Abstract
Purpose
Cerebral palsy is one of the most common reasons of osteopenia in childhood. Patients have a significantly decreased bone mineral density, and painful fractures with minor traumas are common. Biphosphonates in the treatment of childhood osteoporosis are increasingly being used. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of oral alendronate treatment in children with cerebral palsy.
Methods
Twenty-six children (16 boys and 10 girls) aged 3 to 17 years who had quadriplegic cerebral palsy and osteopenia were included in the study. The patients received alendronate (1 mg/kg/week), calcium (600 mg/day), and vitamin D3 (400 U/day) over a year. A complete blood count, kidney and liver functional tests, plasma calcium, phosphate and alkaline phosphatase levels, and lumbar vertebral bone mineral density were measured before and after treatment.
Results
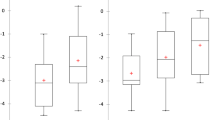
Compared with pretreatment values, bone mineral density, serum calcium, and phosphate levels of the patients statistically increased and alkaline phosphatase levels decreased after treatment. No patient needed to interrupt treatment because of side effects.
Conclusions
Oral alendronate at a dose of 1 mg/kg/week for the treatment of osteopenia in children with cerebral palsy was found to be safe and effective.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-023-05890-8
References
Akcay T, Turan S, Guran T, Bereket A (2008) Alendronate treatment in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Indian Pediatr 45:105–109
Ali O, Shim M, Fowler E, Greenberg M, Perkins D, Oppenheim W, Cohen P (2007) Growth hormone therapy improves bone mineral density in children with cerebral palsy: a preliminary pilot study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:932–937
Allington N, Vivegnis D, Gerard P (2005) Cyclic administration of pamidronate to treat osteoporosis in children with cerebral palsy or a neuromuscular disorder: a clinical study. Acta Orthop Belg 71:91–97
Baroncelli GI, Bertelloni S, Sodini F, Saggese G (2005) Osteoporosis in children and adolescents: etiology and management. Paediatr Drugs 7:295–323
Bass SL, Naughton G, Saxon L, Iuliano-Burns S, Daly R, Briganti EM, Hume C, Nowson C (2007) Exercise and calcium combined results in a greater osteogenic effect than either factor alone: a blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial in boys. J Bone Miner Res 22:458–464
Bianchi ML (2007) Osteoporosis in children and adolescents. Bone 41:486–495
Caulton JM, Ward KA, Alsop CW, Dunn G, Adams JE, Mughal MZ (2004) A randomised controlled trial of standing programme on bone mineral density in non-ambulant children with cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child 89:131–135
Chad KE, Bailey DA, McKay HA, Zello GA, Snyder RE (1999) The effect of a weight-bearing physical activity program on bone mineral content and estimated volumetric density in children with spastic cerebral palsy. J Pediatr 135:115–117
Conwell LS, Chang AB (2009) Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD002010
Demir E, Bereket A, Ozkan B, Topcu M (2000) Effect of alendronate treatment on the clinical picture and bone turnover markers in chronic idiopathic hyperphosphatasia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 13:217–221
Glorieux FH, Bishop NJ, Plotkin H, Chabot G, Lanoue G, Travers R (1998) Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med 339(14):947–952
Goksen D, Darcan S, Coker M, Kose T (2006) Bone mineral density of healthy Turkish children and adolescents. J Clin Densitom 9:84–90
Henderson RC, Kairalla JA, Barrington JW, Abbas A, Stevenson RD (2005) Longitudinal changes in bone density in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. J Pediatr 146:769–775
Henderson RC, Lark RK, Gurka MJ, Worley G, Fung EB, Conaway M, Stallings VA, Stevenson RD (2002) Bone density and metabolism in children and adolescents with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 110(1 Pt 1):e5
Henderson RC, Lark RK, Kecskemethy HH, Miller F, Harcke HT, Bachrach SJ (2002) Bisphosphonates to treat osteopenia in children with quadriplegic cerebral palsy: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Pediatr 141:644–651
Houlihan CM, Stevenson RD (2009) Bone density in cerebral palsy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 20:493–508
Inoue Y, Shimojo N, Suzuki S, Arima T, Tomiita M, Minagawa M, Kohno Y (2008) Efficacy of intravenous alendronate for the treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in children with autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol 27:909–912
Iwasaki T, Takei K, Nakamura S, Hosoda N, Yokota Y, Ishii M (2008) Secondary osteoporosis in long-term bedridden patients with cerebral palsy. Pediatr Int 50:269–275
Kilpinen-Loisa P, Nenonen H, Pihko H, Makitie O (2007) High-dose vitamin D supplementation in children with cerebral palsy or neuromuscular disorder. Neuropediatrics 38:167–172
Kitazaki S, Mitsuyama K, Masuda J, Harada K, Yamasaki H, Kuwaki K, Takedatsu H, Sugiyama G, Tsuruta O, Sata M (2009) Clinical trial: comparison of alendronate and alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-associated osteoporosis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29:424–430
Lee JJ, Lyne ED (1990) Pathologic fractures in severely handicapped children and young adults. J Pediatr Orthop 10:497–500
Noguera A, Ros JB, Pavia C, Alcover E, Valls C, Villaronga M, Gonzalez E (2003) Bisphosphonates, a new treatment for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 16:529–536
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B (1997) Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 39:214–223
Phillipi CA, Remmington T, Steiner RD (2008) Bisphosphonate therapy for osteogenesis imperfecta. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD005088
Plotkin H, Coughlin S, Kreikemeier R, Heldt K, Bruzoni M, Lerner G (2006) Low doses of pamidronate to treat osteopenia in children with severe cerebral palsy: a pilot study. Dev Med Child Neurol 48:709–712
Recker RR, Lewiecki EM, Miller PD, Reiffel J (2009) Safety of bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med 122(2 Suppl):22–32
Salehpour S, Tavakkoli S (2010) Cyclic pamidronate therapy in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 23:73–80
Shaw NJ, White CP, Fraser WD, Rosenbloom L (1994) Osteopenia in cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child 71:235–238
Sugiyama T, Takaki T, Saito T, Taguchi T (2007) Vitamin K therapy for cortical bone fragility caused by reduced mechanical loading in a child with hemiplegia. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 7:219–223
Tasdemir HA, Buyukavci M, Akcay F, Polat P, Yildiran A, Karakelleoglu C (2001) Bone mineral density in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatr Int 43:157–160
Unal E, Abaci A, Bober E, Buyukgebiz A (2006) Efficacy and safety of oral alendronate treatment in children and adolescents with osteoporosis. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 19:523–528
Unay B, Sarici SU, Vurucu S, Inanc N, Akin R, Gokcay E (2003) Evaluation of bone mineral density in children with cerebral palsy. Turk J Pediatr 45:11–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paksu, M.S., Vurucu, S., Karaoglu, A. et al. Osteopenia in children with cerebral palsy can be treated with oral alendronate. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 283–286 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1576-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1576-9