Abstract
Objectives
The management of intractable epilepsy in children is a challenging problem. For those patients who do not respond to antiepileptic drugs and are not candidates for epilepsy surgery, vagal nerve stimulation (VNS), can be a viable alternative for reducing seizure frequency. We have reviewed the historical and clinical background of VNS treatment. We also include our experience at The Hospital for Sick Children in children who underwent VNS implantation.
Methods
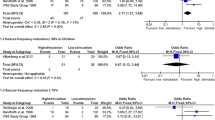
Forty-one children underwent VNS implantation for epilepsy over 6 years. After a mean follow-up of 31 months, 15 (38%) patients had a seizure frequency reduction of more than 90%. Fifteen (38%) children failed to respond to the VNS treatment. The device was removed in five children: in one, due to late infection; the other four could not tolerate the side effects of chronic VNS therapy. Two patients required reimplantation due to electrode failure. The most common side effects in our series were cough and vocal disturbances.
Conclusions
Our results show that VNS implantation can be a safe and effective alternative therapy for children with drug-resistant epilepsy who are not candidates for epilepsy surgery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardell JL, Randall WC (1986) Selective vagal innervation of sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes in canine heart. Am J Physiol 251:H764–H773
Bailey P, Breme F (1938) A sensory cortical representation of the vagus nerve. With a note on the effects of low blood pressure on the cortical electrogram. J Neurophysiol 1:405–412
Ben-Menachem E, Manon-Espaillat R, Ristanovic R, Wilder BJ, Stefan H, Mirza W, Tarver WB, Wernicke JF (1994) Vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of partial seizures: 1. A controlled study of effect on seizures. First International Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. Epilepsia 35:616–626
Ben-Menachem E, Hamberger A, Hedner T, Hammond EJ, Uthman BM, Slater J, Treig T, Stefan H, Ramsay RE, Wernicke JF et al (1995) Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on amino acids and other metabolites in the CSF of patients with partial seizures. Epilepsy Res 20:221–227
Ben-Menachem E, Hellstrom K, Waldton C, Augustinsson LE (1999) Evaluation of refractory epilepsy treated with vagus nerve stimulation for up to 5 years. Neurology 52:1265–1267
Ben-Menachem E, Hellstrom K, Verstappen D (2002) Analysis of direct hospital costs before and 18 months after treatment with vagus nerve stimulation therapy in 43 patients. Neurology 59:S44–S47
Boon P, D’Have M, Van Wallenghem P, Michielsen G, Vonck K, Caemaert J, de Reuck J (2002) Direct medical costs of refractory epilepsy incurred by three different treatment modalities: a prospective assessment. Epilepsia 43:96–102
Carpenter LL, Moreno FA, Kling MA, Anderson GM, Regenold WT, Labiner DM, Price LH (2004) Effect of vagus nerve stimulation on cerebrospinal fluid monoamine metabolites, norepinephrine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid concentrations in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 56:418–426
Charous SJ, Kempster G, Manders E, Ristanovic R (2001) The effect of vagal nerve stimulation on voice. Laryngoscope 111:2028–2031
Chase MH, Sterman MB, Clemente CD (1966) Cortical and subcortical patterns of response to afferent vagal stimulation. Exp Neurol 16:36–49
Chase MH, Nakamura Y, Clemente CD, Sterman MB (1967) Afferent vagal stimulation: neurographic correlates of induced EEG synchronization and desynchronization. Brain Res 5:236–249
DeGiorgio CM, Schachter SC, Handforth A, Salinsky M, Thompson J, Uthman B, Reed R, Collins S, Tecoma E, Morris GL, Vaughn B, Naritoku DK, Henry T, Labar D, Gilmartin R, Labiner D, Osorio I, Ristanovic R, Jones J, Murphy J, Ney G, Wheless J, Lewis P, Heck C (2000) Prospective long-term study of vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of refractory seizures. Epilepsia 41:1195–1200
Dell P, Olson R (1951) Secondary mesencephalic, diencephalic and amygdalian projections of vagal visceral afferences. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 145:1088–1091
Dell P, Olson R (1951) Thalamic, cortical and cerebellar projections of vagal visceral afferences. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 145:1084–1088
