Abstract
Background
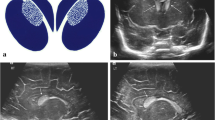
Germinal matrix and intraventricular hemorrhage (GMH/IVH) is a known complication occurring in the first week of life in preterm neonates. However, the precise time of its occurrence and the ideal time to perform diagnostic imaging studies remain controversial. The purpose of this paper is to address these two issues in our patient population to allocate our resources to those at highest risk.
Materials and methods
This study included 282 premature newborns (under 37 weeks of gestation) that were admitted to our neonate ICU in a year’s time and screened for GMH/IVH. They were grouped in four categories according to their weight at birth, and according to their gestational age. All patients had a daily cranial ultrasound during the first week. It was then repeated once in the second week and once in the third.
Results
We found that the incidence of GMH/IVH among preterm neonates was 44.68%. It was inversely related to the weight and the age of the newborn. The onset of bleeding coordinated with the occurrence of hypoxia and respiratory distress requiring mechanical ventilation. The majorities occurred in the first 7 days of life; they were mostly grade I and II according to the Papule classification and silent for the most part. Complications were present in 41% of the survivors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez MD, Villamil M, Reyes G (1994) Predictive factors in the genesis of intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. P R Health Sci J 13(4):251–254
Batton DG, DeWitte DB, Boal DK, Nardis EE, Maisels MJ (1986)Incidence and severity of intraventricular hemorrhage: 1981–1984. Am J Perinatol 3(4):353–356
Burguet A, Monnet E, Roth P, Hirn F, Vouaillat C, Lecourt-Ducret M, Fromentin C, Dornier L, Helias J, Choulot MJ, Allemand H, Maillet R, Menget A (2000) Neurodevelopmental outcome of premature infants born at less than 33 weeks of gestational age and not cerebral palsy at the age of 5 years. Arch Pediatr 7(4):357–368
Chen CH, Wang TM, Wu KH, Chi CS (1993) Intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm neonates—a two-year experience. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 34(5):343–348
Cherian S, Whitelaw A, Thoresen M, Love S (2004) The pathogenesis of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol 14(3):305–311
De Vries LS, Rademaker KJ, Groenendaal F, Eken P, van Haastert IC, Vandertop WP, Gooskens R, Meiners LC (1998) Correlation between neonatal cranial ultrasound, MRI in infancy and neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with a large intraventricular haemorrhage with or without unilateral parenchymal involvement. Neuropediatrics 29(4):180–188
Enzmann D, Murphy-Irwin K, Stevenson D, Ariagno R, Barton J, Sunshine P(1985) The natural history of subependymal germinal matrix hemorrhage. Am J Perinatol 2(2):123–133
Ferrari B, Tonni G, Luzietti R, Ciarlini G, Vadora E, Merialdi A(1992) Neonatal complications and risk of intraventricular–periventricular hemorrhage. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 19(4):253–258
Goldsmith, Karotkin (1996) Assisted ventilation of the neonate. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, pp 397–408
Hamrick SE, Miller SP, Leonard C, Glidden DV, Goldstein R, Ramaswamy V, Piecuch R, Ferriero DM (2004) Trends in severe brain injury and neurodevelopmental outcome in premature newborn infants: the role of cystic periventricular leukomalacia. J Pediatr 145(5):593–599
Harke HT, Haeye RI, Storch A et al (1972)Perinatal Cerebral hemorrhage. J Pediatr 37:80
Hayden CK Jr, Shattuck KE, Richardson CJ, Ahrendt DK, House R, Swischuk LE (1985) Subependymal germinal matrix hemorrhage in full-term neonates. Pediatrics 75 (4):714–718
Jaeger M, Grussner SE, Omwandho CO, Klein K, Tinneberg HR, Klingmuller V (2004) Cranial sonography for newborn screening: a 10-year retrospective study in 11,887 newborns. Rofo 176(6):852–858
Pomerance JJ, Richardson J (1993) Neonatology for the clinician, 1st edn. Applenton & Lange, Norwalk, Connecticut, pp 425–435
Leech RW, Kohnen P (1974) Subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhages in the newborn. Am J Pathol 77(3):465–475
Linder N, Haskin O, Levit O, Klinger G, Prince T, Naor N, Turner P, Karmazyn B, Sirota L (2003) Risk factors for intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight premature infants: a retrospective case-control study. Pediatrics 111(5 Pt 1):e590–e595
McMenamin JB, Shackelford GD, Volpe JJ (1984) Outcome of neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage with periventricular echodense lesions. Ann Neurol 15(3):285–290
