Abstract
Objectives
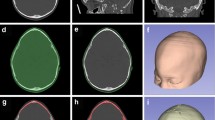
Current multislice computed tomography (CT) technology can be used for diagnosis and surgical planning applying computer-assisted three-dimensional (3D) visualization and surgical simulation. The usefulness of a technique for surgical simulation of frontoorbital advancement is demonstrated here in a child with metopic synostosis.
Materials and methods
Postprocessing of multi-slice CT data was performed using the software 3D slicer. 3D models were created for the purpose of surgical simulation. These allow planning the course of the osteotomies and individually placing the different bony fragments by an assigned matrix to simulate the surgical result. Photo documentation was obtained before and after surgery. Surgical simulation of the procedure allowed determination of the osteotomy course and assessment of the positioning of the individual bony fragments.
Conclusions
Computer-assisted postprocessing and simulation is a useful tool for surgical planning in craniosynostosis surgery. The time–effort for segmentation currently limits the routine clinical use of this technique.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akai T, Iizuka H, Kawakami S (2006) Treatment of craniosynostosis by distraction osteogenesis. Pediatr Neurosurg 42:288–292
Aryan HE, Jandial R, Ozgur BM, Hughes SA, Meltzer HS, Park MS, Levy ML (2005) Surgical correction of metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 21:392–398
Cohen SR, Kawamoto HK, Burstein F, Peacock WJ (1991) Advancement-onlay: an improved technique of fronto-orbital remodeling in craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 7:264–271
Di Rocco C, Velardi F, Ferrario A, Marchese E (1996) Metopic synostosis: in favour of a “simplified” surgical treatment. Childs Nerv Syst 12:654–663
Erdincler P, Kaya AH, Kafadar A, Canbaz B, Kuday C (2004) Bilateral peninsula-shaped linear craniectomy for mild degrees of craniosynostosis: indication, technique and long-term results. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 32:64–70
Girod S, Teschner M, Schrell U, Kevekordes B, Girod B (2001) Computer-aided 3-D simulation and prediction of craniofacial surgery: a new approach. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 29:156–158
Hayward R, Gonsalez S (2005) How low can you go? Intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, and respiratory obstruction in children with complex craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 102:16–22
Hicdonmez T, Parsak T, Cobanoglu S (2006) Simulation of surgery for craniosynostosis: a training model in a fresh cadaveric sheep cranium. Technical note. J Neurosurg 105:150–152
Hilling DE, Mathijssen IM, Mulder PG, Vaandrager JM (2006) Long-term aesthetic results of frontoorbital correction for frontal plagiocephaly. J Neurosurg 105:21–25
Jans G, Vander Sloten J, Gobin R, Van der Perre G, Van Audercke R, Mommaerts M (1999) Computer-aided craniofacial surgical planning implemented in CAD software. Comput Aided Surg 4:117–128
Jünger TH, Reicherts M, Steinberger D, Collmann H, Kotrikova B, Zoller J, Howaldt HP (2001) Standardized evaluation and documentation of findings in patients with craniosynostosis. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 29:25–32
Kim SW, Shim KW, Plesnila N, Kim YO, Choi JU, Kim DS (2007) Distraction vs remodeling surgery for craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23:201–206
Levi D, Rampa F, Barbieri C, Pricca P, Franzini A, Pezzotta S (2002) True 3D reconstruction for planning of surgery on malformed skulls. Childs Nerv Syst 18:705–706
Mathijssen I, Arnaud E, Lajeunie E, Marchac D, Renier D (2006) Postoperative cognitive outcome for synostotic frontal plagiocephaly. J Neurosurg 105:16–20
Medina LS, Richardson RR, Crone K (2002) Children with suspected craniosynostosis: a cost-effectiveness analysis of diagnostic strategies. Am J Roentgenol 179:215–221
Medina LS (2000) Three-dimensional CT maximum intensity projections of the calvaria: a new approach for diagnosis of craniosynostosis and fractures. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1951–1954
Mommaerts MY, Staels PF (2003) Neurocranial suture autotransplantation and periosteal dura stripping to provide a passive growth site in craniosynostosis—a case report. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 31:202–208
Netherway DJ, Abbott AH, Anderson PJ, David DJ (2005) Intracranial volume in patients with nonsyndromal craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 103:137–141
Oi S, Matsumoto S (1987) Trigonocephaly (metopic synostosis). Clinical, surgical and anatomical concepts. Childs Nerv Syst 3:259–265
Piatt JH Jr, Starly B, Sun W, Faerber E (2006) Application of computer-assisted design in craniofacial reconstructive surgery using a commercial image guidance system. Technical note. J Neurosurg 104:64–67
Wiltfang J, Merten HA, Schultze-Mosgau S, Schrell U, Wenzel D, Kessler P (2000) Biodegradable miniplates (LactoSorb): long-term results in infant minipigs and clinical results. J Craniofac Surg 11:239–243
Wiltfang J, Merten HA, Becker HJ, Luhr HG (1999) The resorbable miniplate system Lactosorb in a growing cranio-osteoplasty animal model. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 27:207–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodt, T., Schlesinger, A., Schramm, A. et al. 3D visualization and simulation of frontoorbital advancement in metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 1313–1317 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0455-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0455-x