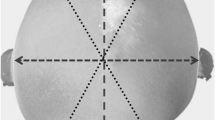
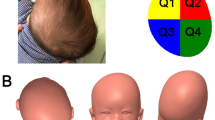
Abstract
Background
The growing number of infants with deformational plagiocephaly (DP) has raised clinical questions about which children, at what age, and how molding helmet therapy (MHT) should be performed especially in Japan.
Methods
A total of 1,011 Japanese pediatric head deformity infants had undergone MHT after being diagnosed with non-synostotic DP. Three ratios of left to right comparison (anterior, posterior, and overall) were created and analyzed comparing age of starting treatment, helmet wearing period, and severity of skull deformity before with after MHT.
Results
The averages of head symmetry ratios after treatment in all groups (for the occipital region) showed apparent improvement; t(930) = −60.86, p = 0.000. (t(932) = −57.8, p = 0.000.) In the “severe” deformation group, the earlier the treatment was started, the higher symmetry ratio recovery was obtained. Treatment was especially effective when started in 4-month-old infants. In contrast to the “severe” group, the “mild” deformation group showed that MHT was most effective if treatment started before 6 months of age. Again, the earlier the treatment was started, the higher symmetry ratio was achieved, but compared to the “severe” group, it had a modest effect when treatment was started in infants older than 8 months.
Conclusion
This is the first large-scale molding helmet study reporting the method and efficacy in Japanese infants. It demonstrated that despite the structural and physiological differences from infants of other races, molding helmet therapy is effective in Asian-born infants, provided that intervention timing and recognition conditions are met.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kluba S, Kraut W, Reinert S, Krimmel M (2011) What is the optimal time to start helmet therapy in positional plagiocephaly? Plast Reconstr Surg 128:492–498
Lipira AB, Gordon S, Darvann TA, Hermann NV, Van Pelt AE, Naidoo SD, Govier D, Kane AA (2010) Helmet versus active repositioning for plagiocephaly: a three-dimensional analysis. Pediatrics 126:e936–e945
Biggs WS (2003) Diagnosis and management of positional head deformity. Am Fam Physician 67:1953–1956
Mortenson P, Steinbok P, Smith D (2012) Deformational plagiocephaly and orthotic treatment: indications and limitations. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1407–1412
Yoo HS, Rah DK, Kim YO (2012) Outcome analysis of cranial molding therapy in nonsynostotic plagiocephaly. Arch Plast Surg 39:338–344
Plank LH, Giavedoni B, Lombardo JR, Geil MD, Reisner A (2006) Comparison of infant head shape changes in deformational plagiocephaly following treatment with a cranial remolding orthosis using a noninvasive laser shape digitizer. J Craniofac Surg 17:1084–1091
Wilbrand JF, Seidl M, Wilbrand M, Streckbein P, Bottger S, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Hahn A, Howaldt HP (2013) A prospective randomized trial on preventative methods for positional head deformity: physiotherapy versus a positioning pillow. J Pediatr 162:1216–1221, 1221 e1211
Paquereau J (2013) Non-surgical management of posterior positional plagiocephaly: orthotics versus repositioning. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 56:231–249
Pogliani L, Mameli C, Fabiano V, Zuccotti GV (2011) Positional plagiocephaly: what the pediatrician needs to know. A review. Childs Nerv Syst 27:1867–1876
Kluba S, Schreiber R, Kraut W, Meisner C, Reinert S, Krimmel M (2012) Does helmet therapy influence the ear shift in positional plagiocephaly? J Craniofac Surg 23:1301–1305
Shamji MF, Fric-Shamji EC, Merchant P, Vassilyadi M (2012) Cosmetic and cognitive outcomes of positional plagiocephaly treatment. Clin Investig Med 35:E266
Rekate HL (1998) Occipital plagiocephaly: a critical review of the literature. J Neurosurg 89:24–30
Davis BE, Moon RY, Sachs HC, Ottolini MC (1998) Effects of sleep position on infant motor development. Pediatrics 102:1135–1140