Foley J, DuBois F (1937) Quantitative studies of the vagus nerve in the cat. I. The ratio of sensory and motor studies. J Comp Neurol 67:49–67
Frost M, Gates J, Helmers SL, Wheless JW, Levisohn P, Tardo C, Conry JA (2001) Vagus nerve stimulation in children with refractory seizures associated with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. Epilepsia 42:1148–1152
George R, Salinsky M, Kuzniecky R, Rosenfeld W, Bergen D, Tarver WB, Wernicke JF (1994) Vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of partial seizures: 3. Long-term follow-up on first 67 patients exiting a controlled study. First International Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. Epilepsia 35:637–643
Handforth A, DeGiorgio CM, Schachter SC, Uthman BM, Naritoku DK, Tecoma ES, Henry TR, Collins SD, Vaughn BV, Gilmartin RC, Labar DR, Morris GL, 3rd, Salinsky MC, Osorio I, Ristanovic RK, Labiner DM, Jones JC, Murphy JV, Ney GC, Wheless JW (1998) Vagus nerve stimulation therapy for partial-onset seizures: a randomized active-control trial. Neurology 51:48–55
Helmers SL, Griesemer DA, Dean JC, Sanchez JD, Labar D, Murphy JV, Bettis D, Park YD, Shuman RM, Morris GL III (2003) Observations on the use of vagus nerve stimulation earlier in the course of pharmacoresistant epilepsy: patients with seizures for six years or less. Neurologist 9:160–164
Helmers SL, Wheless JW, Frost M, Gates J, Levisohn P, Tardo C, Conry JA, Yalnizoglu D, Madsen JR (2001) Vagus nerve stimulation therapy in pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy: retrospective study. J Child Neurol 16:843–848
Henry TR (2002) Therapeutic mechanisms of vagus nerve stimulation. Neurology 59:S3–14
Henry TR, Bakay RA, Votaw JR, Pennell PB, Epstein CM, Faber TL, Grafton ST, Hoffman JM (1998) Brain blood flow alterations induced by therapeutic vagus nerve stimulation in partial epilepsy: I. Acute effects at high and low levels of stimulation. Epilepsia 39:983–990
Henry TR, Votaw JR, Pennell PB, Epstein CM, Bakay RA, Faber TL, Grafton ST, Hoffman JM (1999) Acute blood flow changes and efficacy of vagus nerve stimulation in partial epilepsy. Neurology 52:1166–1173
Hornig GW, Murphy JV, Schallert G, Tilton C (1997) Left vagus nerve stimulation in children with refractory epilepsy: an update. South Med J 90:484–488
Kalkanis JG, Krishna P, Espinosa JA, Naritoku DK (2002) Self-inflicted vocal cord paralysis in patients with vagus nerve stimulators. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 96:949–951
Kirse DJ, Werle AH, Murphy JV, Eyen TP, Bruegger DE, Hornig GW, Torkelson RD (2002) Vagus nerve stimulator implantation in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:1263–1268
Krahl SE, Clark KB, Smith DC, Browning RA (1998) Locus coeruleus lesions suppress the seizure-attenuating effects of vagus nerve stimulation. Epilepsia 39:709–714
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2000) Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N Engl J Med 342:314–319
Lundgren J, Amark P, Blennow G, Stromblad LG, Wallstedt L (1998) Vagus nerve stimulation in 16 children with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 39:809–813
Majoie HJ, Berfelo MW, Aldenkamp AP, Evers SM, Kessels AG, Renier WO (2001) Vagus nerve stimulation in children with therapy-resistant epilepsy diagnosed as Lennox–Gastaut syndrome: clinical results, neuropsychological effects, and cost-effectiveness. J Clin Neurophysiol 18:419–428
Majoie HJ, Berfelo MW, Aldenkamp AP, Renier WO, Kessels AG (2005) Vagus nerve stimulation in patients with catastrophic childhood epilepsy, a 2-year follow-up study. Seizure 14:10–18
McGregor A, Wheless J, Baumgartner J, Bettis D (2005) Right-sided vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for refractory epilepsy in humans. Epilepsia 46:91–96
McLachlan RS (1993) Suppression of interictal spikes and seizures by stimulation of the vagus nerve. Epilepsia 34:918–923
Morris GL 3rd, Mueller WM (1999) Long-term treatment with vagus nerve stimulation in patients with refractory epilepsy. The Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group E01–E05. Neurology 53:1731–1735
Murphy JV, Hornig GW, Schallert GS, Tilton CL (1998) Adverse events in children receiving intermittent left vagal nerve stimulation. Pediatr Neurol 19:42–44
