Abstract
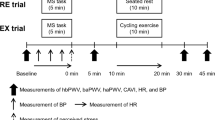
Thrombin generation is an important factor in the pathogenesis of thrombogenic disorders and acute coronary syndromes. Increase in mental stress has been associated with the initiation of the acute coronary syndromes, but the exact mechanism is not known. The present study examined the effects of physical exercise and mental stress on platelet-dependent thrombin generation. Twelve healthy men (mean age 34.2 ± 2.4 years) underwent a treadmill exercise test and a mental stress test by performing mental arithmetic. Platelet-dependent thrombin generation and plasma concentrations of catecholamines, thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT), plasmin-α2 plasmin inhibitor complex (PIC), and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) were measured before, immediately after, and at 10 and 30 min after stress. Thrombin generation increased significantly immediately after exercise, followed by rapid normalization. Mental stress caused a significant increase in thrombin generation 10 min after stress. While plasma concentrations of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine were elevated immediately after exercise, and rapidly returned to baseline, only plasma norepinephrine increased immediately after mental stress. TAT and PIC concentrations did increase immediately after exercise; however, PAI-1 remained unchanged. The increase in thrombin generation with exercise and mental stress was unaffected by treatment with 81 mg/day of aspirin of 7 days. However, it was inhibited by a single oral 40-mg dose of metoprolol. Both exercise and mental stress cause an increase in platelet-dependent thrombin generation, which was suppressed by β-blocker therapy, but not by aspirin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 15, 2001 / Accepted: August 3, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawano, T., Aoki, N., Homori, M. et al. Mental stress and physical exercise increase platelet-dependent thrombin generation. Heart Vessels 15, 280–288 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003800070006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003800070006