Abstract
Rationale
The long-term outcome of idiopathic macrocephaly is presently unknown.
Methods and results
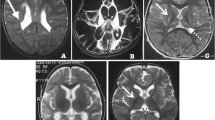
In the current study (n=15), MRI conducted at long-term review showed regression of orbito-frontal extradural collections and normal or slightly enlarged ventricular space compared to infant examination. Head circumference had normalised in all but one participant. Neuropsychological assessments of nine participants showed general intellectual ability within the normal range in the majority of participants; however, specific deficits in attention were evident. Clinical interviews conducted with a smaller sub-group revealed anecdotal histories of behavioural difficulties and reading or arithmetic difficulties in half of the total sample.
Conclusions
Prospective review studies such as this indicate that abnormal radiological findings in infancy are not necessarily predictive of neurodevelopmental problems and may reflect a normal variant. However, while overall intellectual ability may be within average limits in this diagnostic sample, considerable individual variations remain in specific areas of neuropsychological function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The WAIS-R short form utilised for this study has a validity coefficient of .94, comprising subtests of Picture Completion, Vocabulary, Digit Span, Digit Symbol, Arithmetic and Similarities.
References
Alper G, Ekinci G, Yilmax Y, Arikan C, Telyar G, Erzen F (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of benign macrocephaly in children. J Child Neurol 14:678–682
Pettit RE, Kilroy AW, Allen JH (1980) Macrocephaly and head growth parallel to normal growth pattern: neurological, developmental, and computerized tomography findings in full-term infants. Arch Neurol 37:518–521
Bodensteiner J (2000) Benign macrocephaly: a common cause of big heads in the first year. J Child Neurol 15:630–632
Nellhaus G (1972) Benign idiopathic megalencephaly: neuroradiologic confirmation. Neuroradiology 4:128
Ment LR, Duncan CC, Geehr R (1981) Benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces in the infant. J Neurosurg 54:504–508
Wilms G, Vanderscheuren G, Demaerel PH, Smet MH, Van Calenbergh F, Plets C, Goffin J, Casaer P (1993) CT and MR in infants with pericerebral collections and macrocephaly: benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces versus subdural collections. Am J Neuroradiol 14:855–860
Gherpelli JL, Scaramuzzi V, Manreza ML, Diament AJ (1992) Follow-up study of macrocephalic children with enlargement of the subarachnoid space. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 50:156–162
Laubscher B, Deonna T, Uske A, van Melle G (1990) Primitive megalencephaly in children: natural history, medium term prognosis with special reference to external hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediatr 149:502–507
Sandler AD, Knudsen MW, Brown TT, Christian BM (1997) Neurodevelopmental dysfunction among nonreferred children with idiopathic megalencephaly. J Pediatr 131:320–324
Compen-Kong R, Landeras L (1991) The neuroevolutionary profile of the nursing infant with macrocephaly and benign enlargement of the subarachnoid space, abstract. Bol Med Hosp Infant 48:440–444
Odita JC (1992) The widened frontal subarachnoid space: a CT comparative study between macrocephalic, microcephalic, and normocephalic infants and children. Childs Nerv Syst 8:36–39
Cole TKP, Hughes HE (1991) Autosomal dominant macrocephaly: benign familial macrocephaly or a new syndrome? Am J Med Genet 41:115–124
Day RE, Shutt WH (1979) Normal children with large heads—benign familial megalencephaly. Arch Dis Child 54:512–517
Maytal J, Alvarez L, Elkin CM, Shinnar S (1987) External hydrocephalus: radiologic spectrum and differentiation from cerebral atrophy. Am J Neuroradiol 8:271–278
Nickel RE, Gallenstein JS (1987) Developmental prognosis for infants with benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces. Dev Med Child Neurol 29:181–186
Sattler JM (1992) Assessment of children. Maple Vail, San Diego
Appleton RE, Bushby K, Gardner-Medwin D, Welch J, Kelly PJ (1991) Head circumference and intellectual performance of patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Dev Med Child Neurol 33:884–890
Asch AJ, Myers GJ (1976) Benign familial macrocephaly: report of a family and review of the literature. Pediatrics 57:535–539
Gooskens RHJM, Willemse J, Faber JA, Verdonck AFMM (1989) Macrocephalies — a differentiated approach. Neuropediatrics 20:164–169
Pollack IF, Pang D, Albright L (1994) The long-term outcome in children with late-onset aqueductal stenosis resulting from benign intrinsic tectal tumours. J Neurosurg 80:681–688
Smith RD, Ashley J, Hardesty RA, Tulley R, Hewitt J (1984) Macrocephaly and minor congenital anomalies in children with learning problems. J Dev Behav Pediatr 5:231–236
Densch LW, Anderson SK, Snow JH (1990) Relationship of head circumference to measures of school performance. Clin Pediatr 29:389–392
Tanner JM (1978) Boys: birth–16 years: head circumference. Castlemead Publications, Welwyn Garden City, Herts
Tanner JM (1978) Girls: birth–16 years: head circumference. Castlemead Publications, Welwyn Garden City, Herts
Hamill PVV, Drizd TA, Johnson CL (1979) Physical growth: National Centre for Health Statistics percentiles. Am J Clin Nutr 32:607–629
Bushby KMD, Cole T, Matthews JNS, Goodship JA (1992) Centiles for adult head circumference. Arch Dis Child 67:1286–1287
Wechsler D (1981) Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—revised. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Meyers J, Meyers K (1995) The Meyers scoring system for the Rey Complex Figure and the recognition trial: professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Conners CK, Multi-Health Systems Staff (1995) Conners Continuous Performance Test. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Lezak MD (1995) Neuropsychological assessment, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler Memory Scale—revised. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
DeFilippis NA, McCampbell E (1979) Manual for the Booklet Category Test. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Reitan RM, Wolfson D (1988) The Halstead–Reitan neuropsychological test battery. Neuropsychology Press, Tucson
Lovibond SH, Lovibond PF (1995) Manual for the depression, anxiety and stress scales, 2nd edn. Psychology Foundation, Sydney
Kaufman AS (1990) Assessing adolescent and adult intelligence. Allyn and Bacon, London
Spreen O, Strauss E (eds) (1999) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms, and commentary. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the early work of Dr. Ian Johnson and Dr. Elizabeth Fagan that lead to the preparation of the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muenchberger, H., Assaad, N., Joy, P. et al. Idiopathic macrocephaly in the infant: long-term neurological and neuropsychological outcome. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 1242–1248 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0080-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0080-0