Abstract
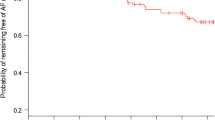
Relaxin, an emerging biomarker in heart failure, is involved in fibrosis and inflammation. The value of relaxin in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) after radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) is unknown and the subject of this study. We prospectively enrolled 248 consecutive patients with AF (paroxysmal in 127 and persistent in 121) who underwent RFCA at our center after measurement of circulating levels of relaxin by ELISA. Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test and multivariate analysis were used to assess the association between pre-RFCA relaxin levels and post-RFCA AF recurrence at 18 months follow-up. At mean 16.3 ± 3.8 months post-RFCA, 195 (78.6%) patients maintained sinus rhythm, and their pre-RFCA relaxin level was lower than that in patients with AF recurrence (P < 0.001). From lowest to highest pre-RFCA relaxin level tertiles (T1; 82.10–< 234.36; T2; 234.36–< 342.26; and T3; 342.26–740.63 ng/L), AF recurrence rate increased significantly (8.5%, 20.5% and 34.9%, respectively; Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test, χ2 = 18.44, P < 0.001). Using a cutoff of 285.4 ng/L, pre-RFCA relaxin level predicted AF recurrence during follow-up with sensitivity of 77.4% and specificity of 55.9% (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve = 0.71). On multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, relaxin level by tertile (T2, hazard ratio 2.678; 95% confidence interval 1.110–6.460; P = 0.028, and T3, hazard ratio 4.745; 95% confidence interval 2.075–10.854; P < 0.001, respectively compared with the T1) was the independent factor predicting recurrence. Elevated pre-RFCA relaxin level is associated with post-RFCA AF recurrence. A simple measurement of relaxin level therefore might help identify patients at high risk of AF recurrence after RFCA.
Clinical Trial Registration chictr.org.cn identifier: ChiCTR-OOC-15006130.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- RFCA:
-
Radiofrequency catheter ablation
- Ang II:
-
Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and angiotensin II
- PaAF:
-
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- PeAF:
-
Persistent atrial fibrillation
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiography
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- BNP:
-
Brain natriuretic peptide
- LAD:
-
Left atrial diameter
- LVMI:
-
Left ventricular mass index
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- AUC:
-
Area under the ROC curve
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- LA:
-
Left atrial
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LVEDD:
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter
References
Kostin S, Klein G, Szalay Z, Hein S, Bauer EP, Schaper J (2002) Structural correlate of atrial fibrillation in human patients. Cardiovasc Res 54:361–379
Sardu C, Santamaria M, Paolisso G, Marfella R (2015) microRNA expression changes after atrial fibrillation catheter ablation. Pharmacogenomics 16:1863–1877
Tan AY, Zimetbaum P (2011) Atrial fibrillation and atrial fibrosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 57:625–629
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ Jr, Davies DW, DiMarco J, Edgerton J, Ellenbogen K, Ezekowitz MD, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jalife J, Jais P, Kalman J, Keane D, Kim YH, Kirchhof P, Klein G, Kottkamp H, Kumagai K, Lindsay BD, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Reddy V, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ, Tsao HM, Wilber D (2012) 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Europace 14:528–606
Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Métayer P, Clémenty J (1998) Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 339:659–666
Balk EM, Garlitski AC, Alsheikh-Ali AA, Terasawa T, Chung M, Ip S (2010) Predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence after radiofrequency catheter ablation: a systematic review. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 21:1208–1216
Cao H, Xue L, Xu X, Wu Y, Zhu J, Chen L, Chen D, Chen Y (2011) Heat shock proteins in stabilization of spontaneously restored sinus rhythm in permanent atrial fibrillation patients after mitral valve surgery. Cell Stress Chaperones 16:517–528
Sotomi Y, Inoue K, Ito N, Kimura R, Toyoshima Y, Masuda M, Doi A, Iwakura K, Okamura A, Koyama Y, Date M, Fujii K (2013) Cause of very late recurrence of atrial fibrillation or flutter after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 111:552–556
Cai L, Yin Y, Ling Z, Su L, Liu Z, Wu J, Du H, Lan X, Fan J, Chen W, Xu Y, Zhou P, Zhu J, Zrenner B (2013) Predictors of late recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Int J Cardiol 164:82–87
Letsas KP, Weber R, Bürkle G, Mihas CC, Minners J, Kalusche D, Arentz T (2009) Pre-ablative predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence following pulmonary vein isolation: the potential role of inflammation. Europace 11:158–163
Zhao Z, Ng CY, Liu T, Li H, Li G (2014) Relaxin as novel strategy in the management of atrial fibrillation: potential roles and future perspectives. Int J Cardiol 171:e72–e73
Mookerjee I, Unemori EN, Du XJ, Tregear GW, Samuel CS (2005) Relaxin modulates fibroblast function, collagen production, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by cardiac fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1041:190–193
