Abstract
Objectives
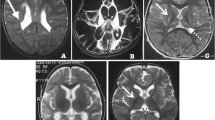
The authors present the case of an adolescent affected with refractory epilepsy due to a neonatal ischemic infarction of the right medial cerebral artery. Hemiplegic since the first months of life, she began presenting motor partial seizures associated with drop attacks at 4.5 years; these were initially well controlled by antiepileptic drugs, but at 10 years seizures appeared again and became refractory. Thus, at 14 years and 10 months, she was submitted to a right hemispherectomy that made her rapidly seizure free. In the post-surgical follow-up lasting 5 years, neuropsychological serial assessments showed an impressive progressive improvement of cognitive skills, namely, visuospatial abilities. This case seems to challenge the widely spread feeling that functional catch-up in brain-injured children could only occur early in life. In effect, the astonishing recovery especially of visuospatial skills in our case occurred in adolescence after a late surgical intervention of right hemispherectomy.
Methods
Different neuropsychological aspects are discussed. The reorganisation process recovered the spatial and linguistic abilities as well as the verbal and visuospatial memory; however, there was a persistent impairment of complex spatial and perceptual skills as well as recall abilities. Despite the deficit of complex visual stimuli processing, the patient showed a good performance in the recognition of unknown faces.
Conclusions
Probably, the absence of seizures in the first 4 years of life could have allowed a generally adequate compensatory reorganisation, successively masked by the persistent and diffuse epileptic disorder. The seizure control produced by surgery eventually made evident the effectiveness of the brain reorganisation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert ML (1973) A simple test of visual neglect. Neurology 23:658–664
Aram DM, Ekelman BL, Whitaker HA (1987) Lexical retrieval in left and right brain lesioned children. Brain Lang 31:61–87
Beardsworth ED, Adams CBT (1988) Modified hemispherectomy for epilepsy: early results in 10 cases. Br J Neurosurg 2:73–84
Beery KE (1997) Developmental test of visual–motor integration. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Bennett GK, Seashore HG, Wesman AG (1987) D.A.T. Differential aptitude tests. Manuale d’istruzioni. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Benton AL, Varney NR, Hamsher K (1992) Test di Giudizio di Orientamento di Linee. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Benton AL, Hamsher K, Varney NR, Spreen O (1992) Test di Riconoscimento di Volti Ignoti. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Biancardi A, Stoppa E (1997) The bells test revised: a proposal for the study of attention in childhood. Psichiatr Infanz Adolesc 64:73–84
Borkowsky JG, Benton AL, Spreen O (1967) Word fluency and brain damage. Neuropsychologia 5:135–140
Carlesimo GA, Caltagirone C, Gainotti G, Nocentini U, Gruppo per la standardizzazione della Batteria per il Deterioramento Mentale (1985) Batteria per la valutazione del deterioramento mentale (parte II): standardizzazone e affidabilità diagnostica nella identificazione di pazienti affetti da sindrome demenziale. Arch Psicol Neurol Psichiatr 56:471–488
Corballis MC, Seargent J (1989) Hemispheric specialization for mental rotation. Cortex 25:15–25
Corbellis M, Morgan M (1978) On the biological basis of human laterality. Evidence for a maturational left–right gradient. Behav Brain Sci 21:261–316
Day PS, Ulatowska HK (1979) Perceptual, cognitive and linguistic development after early hemispherectomy: two cases studies. Brain Lang 7:17–33
Ghent L (1956) Perception of overlapping and embedded figures by children of different ages. Am J Psychol 575–587
Gollin ES (1960) Developmental studies of visual recognition of incomplete objects. Percept Mot Skills 11:289–298
Irle E (1987) Lesion size and recovery of function: some new perspectives. Brain Res Rev 12:307–320
Jones-Gotman M, Zatorre RJ, Olivier A, Andermann F, Cendes F, Staunton H, McMackin D, Sigel AM, Wieser HG (1997) Learning and retention of words and designs following excision from medial or lateral temporal-lobe structures. Neuropsychologia 35:963–973
Kennard MA (1938) Reorganization of motor function in the cerebral cortex of monkeys deprived of motor and premotor areas in infancy. J Neurophysiol 1:477–496
Kennard MA (1940) Relation of age to motor impairment in man and subhuman primates. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 44:377–397
Kohn B, Dennis M (1974) Selective impairments of visuo-spatial abilities in infantile hemiplegics after right cerebral hemidecortication. Neuropsychologia 12:505–512
