and somatosensory-evoked potentials. Am J Med Genet 59:460–466
Hecht JT, Thompson NM, Weir T, Patchell L, Horton WA (1991) Cognitive and motor skills in achondroplastic infants: neurologic and respiratory correlates. Am J Med Genet 41:208–211
Hill CM, Hogan AM, Karmiloff-Smith A (2007) To sleep, perchance to enrich learning? Arch Dis Child 92:637–643
Wang H, Rosenbaum AE, Reid CS, Zinreich SJ, Pyeritz RE (1987) Pediatric patients with achondroplasia: CT evaluation of the craniocervical junction. Radiology 164:515–519
Hecht JT, Horton WA, Reid CS, Pyeritz RE, Chakraborty R (1989) Growth of the foramen magnum in achondroplasia. Am J Med Genet 32:528–535
Horton WA, Hall JG, Hecht JT (2007) Achondroplasia. Lancet 370:162–172
Ireland PJ, Johnson S, Donaghey S, Johnston L, Ware RS, Zankl A, Pacey V, Ault J, Savarirayan R, Sillence D, Thompson E, Townshend S, McGill J (2012) Medical management of children with achondroplasia: evaluation of an Australasian cohort aged 0–5 years. J Paediatr Child Health 48:443–449
King JA, Vachhrajani S, Drake JM, Rutka JT (2009) Neurosurgical implications of achondroplasia. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:297–306
Hunter AG, Bankier A, Rogers JG, Sillence D, Scott CI Jr (1998) Medical complications of achondroplasia: a multicentre patient review. J Med Genet 35:705–712
Afsharpaiman S, Sillence DO, Sheikhvatan M, Ault JE, Waters K (2011) Respiratory events and obstructive sleep apnea in children with achondroplasia: investigation and treatment outcomes. Sleep Breath 15:755–761
Ednick M, Tinkle BT, Phromchairak J, Egelhoff J, Amin R, Simakajornboon N (2009) Sleep-related respiratory abnormalities and arousal pattern in achondroplasia during early infancy. J Pediatr 155:510–515
Pauli RM, Scott CI, Wassman ER Jr, Gilbert EF, Leavitt LA, Ver Hoeve J, Hall JG, Partington MW, Jones KL, Sommer A et al (1984) Apnea and sudden unexpected death in infants with achondroplasia. J Pediatr 104:342–348
Pauli RM, Horton VK, Glinski LP, Reiser CA (1995) Prospective assessment of risks for cervicomedullary-junction compression in infants with achondroplasia. Am J Hum Genet 56:732–744
Simmons K, Hashmi SS, Scheuerle A, Canfield M, Hecht JT (2014) Mortality in babies with achondroplasia: revisited. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 100:247–249
Wynn J, King TM, Gambello MJ, Waller DK, Hecht JT (2007) Mortality in achondroplasia study: a 42-year follow-up. Am J Med Genet A 143A:2502–2511
Hecht JT, Butler IJ, Scott CI Jr (1984) Long-term neurological sequelae in achondroplasia. Eur J Pediatr 143:58–60
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
There are no prior publications or submissions with any overlapping information including studies and patients
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimony, N., Ben-Sira, L., Sivan, Y. et al. Surgical treatment for cervicomedullary compression among infants with achondroplasia. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 743–750 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2624-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2624-7