Abstract
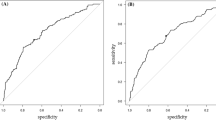
The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential predictive significance of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistant Kawasaki disease (KD). The PNI, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were analyzed in 1257 eligible patients with KD. Receiver operating curve analysis was used to explore the prediction accuracy for IVIG-resistant KD. The optimal cut-off values were identified as 49.5 for PNI, 3.58 for NLR and 164.00 for PLR, respectively. Lower pretreatment PNI (< 49.5) was demonstrated to be associated with lower age, serum sodium levels and platelet counts, and with a higher incidence of IVIG resistance and higher C-reactive protein levels. There was a significantly negative association between the PNI and NLR, and PLR. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that PNI, NLR and PLR were independent predictive factors for IVIG resistance. The discriminatory ability of PNI was not inferior to NLR, PLR and their combination (NLR > 3.58 and PLR > 164) for predicting IVIG resistance, respectively. Pretreatment PNI may serve as a novel surrogate independent predictor for IVIG-resistant KD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns JC, Capparelli EV, Brown JA, Newburger JW, Glode MP (1998) Intravenous gamma-globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease. US/Canadian Kawasaki Syndrome Study Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17(12):1144–1148
Wallace CA, French JW, Kahn SJ, Sherry DD (2000) Initial intravenous gammaglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 105(6):E78
Wu S, Liao Y, Sun Y, Zhang CY, Zhang QY, Yan H, Qi JG, Liu XQ, Chen YH, Wang YL, Li XY, Jin HF, Du JB (2020) Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease in children. World J Pediatr 16(6):607–613
Ha KS, Lee J, Jang GY, Lee J, Lee KC, Son CS, Lee JW (2015) Value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in predicting outcomes in Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol 116(2):301–306
Chen Y, Hua Y, Zhang C, Chen S, Zhang Q, Liao Y, Yan H, Wang Y, Liu P, Qi J, Liu X, Chen Y, Tang C, Jin H, Du J (2019) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts intravenous immunoglobulin-resistance in infants under 12-months old with Kawasaki disease. Front Pediatr 7:81
Wu G, Yue P, Ma F, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Li Y (2020) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a biomarker for predicting the intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 99(6):e18535
Takeshita S, Kanai T, Kawamura Y, Yoshida Y, Nonoyama S (2017) A comparison of the predictive validity of the combination of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and other risk scoring systems for intravenous immunoglobulin (ivig)-resistance in Kawasaki disease. PLoS ONE 12(5):e0176957
Kawamura Y, Takeshita S, Kanai T, Yoshida Y, Nonoyama S (2016) The combined usefulness of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in predicting intravenous immunoglobulin resistance with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 178:281-284.e1
Tan XH, Zhang XW, Wang XY, He XQ, Fan C, Lyu TW, Tian J (2019) A new model for predicting intravenous immunoglobin-resistant Kawasaki disease in Chongqing: a retrospective study on 5277 patients. Sci Rep 9(1):1722
Qi F, Zhou X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Cong R, Yang J, Song N (2018) Pre-treatment prognostic nutritional index may serve as a potential biomarker in urinary cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int 18:207
Lu Z, Yan W, Liang J, Yu M, Liu J, Hao J, Wan Q, Liu J, Luo C, Chen Y (2020) Nomogram based on systemic immune-inflammation index to predict survival of tongue cancer patients who underwent cervical dissection. Front Oncol 10:341
Huang X, Hu H, Zhang W, Shao Z (2019) Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with osteosarcoma. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18408–18414
Wang X, Wang Y (2019) The prognostic nutritional index is prognostic factor of gynecological cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 67:79–86
Hu Y, Shen J, Liu R, Feng Z, Zhang C, Ling L, Chen L (2018) Prognostic value of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers 33(4):372–378
Hayıroğlu Mİ, Keskin M, Keskin T, Uzun AO, Altay S, Kaya A, Öz A, Çinier G, Güvenç TS, Kozan Ö (2018) A novel independent survival predictor in pulmonary embolism: prognostic nutritional index. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 24(4):633–639
Chen QJ, Qu HJ, Li DZ, Li XM, Zhu JJ, Xiang Y, Li L, Ma YT, Yang YN (2017) Prognostic nutritional index predicts clinical outcome in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Sci Rep 7(1):3285
Keskin M, Hayıroğlu MI, Keskin T, Kaya A, Tatlısu MA, Altay S, Uzun AO, Börklü EB, Güvenç TS, Avcı II, Kozan Ö (2017) A novel and useful predictive indicator of prognosis in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the prognostic nutritional index. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 27(5):438–446
Chen XL, Wei XB, Huang JL, Ke ZH, Tan N, Chen JY, Liu YH, Yu DQ (2020) The prognostic nutritional index might predict clinical outcomes in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 30(3):393–399
Shirakabe A, Hata N, Kobayashi N, Okazaki H, Matsushita M, Shibata Y, Nishigoori S, Uchiyama S, Asai K, Shimizu W (2018) The prognostic impact of malnutrition in patients with severely decompensated acute heart failure, as assessed using the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score. Heart Vessels 33(2):134–144
Tai IH, Wu PL, Guo MM, Lee J, Chu CH, Hsieh KS, Kuo HC (2020) Prognostic nutrition index as a predictor of coronary artery aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease. BMC Pediatr 20(1):203