Likert R, Quasha WH (1948) The revised Minnesota paper form board test. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Mariotti P, Iuvone L, Torrioli MG, Silveri MC (1998) Linguistic and non-linguistic abilities in a patient with early left hemispherectomy. Neuropsychologia 36:1303–1312
Mc Fie J (1961) The effects of hemispherectomy on intellectual functioning in cases of infantile hemiplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 24:240–249
Mc Carthy RA, Warrington EK (2000) Neuropsicologia cognitiva. Un’introduzione clinica. Edizioni Raffaello Cortina, Milan
Mehta Z, Newcombe F, Damasio H (1987) A left hemisphere contribution to visuospatial processing. Cortex 23:447–461
Miceli G, Laudanna A, Burani C, Capasso R (1994) Batteria per l’Analisi dei Deficit Afasici B.A.D.A. CEPSAG, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome
Muter V, Taylor S, Vargha-Khadem F (1997) A longitudinal study of early intellectual development in hemiplegic children. Neuropsychologia 35(3):289–298
Muter V (1994) Phonology and learning to read in normal and hemiplegic children. Thesis, University of London, London
Oguni H, Mukahira K, Tanaka T, Awaya Y, Saito K, Shimizu H, Oda M, Arai N, Suzuki I, Osawa M (2000) Symposium I: surgical indication for refractory childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 9):S21–S25
Ornstein R, Johnstone J, Herron J, Swencionis C (1980) Differential right hemisphere engagement in visuospatial tasks. Neuropsychologia 18:49–64
Pulsifer MB, Brandt J, Salorio CF, Vining EP, Carson BS, Freeman JM (2004) The cognition outcome of hemispherectomy in 71 children. Epilepsia 45(3):243–254
Rebolledo FA, Garcia CR, Mares DR, Rojas JC (2002) Sindrome de Rasmussen. Seguimiento de siete anos. Aspectos relacionades con plasticidad cerebral en epilepsia. Rev Invest Clin 54(3):209–217
Rey A (1958) Mémorisation d’une série de 15 mots en 5 répétitions. L’examen clinique en psychologie. Presses Universitaires de France, Paris
Rey A (1968) Reattivo della figura complessa. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Reynolds CR, Bigler ED (1995) Test of memory and learning. Centro Studi Erickson, Trento
Reynolds DM, Jeeves MA (1978) A developmental study of hemisphere specialization for recognition of faces in normal subjects. Cortex 14(4):511–520
Riva D, Nichelli F, Devoti M (2000) Developmental aspects of verbal fluency and confrontation naming in children. Brain Lang 71:267–284
Teuber HL (1975) Recovery of function after brain injury in man. In: Porter R and Fitzsimmons DW (eds) Outcome of severe damage to the central nervous system. CIBA Foundation Symposium, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 159–190
Vargha-Khadem F, Isaacs E, Van Der Werf S, Robb S, Wilson J (1992a) Development of intelligence and memory in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Brain 115:315–329
Vargha-Khadem F, Polkey CE (1992b) A review of cognitive outcome after hemidecortication in humans. In: Rose FD, Johnson DA (eds) Recovery from brain damage: advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 35. Reflections and directions. Plenum, New York, pp 137–151
Vargha-Khadem F, Isaacs E, Muter V (1994) A review of cognitive outcome after unilateral lesions sustained during childhood. J Child Neurol 9(Suppl 2):2S67–2S73
Vargha-Khadem F, Mishkin M (1997) Speech and language outcome after hemispherectomy in childhood. In: Tuxhorn I, Holthausen H, Boenig KH et al (eds) Pediatric epilepsy syndromes and their surgical treatment. John Libbey, London, pp 774–784
Vargha-Khadem F (2001) Generalized versus selective cognitive impairments resulting from brain damage sustained in childhood. Epilepsia 42(Suppl 1):37–40
Vicari S, Pasqualetti P, Marotta L, Carlesimo GA (1999) Word-list learning in normally developing children: effects of semantic organization and retention interval. Ital J Neurol Sci 12:119–128
Warrington EK, James M (1991) The visual object and space perception battery. Thames Valley Test Company, Bury St Edmunds
Wechsler D (1992) WAIS—Scala di Intelligenza Wechsler per Adulti—Manuale. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Wechsler D (1998) WISC-R—Scala di Intelligenza Wechsler per Bambini Riveduta—Manuale. O.S. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Zazzo R (1960) Le test des deux barrages. Manuel pour l’examen psychologique de l’enfant. Delchaux et Niestlé, Neuchâtel, pp 229–313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiricozzi, F., Chieffo, D., Battaglia, D. et al. Developmental plasticity after right hemispherectomy in an epileptic adolescent with early brain injury. Childs Nerv Syst 21, 960–969 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1148-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1148-y