Abstract
Purpose
Medulloblastomas are the most common malignant tumors of the central nervous system in childhood. The incidence is about 19–20% between children younger than 16 years old with peak incidence between 4 and 7 years. Despite its sensibility to no specific therapeutic means like chemotherapy and radiotherapy, the treatment is very aggressive and frequently results in regression, growth deficit, and endocrine dysfunction. From this point of view, new treatment approaches are needed such as molecular targeted therapies. Studies in glioblastoma demonstrated that ASPM gene was overexpressed when compared to normal brain and ASPM inhibition by siRNA-mediated inhibits tumor cell proliferation and neural stem cell proliferation, supporting ASPM gene as a potential molecular target in glioblastoma. The aim of this work was to evaluate ASPM expression in medulloblastoma fragment samples, and to compare the results with the patient clinical features.
Methods
Analysis of gene expression was performed by quantitative PCR real time using SYBR Green system in tumor samples from 37 children. The t test was used to analyze the gene expression, and Mann–Whitney test was performed to analyze the relationship between gene expressions and clinical characteristics. Kaplan–Meier test evaluated curve survival.
Results
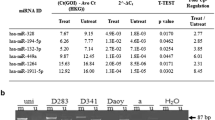
All samples overexpressed ASPM gene more than 40-fold. However, we did not find any association between the overexpressed samples and the clinical parameters.
Conclusion
ASPM overexpression may modify the ability of stem cells to differentiate during the development of the central nervous system, contributing to the development of medulloblastoma, a tumor of embryonic origin from cerebellar progenitor cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond J, Roberts E, Mochida GH, Hampshire DJ, Scott S, Askham JM, Springell K, Mahadevan M, Crow YJ, Markham AF, Walsh CA, Woods CG (2002) ASPM is a major determinant of cerebral cortical size. Nat Genet 32:316–320
Brinkley BR (2001) Managing the centrosome numbers game: from chaos to stability in cancer cell division. Trends Cell Biol 11:18–21
Chang CH, Housepian EM, Herbert C Jr (1969) An operative staging system and a megavoltage radiotherapeutic technic for cerebellar medulloblastomas. Radiology 93:1351–1359
Fish JL, Kosodo Y, Enard W, Paabo S, Huttner WB (2006) Aspm specifically maintains symmetric proliferative divisions of neuroepithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10438–10443
Guessous F, Li Y, Abounader R (2008) Signaling pathways in medulloblastoma. J Cell Physiol 217:577–583
Horvath S, Zhang B, Carlson M, Lu KV, Zhu S, Felciano RM, Laurance MF, Zhao W, Qi S, Chen Z, Lee Y, Scheck AC, Liau LM, Wu H, Geschwind DH, Febbo PG, Kornblum HI, Cloughesy TF, Nelson SF, Mischel PS (2006) Analysis of oncogenic signaling networks in glioblastoma identifies ASPM as a molecular target. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17402–17407
Korshunov A, Benner A, Remke M, Lichter P, von Deimling A, Pfister S (2008) Accumulation of genomic aberrations during clinical progression of medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol 116:383–390
Kouprina N, Pavlicek A, Collins NK, Nakano M, Noskov VN, Ohzeki J, Mochida GH, Risinger JI, Goldsmith P, Gunsior M, Solomon G, Gersch W, Kim JH, Barrett JC, Walsh CA, Jurka J, Masumoto H, Larionov V (2005) The microcephaly ASPM gene is expressed in proliferating tissues and encodes for a mitotic spindle protein. Hum Mol Genet 14:2155–2165
Lin SY, Pan HW, Liu SH, Jeng YM, Hu FC, Peng SY, Lai PL, Hsu HC (2008) ASPM is a novel marker for vascular invasion, early recurrence, and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14:4814–4820
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
MacDonald TJ (2008) Aggressive infantile embryonal tumors. J Child Neurol 23:1195–1204
Pizer B, Clifford S (2008) Medulloblastoma: new insights into biology and treatment. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 93:137–144
Rhoads A, Kenguele H (2005) Expression of IQ-motif genes in human cells and ASPM domain structure. Ethn Dis 15: S5-88-91
Riparbelli MG, Callaini G, Glover DM, Avides Mdo C (2002) A requirement for the abnormal spindle protein to organise microtubules of the central spindle for cytokinesis in Drosophila. J Cell Sci 115:913–922
Shimada M, Komatsu K (2009) Emerging connection between centrosome and DNA repair machinery. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 50:295–301
Wakefield JG, Bonaccorsi S, Gatti M (2001) The drosophila protein asp is involved in microtubule organization during spindle formation and cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 153:637–648
Ackowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Grupo de Apoio ao Adolescente e à Criança com Câncer (GRAACC/UNIFESP).
It is declared in this work that there is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial and material support
GRAACC/CAPES/FAPESP N° 04/12133-6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vulcani-Freitas, T.M., Saba-Silva, N., Cappellano, A. et al. ASPM gene expression in medulloblastoma. Childs Nerv Syst 27, 71–74 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1252-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1252-5