Binder H, Eng GD, Gaiser JF, Koch B (1987) Congenital muscular torticollis: results of conservative management with long-term follow-up in 85 cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 68:222–225
Seruya M, Oh AK, Taylor JH, Sauerhammer TM, Rogers GF (2013) Helmet treatment of deformational plagiocephaly: the relationship between age at initiation and rate of correction. Plast Reconstr Surg 131:55e–61e
Wilbrand JF, Wilbrand M, Malik CY, Howaldt HP, Streckbein P, Schaaf H, Kerkmann H (2012) Complications in helmet therapy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40:341–346
Ifflaender S, Rudiger M, Konstantelos D, Wahls K, Burkhardt W (2013) Prevalence of head deformities in preterm infants at term equivalent age. Early Hum Dev 89:1041–1047
Mawji A, Vollman AR, Hatfield J, McNeil DA, Sauve R (2013) The incidence of positional plagiocephaly: a cohort study. Pediatrics 132:298–304
van Wijk RM, van Vlimmeren LA, Groothuis-Oudshoorn CG, Van der Ploeg CP, Ijzerman MJ, Boere-Boonekamp MM (2014) Helmet therapy in infants with positional skull deformation: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 348:g2741
Roby BB, Finkelstein M, Tibesar RJ, Sidman JD (2012) Prevalence of positional plagiocephaly in teens born after the “Back to Sleep” campaign. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:823–828
Meyer-Marcotty P, Bohm H, Linz C, Kunz F, Keil N, Stellzig-Eisenhauer A, Schweitzer T (2012) Head orthesis therapy in infants with unilateral positional plagiocephaly: an interdisciplinary approach to broadening the range of orthodontic treatment. J Orofac Orthop 73:151–165
Schweitzer T, Bohm H, Linz C, Jager B, Gerstl L, Kunz F, Stellzig-Eisenhauer A, Ernestus RI, Krauss J, Meyer-Marcotty P (2013) Three-dimensional analysis of positional plagiocephaly before and after molding helmet therapy in comparison to normal head growth. Childs Nerv Syst
Schaaf H, Wilbrand JF, Boedeker RH, Howaldt HP (2010) Accuracy of photographic assessment compared with standard anthropometric measurements in nonsynostotic cranial deformities. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 47:447–453
Schaaf H, Malik CY, Streckbein P, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Howaldt HP, Wilbrand JF (2010) Three-dimensional photographic analysis of outcome after helmet treatment of a nonsynostotic cranial deformity. J Craniofac Surg 21:1677–1682
Wilbrand JF, Wilbrand M, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Blecher JC, Christophis P, Howaldt HP, Schaaf H (2011) Value and reliability of anthropometric measurements of cranial deformity in early childhood. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 39:24–29
Wilbrand JF, Schmidtberg K, Bierther U, Streckbein P, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Christophis P, Hahn A, Schaaf H, Howaldt HP (2012) Clinical classification of infant nonsynostotic cranial deformity. J Pediatr 161:1120–1125
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Kostadin Karagiozov for his advice and manuscript review and David Huang for his guidance, and we gratefully acknowledge the radiological technologists, nurses, and staff of the Departments of Neurosurgery, Tokyo Women’s Medical University, in preparing this paper.
Disclose financial relationships for all authors
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Funding
None.
Contributors’ statement page
Yasuo Aihara—Dr. Aihara conceptualized and designed the study and drafted the initial manuscript.
Kana Komatsu Osami Kubo, Tomokatsu Hori—Ms. Komatsu and Dr. Kubo and Dr. Hori carried out the initial analyses and reviewed the manuscript.
Hitoshi Dairoku Yoshikazu Okada—Mr Dairoku designed the data collection instruments and coordinated and supervised data collection. Dr. Okada critically reviewed the manuscript.
All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aihara, Y., Komatsu, K., Dairoku, H. et al. Cranial molding helmet therapy and establishment of practical criteria for management in Asian infant positional head deformity. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 1499–1509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2471-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2471-y