Abstract
Background
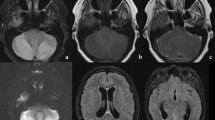
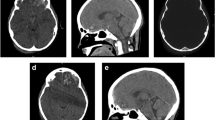
We present two cases of children who were diagnosed with cerebellitis with acute cerebellar swelling. This rare pathology is potentially fatal, and no clear treatment guidelines are described in the literature.
Discussion
Considering our experience, we discuss the different therapeutic strategies and propose aggressive surgical measures consisting of external ventricular drainage and posterior fossa decompression in case of failure of early response to medical treatment to limit secondary cerebellar and brainstem lesions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakshi R, Bates VE, Kinkel PR, Mechtler LL, Kinkel WR (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging findings in acute cerebellitis. Clin Imaging 22:79–85
Montenegro MA, Santos SL, Li LM, Cendes F (2002) Neuroimaging of acute cerebellitis. J Neuroimaging 12(1):72–74
de Fraiture DMI, Sie TH, Boezeman EHJF, Haanen HCM (1997) Cerebellitis as a uncommon complication of infectious mononucleosis. Neth J Med 51:79–82
Hamada H, Kurimoto M, Masuoka T, Hirashima Y, Endo S, Harada J (2001) A case of surgically treated acute cerebellitis with hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 17:500–502
Drost G, Verrips A, Thijssen HO, Gabreels (2000) Cerebellar involvement as a rare complication of pneumococcal meningitis. Neuropediatrics 31(2):97–99
Majda-Stanislawska E (2000) Mumps cerebellitis. Eur Neurol 43(2):117
Mario-Ubaldo M (1995) Cerebellitis associated with Lyme disease. Lancet 345(8956):1060
Aylett SE, O’Neill KS, De Sousa C, Britton J (1998) Cerebellitis presenting as acute hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 14:139–141
Gohlich-Ratmann G, Wallot M, Baethmann M, Schaper J, Roggendorf M, Roll C et al (1998) Acute cerebellitis with near-fatal cerebellar swelling and benign outcome under conservative treatment with high dose steroids. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2(3):157–162
Horowitz MB, Pang D, Hirsch W (1991) Acute cerebellitis: case report and review. Pediatr Neurosurg 17(3):142–145
Asenbauer B, McConachie NS, Allcutt D, Farrell MA, King MD (1997) Acute near-fatal parainfectious cerebellar swelling with favourable outcome. Neuropediatrics 28(2):122–125
Roulet Perez E, Maeder P, Cotting J, Eskenazy-Cottier AC, Deonna T (1993) Acute fatal parainfectious cerebellar swelling in two children. A rare or an overlooked situation? Neuropediatrics 24(6):346–351
Levy EI, Harris AE, Omalu BI, Hamilton RL, Branstetter BF, Pollack IF (2001) Sudden death from fulminant acute cerebellitis. Pediatr Neurosurg 35(1):24–28
Hayakawa H, Katoh T (1995) Severe cerebellar atrophy following acute cerebellitis. Pediatr Neurol 12:159–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Ribaupierre, S., Meagher-Villemure, K., Villemure, J.G. et al. The role of posterior fossa decompression in acute cerebellitis. Childs Nerv Syst 21, 970–974 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1176-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1176-7