Ment LR, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, Lange RC, Taylor KJ, Kleinman CS, Scott DT, Sivo J, Gettner P (1984) Intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm neonate: timing and cerebral blood flow changes. J Pediatr 104(3):419–425
Ment LR, Duncan CC, Scott DT, Ehrenkranz RA (1984) Post hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Low incidence in very low birth weight neonates with intraventricular hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 60(2):343–347
Paneth N, Pinto-Martin J, Gardiner J, Wallenstein S, Katsikiotis V, Hegyi T, Hiatt IM, Susser M (1993) Incidence and timing of germinal matrix/intraventricular hemorrhage in low birth weight infants. Am J Epidemiol 137(11):1167–1176
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H ( 1978) Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 92(4):529–534
Partridge JC, Babcock DS, Steichen JJ, Han BK (1983) Optimal timing for diagnostic cranial ultrasound in low-birth-weight infants: detection of intracranial hemorrhage and ventricular dilation. J Pediatr 102(2):281–287
Perlman JM, Volpe JJ (1986) Intraventricular hemorrhage in extremely small premature infants. Am J Dis Child 140(11):1122–1124
Philip AG, Allan WC, Tito AM, Wheeler LR (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants: declining incidence in the 1980’s. Pediatrics 84(5):797–801
Roland EH, Hill A (2003) Germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature newborn: management and outcome. Neurol Clin 21(4):833–851 (vi–vii)
Sann L, Bourgeois J, Stephant A, Putet G (2001) Outcome of 249 premature infants, less than 29 weeks gestational age. Arch Pediatr 8(3):250–258
Schellinger D, Grant EG, Manz HJ, Patronas NJ (1988) Intraparenchymal hemorrhage in preterm neonates: a broadening spectrum. Am J Roentgenol 150(5):1109–1115
Staneva KN, Hartmann S, Uhlemann M, Dietze H, Reschke E, Koepcke E, Sadenwasser W, Kulz T (2002) Neonatal ultrasonographic cerebral findings: association with risk factor for cerebral palsy. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol 206(4):142–150
Szymonowicz W, Yu VY (1986) Periventricular haemorrhage and leukomalacia in extremely low birthweight infants. Aust Paediatr J 22(3):207–210
Takashima S, Becker LE (1983) Intraventricular and subependymal haemorrhage in infants dying within 10 hours of birth. Brain Dev 5(1):9–13
Trounce JQ, Rutter N, Levene MI (1986) Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child 61(12):1196–1202
Tsiantos A, Victorin L, Relier JP, Dyer N, Sundell H, Brill AB, Stahlman M. (1974) Intracranial hemorrhage in the prematurely born infant: timing of clots and evaluation of clinical signs and symptoms. J Pediatr 85(6):854–859
Urlesberger B, Muller W ( 2004) Prognosis of preterm infants with a birth weight <1,501 g. Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch 44(1):19–24
Valleur D, Magny JF, Rigourd V, Kieffer F (2004) Mid and long-term neurological prognosis of preterm infants less than 28 weeks gestational age. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 33(1 Suppl):S72–S78 (Feb)
Vohr B, Ment LR (1996) Intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm infant. Early Hum Dev 44(1):1–16
Vollmer B, Roth S, Baudin J, Stewart AL, Neville BG, Wyatt JS (2003) Predictors of long-term outcome in very preterm infants: gestational age versus neonatal cranial ultrasound. Pediatrics 112(5):1108–1114
Volpe JJ (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage and brain injury in the premature infant. Diagnosis, prognosis, and prevention. Clin Perinatol 16(2):387–411
Volpe JJ (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant—current concepts. Part I. Ann Neurol 25(1):3–11
Volpe JJ (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant—current concepts. Part II. Ann Neurol 25(2):109–116
Whitelaw A, Cherian S, Thoresen M, Pople I (2004) Posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation: new mechanisms and new treatment. Acta Paediatr Suppl 93(444):11–14
Wildrick D (1997) Intraventricular hemorrhage and long-term outcome in the premature infant. J Neurosci Nurs 29(5):281–289
Zaramella P, Lago P, Freato F, Battajon N, Saia OS, Chiandetti L (2004) Retrospective analysis of post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation in very low birth weight infants, short and long-term outcome. Minerva Pediatric 56(5):527–536
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadri, H., Mawla, A.A. & Kazah, J. The incidence, timing, and predisposing factors of germinal matrix and intraventricular hemorrhage (GMH/IVH) in preterm neonates. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 1086–1090 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0050-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0050-6