Murphy JV, Torkelson R, Dowler I, Simon S, Hudson S (2003) Vagal nerve stimulation in refractory epilepsy: the first 100 patients receiving vagal nerve stimulation at a pediatric epilepsy center. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 157:560–564
Neufeld M, Quaknine G, Korczyn A (1995) Vagus nerve stimulation for partial seizures. Harefuah 129:5–7, 80
Paolicchi JM, Jayakar P, Dean P, Yaylali I, Morrison G, Prats A, Resnik T, Alvarez L, Duchowny M (2000) Predictors of outcome in pediatric epilepsy surgery. Neurology 54:642–647
Parain D, Penniello MJ, Berquen P, Delangre T, Billard C, Murphy JV (2001) Vagal nerve stimulation in tuberous sclerosis complex patients. Pediatr Neurol 25:213–216
Patwardhan RV, Stong B, Bebin EM, Mathisen J, Grabb PA (2000) Efficacy of vagal nerve stimulation in children with medically refractory epilepsy. Neurosurgery 47:1353–1357; discussion 1357–1358
Penry JK, Dean JC (1990) Prevention of intractable partial seizures by intermittent vagal stimulation in humans: preliminary results. Epilepsia 31(Suppl 2):S40–S43
Randall WC, Ardell JL, Becker DM (1985) Differential responses accompanying sequential stimulation and ablation of vagal branches to dog heart. Am J Physiol 249:H133–H140
Ricardo JA, Koh ET (1978) Anatomical evidence of direct projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract to the hypothalamus, amygdala, and other forebrain structures. Brain Res 153:1–26
Schachter SC (2002) Vagus nerve stimulation therapy summary: five years after FDA approval. Neurology 59:S15–S20
Smyth MD, Tubbs RS, Bebin EM, Grabb PA, Blount JP (2003) Complications of chronic vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy in children. J Neurosurg 99:500–503
Tatum WOt, Moore DB, Stecker MM, Baltuch GH, French JA, Ferreira JA, Carney PM, Labar DR, Vale FL (1999) Ventricular asystole during vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy in humans. Neurology 52:1267–1269
The Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group (1995) A randomized controlled trial of chronic vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of medically intractable seizures. Neurology 45:224–230
Uthman BM, Wilder BJ, Hammond EJ, Reid SA (1990) Efficacy and safety of vagus nerve stimulation in patients with complex partial seizures. Epilepsia 31(Suppl 2):S44–S50
Uthman BM, Wilder BJ, Penry JK, Dean C, Ramsay RE, Reid SA, Hammond EJ, Tarver WB, Wernicke JF (1993) Treatment of epilepsy by stimulation of the vagus nerve. Neurology 43:1338–1345
Uthman BM, Reichl AM, Dean JC, Eisenschenk S, Gilmore R, Reid S, Roper SN, Wilder BJ (2004) Effectiveness of vagus nerve stimulation in epilepsy patients: a 12-year observation. Neurology 63:1124–1126
Valencia I, Holder DL, Helmers SL, Madsen JR, Riviello JJ Jr (2001) Vagus nerve stimulation in pediatric epilepsy: a review. Pediatr Neurol 25:368–376
Walker BR, Easton A, Gale K (1999) Regulation of limbic motor seizures by GABA and glutamate transmission in nucleus tractus solitarius. Epilepsia 40:1051–1057
Wheless JW, Maggio V (2002) Vagus nerve stimulation therapy in patients younger than 18 years. Neurology 59:S21–S25
Wyllie E, Comair YG, Kotagal P, Bulacio J, Bingaman W, Ruggieri P (1998) Seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery in children and adolescents. Ann Neurol 44:740–748
Zabara J (1985) Peripheral control of hypersynchronous discharge in epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 61:S162
Zabara J (1985) Time course of seizure control to brief repetitive stimuli. Epilepsia 26:518
Zabara J (1987) Controlling seizures by changing GABA receptor sensitivity. Epilepsia 28:604
Zanchetti A, Wang SC, Moruzzi G (1952) The effect of vagal afferent stimulation on the EEG pattern of the cat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 4:357–361
Acknowledgement
Dr. Benifla and this study were supported by the Wiley Fund at The Hospital for Sick Children.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benifla, M., Rutka, J.T., Logan, W. et al. Vagal nerve stimulation for refractory epilepsy in children: indications and experience at The Hospital for Sick Children. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 1018–1026 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0123-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0123-6