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA, Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease CoCDitY, Association AH (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114(6):1708–1733
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M, Shah PB, Kobayashi T, Wu MH, Saji TT, Pahl E, American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, Young aKDCotCoCDit, Nursing CoCaS, Anesthesia CoCSa, Prevention aCoEa (2017) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American heart association. Circulation 135(17):e927-927e999
Wang Y, Wang W, Gong F, Fu S, Zhang Q, Hu J, Qi Y, Xie C, Zhang Y (2013) Evaluation of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in relation to Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum 65(3):805–814
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1983) A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology 148(3):839–843
Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, Okada Y, Tamura K, Tomomasa T, Kobayashi T, Morikawa A (2006) Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 113(22):2606–2612
Kuo HC, Liang CD, Wang CL, Yu HR, Hwang KP, Yang KD (2010) Serum albumin level predicts initial intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr 99(10):1578–1583
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2009) Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 30(7):1073–1081
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140(6):883–899
Zahorec R (2001) Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts–rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl Lek Listy 102(1):5–14
Ray-Coquard I, Cropet C, Van Glabbeke M, Sebban C, Le Cesne A, Judson I, Tredan O, Verweij J, Biron P, Labidi I, Guastalla JP, Bachelot T, Perol D, Chabaud S, Hogendoorn PC, Cassier P, Dufresne A, Blay JY, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (2009) Lymphopenia as a prognostic factor for overall survival in advanced carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas. Cancer Res 69(13):5383–539191
Liu X, Zhou K, Hua Y, Wu M, Liu L, Shao S, Wang C (2020) Prospective evaluation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in a large cohort of Kawasaki disease patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J 39(3):229–231
Do YS, Kim KW, Chun JK, Cha BH, Namgoong MK, Lee HY (2010) Predicting factors for refractory Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J 40(5):239–242
Yang S, Song R, Zhang J, Li X, Li C (2019) Predictive tool for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance of Kawasaki disease in Beijing. Arch Dis Child 104(3):262–267
Kanai T, Takeshita S, Kawamura Y, Kinoshita K, Nakatani K, Iwashima S, Takizawa Y, Hirono K, Mori K, Yoshida Y, Nonoyama S (2020) The combination of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as a novel predictor of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in patients with Kawasaki disease: a multicenter study. Heart Vessels 35(10):1463–1472
Ahn SS, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW (2018) Prognostic nutritional index is correlated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 27(10):1697–1705
Correa-Rodríguez M, Pocovi-Gerardino G, Callejas-Rubio JL, Fernández RR, Martín-Amada M, Cruz-Caparros MG, Ortego-Centeno N, Rueda-Medina B (2019) The prognostic nutritional index and nutritional risk index are associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nutrients 11(3):638
Cheng YL, Sung SH, Cheng HM, Hsu PF, Guo CY, Yu WC, Chen CH (2017) Prognostic nutritional index and the risk of mortality in patients with acute heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc 6(6):e004876
Min JY, Woo A, Chae MS, Hong SH, Park CS, Choi JH, Chung HS (2020) Predictive impact of modified-prognostic nutritional index for acute kidney injury within 1-week after living donor liver transplantation. Int J Med Sci 17(1):82–88
Wu S, Long Y, Chen S, Huang Y, Liao Y, Sun Y, Zhang Q, Zhang C, Yan H, Qi J, Liu X, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Du J (2019) A New scoring system for prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance of Kawasaki disease in infants under 1-year old. Front Pediatr 7:514
Mirili C, Yılmaz A, Demirkan S, Bilici M, Basol Tekin S (2019) Clinical significance of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in malignant melanoma. Int J Clin Oncol 24(10):1301–1310
Sun Y, Huang Z, Chi P (2020) An inflammation index-based prediction of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal mucinous adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol 25(7):1299–1307
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge for their contribution Ju Zeng (The First People's Hospital of Yibin, SiChuan, China), Zhengxia Han (The Second People's Hospital of Yibin, SiChuan, China), Guoguang Jian (Luzhou people's Hospital, SiChuan, China) and Zhiling Ran (Southwest Medical University Affiliated Hospital of traditional Chinese Medicine, SiChuan, China).
Funding
This work was supported by Foundation of Southwest Medical University (NO. 2017-ZRQN-061 and NO. 2017-ZRQN-120).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GL and XX conceived of and designed this study, designed the data collection instrument, joined the consensus conference, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript, approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. PC participated in the data collection. RZ participated in the consensus conference, critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content, approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. BL analyzed the data and drafted the initial manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Xu, X., Chen, P. et al. Prognostic value of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index in intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Heart Vessels 36, 1366–1373 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01819-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01819-w