Abstract
Introduction
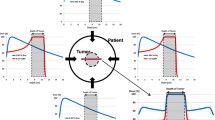
Proton radiation therapy is a form of radiation with physical properties that can provide an advantage in normal tissue sparing compared to the more commonly used photon therapy.
Discussion
The greatest benefit may be for young patients with tumors requiring relatively high doses of radiation and adjacent to critical structures. Children with central nervous system ependymomas meet these criteria and have a very high likelihood of benefit from proton radiation. At present, proton radiation is limited to select centers. However, knowledge of many of the physical advantages of proton therapy has spread rapidly over the past several years, and its availability is becoming more widespread.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JC, Siffert J, Hukin J (1998) Clinical manifestations of childhood ependymoma: a multitude of syndromes. Pediatr Neurosurg 28:49–55
Bussiere MR, Adams JA (2003) Treatment planning for conformal proton radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2:389–399
Constine LS, Woolf PD, Cann D, Mick G, McCormick K, Raubertas RF, Rubin P (1993) Hypothalamic–pituitary dysfunction after radiation for brain tumors. N Engl J Med 328:87–94
Donahue B (1992) Short- and long-term complications of radiation therapy for pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 18:207–217
Duffner PK, Horowitz ME, Krischer JP, Friedman HS, Burger PC, Cohen ME, Sanford RA, Mulhern RK, James HE, Freeman CR et al (1993) Postoperative chemotherapy and delayed radiation in children less than three years of age with malignant brain tumors. N Engl J Med 328:1725–1731
Evans AE, Anderson JR, Lefkowitz-Boudreaux IB, Finlay JL (1996) Adjuvant chemotherapy of childhood posterior fossa ependymoma: cranio-spinal irradiation with or without adjuvant CCNU, vincristine, and prednisone: a Childrens Cancer Group study. Med Pediatr Oncol 27:8–14
Fong RS, Beste DJ, Murray KJ (1995) Pediatric sensorineural hearing loss after temporal bone radiation. Am J Otol 16:793–796
Foreman NK, Love S, Thorne R (1996) Intracranial ependymomas: analysis of prognostic factors in a population-based series. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:119–125
Goldwein JW, Leahy JM, Packer RJ, Sutton LN, Curran WJ, Rorke LB, Schut L, Littman PS, D'Angio GJ (1990) Intracranial ependymomas in children. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 19:1497–1502
Goldwein JW, Corn BW, Finlay JL, Packer RJ, Rorke LB, Schut L (1991) Is craniospinal irradiation required to cure children with malignant (anaplastic) intracranial ependymomas? Cancer 67:2766–2771
Hall EJ (2000) Radiobiology for the radiologist, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, p 546
Hukin J, Epstein F, Lefton D, Allen J (1998) Treatment of intracranial ependymoma by surgery alone. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:40–45
Kahan FM (2003) The physics of radiation therapy, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, p 481
Lomax AJ, Bortfeld T, Goitein G, Debus J, Dykstra C, Tercier PA, Coucke PA, Mirimanoff RO (1999) A treatment planning inter-comparison of proton and intensity modulated photon radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 51:257–271
Lomax AJ, Pedroni E, Rutz H, Goitein G (2004) The clinical potential of intensity modulated proton therapy. Z Med Phys 14:147–152
Macdonald SM, Safai S, Trofimov A, Wolfgang J, Fullerton B, Yeap BY, Bortfeld T, Tarbell NJ, Yock T (2008) Proton radiotherapy for childhood ependymoma: initial clinical outcomes and dose comparisons. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:979–986
Mason KA, Gillin MT, Mohan R, Cox JD (2007) Preclinical biologic assessment of proton beam relative biologic effectiveness at Proton Therapy Center Houston. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:968–970
Merchant TE, Haida T, Wang MH, Finlay JL, Leibel SA (1997) Anaplastic ependymoma: treatment of pediatric patients with or without craniospinal radiation therapy. J Neurosurg 86:943–949
Merchant TE (2002) Current management of childhood ependymoma. Oncology (Williston Park) 16:629–642 644; discussion 645–626, 648
Merchant TE, Mulhern RK, Krasin MJ, Kun LE, Williams T, Li C, Xiong X, Khan RB, Lustig RH, Boop FA, Sanford RA (2004) Preliminary results from a phase II trial of conformal radiation therapy and evaluation of radiation-related CNS effects for pediatric patients with localized ependymoma. J Clin Oncol 22:3156–3162
Merchant TE, Fouladi M (2005) Ependymoma: new therapeutic approaches including radiation and chemotherapy. J Neurooncol 75:287–299
