Abstract
Introduction
Nonsynostotic posterior plagiocephaly has become the most common skull deformation since pediatricians have suggested the supine position for the newborns to reduce the risk of sudden death. Prevention of such a “positional” deformation or its management once it has occurred is mainly based on physical maneuvers such as physiotherapy and active positional corrective measures.
Selection criteria
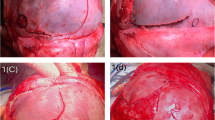
Surgical correction, however, may be suggested in rare cases where deformation of the skull is so severe or the referral of the child is so late that physical corrective treatment cannot be taken into consideration. Surgical management is based on the creation of a posterior bone flap to be repositioned after the opportune contouring and rotation.
Purpose
The aim of this paper is to describe the surgical technique used for posterior vault remodeling in posterior plagiocephaly at the craniofacial unit of Hopital Necker Enfants Malades (French National Referral Center for Faciocraniosynostosis) focusing on its advantages and limitations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud E, Renier D (2006) Pediatric craniofacial osteosynthesis using an ultrasonic-assisted pinned resorbable system: a prospective report with a minimum 30 months follow-up. J Craniofac Surg 20(6):2081–2086
Dahmani S, Orliaguet GA, Meyer PG, Blanot S, Renier D, Carli PA (2000) Perioperative blood salvage during surgical correction of craniosynostosis in infants. Br J Anaesth 85(4):550–555
Marchac A, Arnaud E, Di Rocco F, Michienzi J, Renier D (2011) Severe deformational plagiocephaly: long-term results of surgical treatment. J Craniofac Surg 22(1):24–29
Mottolese C, Szathmari A, Ricci AC, Ginguene C, Simon E, Paulus C (2006) Positional plagiocephaly: the place of cranial orthotics. Neurochirurgie 52(2–3):184–194
Mulliken JB, Vander Woude DL, Hansen M, LaBrie RA, Scott RM (1999) Analysis of posterior plagiocephaly: deformational versus synostotic. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(2):371–380
Orliaguet GA, Bruyere M, Meyer PG, Blanot S, Renier D, Carli PA (2003) Comparison of perioperative blood salvage and postoperative reinfusion of drained blood during surgical correction of craniosynostosis in infants. Paediatr Anaesth 13(9):797–804
Rogers GF (2011) Severe deformational plagiocephaly: long-term results of surgical treatment. J Craniofac Surg 22(1):1–3
Shin JH, Persing J (2003) Asymmetric skull shapes: diagnostic and therapeutic consideration. J Craniofac Surg 14(5):696–699
Turk AE, McCarthy JG, Thorne CH, Wisoff JH (1996) The "back to sleep campaign" and deformational plagiocephaly: is there cause for concern? J Craniofac Surg 7(1):12–18
Vergnaud E, Vecchione A, Blanot S, di Rocco F, Arnaud E, Renier D, Meyer P, the Pediatric Craniofacial Group (2012) Reducing blood losses and transfusion requirements in craniosynostosis surgery: an endless quest? Anesthesiology 116(3):733–734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Rocco, F., Marchac, A., Duracher, C. et al. Posterior remodeling flap for posterior plagiocephaly. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 1395–1397 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1842-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1842-5