Merchant TE, Kiehna EN, Li C, Xiong X, Mulhern RK (2005) Radiation dosimetry predicts IQ after conformal radiation therapy in pediatric patients with localized ependymoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:1546–1554
Needle MN, Goldwein JW, Grass J, Cnaan A, Bergman I, Molloy P, Sutton L, Zhao H, Garvin JH Jr, Phillips PC (1997) Adjuvant chemotherapy for the treatment of intracranial ependymoma of childhood. Cancer 80:341–347
Oelfke U, Bortfeld T (2000) Intensity modulated radiotherapy with charged particle beams: studies of inverse treatment planning for rotation therapy. Med Phys 27:1246–1257
Oelfke U, Bortfeld T (2001) Inverse planning for photon and proton beams. Med Dosim 26:113–124
Paganetti H, Niemierko A, Ancukiewicz M, Gerweck LE, Goitein M, Loeffler JS, Suit HD (2002) Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:407–421
Palma L, Celli P, Mariottini A, Zalaffi A, Schettini G (2000) The importance of surgery in supratentorial ependymomas. Long-term survival in a series of 23 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 16:170–175
Paulino AC (2001) The local field in infratentorial ependymoma: does the entire posterior fossa need to be treated? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:757–761
Paulino AC, Wen BC, Buatti JM, Hussey DH, Zhen WK, Mayr NA, Menezes AH (2002) Intracranial ependymomas: an analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. Am J Clin Oncol 25:117–122
Pedroni E, Bacher R, Blattmann H, Bohringer T, Coray A, Lomax A, Lin S, Munkel G, Scheib S, Schneider U et al (1995) The 200-MeV proton therapy project at the Paul Scherrer Institute: conceptual design and practical realization. Med Phys 22:37–53
Perilongo G, Massimino M, Sotti G, Belfontali T, Masiero L, Rigobello L, Garre L, Carli M, Lombardi F, Solero C, Sainati L, Canale V, del Prever AB, Giangaspero F, Andreussi L, Mazza C, Madon E (1997) Analyses of prognostic factors in a retrospective review of 92 children with ependymoma: Italian Pediatric Neuro-oncology Group. Med Pediatr Oncol 29:79–85
Ries L (2000) Cancer statistics review. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda
Rousseau P, Habrand JL, Sarrazin D, Kalifa C, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Rekacewicz C, Rey A (1994) Treatment of intracranial ependymomas of children: review of a 15-year experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28:381–386
Salazar OM, Castro-Vita H, VanHoutte P, Rubin P, Aygun C (1983) Improved survival in cases of intracranial ependymoma after radiation therapy. Late report and recommendations. J Neurosurg 59:652–659
Smyth MD, Horn BN, Russo C, Berger MS (2000) Intracranial ependymomas of childhood: current management strategies. Pediatr Neurosurg 33:138–150
Timmermann B, Kortmann RD, Kuhl J, Meisner C, Slavc I, Pietsch T, Bamberg M (2000) Combined postoperative irradiation and chemotherapy for anaplastic ependymomas in childhood: results of the German prospective trials HIT 88/89 and HIT 91. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:287–295
Trofimov A, Bortfeld T (2003) Optimization of beam parameters and treatment planning for intensity modulated proton therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2:437–444
van Veelen-Vincent ML, Pierre-Kahn A, Kalifa C, Sainte-Rose C, Zerah M, Thorne J, Renier D (2002) Ependymoma in childhood: prognostic factors, extent of surgery, and adjuvant therapy. J Neurosurg 97:827–835
Vargas C, Fryer A, Mahajan C, Indelicato D, Horne D, Chellini A, McKenzie C, Lawlor P, Henderson R, Li Z, Lin L, Olivier K, Keole S (2008) Dose–volume comparison of proton therapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:744–751
Weber DC, Trofimov AV, Delaney TF, Bortfeld T (2004) A treatment planning comparison of intensity modulated photon and proton therapy for paraspinal sarcomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1596–1606
Zacharoulis S, Levy A, Chi SN, Gardner S, Rosenblum M, Miller DC, Dunkel I, Diez B, Sposto R, Ji L, Asgharzadeh S, Hukin J, Belasco J, Dubowy R, Kellie S, Termuhlen A, Finlay J (2007) Outcome for young children newly diagnosed with ependymoma, treated with intensive induction chemotherapy followed by myeloablative chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:34–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacDonald, S.M., Yock, T.I. Proton beam therapy following resection for childhood ependymoma. Childs Nerv Syst 26, 285–291 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1059-4