Zhou H, Qu X, Gao Z, Zheng G, Lin J, Su L, Huang Z, Li H, Huang W (2016) Relaxin level in patients with atrial fibrillation and association with heart failure occurrence: a STROBE compliant article. Medicine (Baltim) 95:e3664
European Heart Rhythm Association; European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G, Prendergast B, Heidbuchel H, Alfieri O, Angelini A, Atar D, Colonna P, De Caterina R, De Sutter J, Goette A, Gorenek B, Heldal M, Hohloser SH, Kolh P, Le Heuzey JY, Ponikowski P, Rutten FH (2010) Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 31:2369–2429
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) (2012) 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 33:2719–2747
Nattel S, Opie LH (2006) Controversies in atrial fibrillation. Lancet 367:262–272
Beyerbach DM, Zipes DP (2004) Mortality as an endpoint in atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 1:8–18
Wijffels MC, Kirchhof CJ, Dorland R, Allessie MA (1995) Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation 92:1954–1968
Allessie M, Ausma J, Schotten U (2002) Electrical, contractile and structural remodeling during atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 54:230–246
Goudis CA, Kallergis EM, Vardas PE (2012) Extracellular matrix alterations in the atria: insights into the mechanisms and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. Europace 14:623–630
Xu J, Cui G, Esmailian F, Plunkett M, Marelli D, Ardehali A, Odim J, Laks H, Sen L (2004) Atrial extracellular matrix remodeling and the maintenance of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 109:363–368
Mulukutla S, Althouse AD, Jain SK, Saba S (2018) Increased left atrial size is associated with higher atrial fibrillation recurrence in patients treated with antiarrhythmic medications. Clin Cardiol 41:825–829
Kohári M, Zado E, Marchlinski FE, Callans DJ, Han Y (2014) Left atrial volume best predicts recurrence after catheter ablation in patients with persistent and longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 37:422–429
Montserrat S, Gabrielli L, Borras R, Poyatos S, Berruezo A, Bijnens B, Brugada J, Mont L, Sitges M (2014) Left atrial size and function by three-dimensional echocardiography to predict arrhythmia recurrence after first and repeated ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15:515–522
Zhou T, Wang Z, Fan J, Chen S, Tan Z, Yang H, Yin Y (2015) Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 overexpression improves atrial remodeling and function in a canine model of atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 4(3):e001530
Henry BL, Gabris B, Li Q, Martin B, Giannini M, Parikh A, Patel D, Haney J, Schwartzman DS, Shroff SG, Salama G (2016) Relaxin suppresses atrial fibrillation in aged rats by reversing fibrosis and upregulating Na+ channels. Heart Rhythm 13:983–991
Teichman SL, Unemori E, Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Metra M (2010) Relaxin: review of biology and potential role in treating heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 7:75–82
Metra M, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Ponikowski P, Unemori E, Voors AA, Adams KF Jr, Dorobantu MI, Grinfeld L, Jondeau G, Marmor A, Masip J, Pang PS, Werdan K, Prescott MF, Edwards C, Teichman SL, Trapani A, Bush CA, Saini R, Schumacher C, Severin T, Teerlink JR, Investigators RELAX-AHF (2013) Effect of serelaxin on cardiac, renal, and hepatic biomarkers in the Relaxin in Acute Heart Failure (RELAX-AHF) development program: correlation with outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:196–206
Samuel CS, Cendrawan S, Gao XM, Ming Z, Zhao C, Kiriazis H, Xu Q, Tregear GW, Bathgate RA, Du XJ (2011) Relaxin remodels fibrotic healing following myocardial infarction. Lab Invest 91:675–690
Parikh A, Patel D, McTiernan CF (2013) Relaxin suppresses atrial fibrillation by reversing fibrosis and myocyte hypertrophy and increasing conduction velocity and sodium current in spontaneously hypertensive rat hearts. Circ Res 113:313–321
Marrouche NF, Wilber D, Hindricks G, Jais P, Akoum N, Marchlinski F, Kholmovski E, Burgon N, Hu N, Mont L, Deneke T, Duytschaever M, Neumann T, Mansour M, Mahnkopf C, Herweg B, Daoud E, Wissner E, Bansmann P, Brachmann J (2014) Association of atrial tissue fibrosis identified by delayed enhancement MRI and atrial fibrillation catheter ablation the DECAAF study. JAMA 311:498–506
Kuck KH, Fürnkranz A, Chun KR, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Schlüter M, Elvan A, Lim HW, Kueffer FJ, Arentz T, Albenque JP, Tondo C, Kühne M, Sticherling C, Brugada J, Investigators FIREANDICE (2016) Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: reintervention, rehospitalization, and quality-of-life outcomes in the FIRE AND ICE trial. Eur Heart J 37:2858–2865
Kalil C, Bartholomay E, Borges A, Gazzoni G, Lima ED, Etchepare R, Moraes R, Sussenbach C, Andrade K, Kalil R (2014) Atrial fibrillation ablation by use of electroanatomical mapping: efficacy and recurrence factors. Arq Bras Cardiol 102:30–38
D’Ascenzo F, Corleto A, Biondi-Zoccai G, Anselmino M, Ferraris F, di Biase L, Natale A, Hunter RJ, Schilling RJ, Miyazaki S, Tada H, Aonuma K, Yenn-Jiang L, Tao H, Ma C, Packer D, Hammill S, Gaita F (2013) Which are the most reliable predictors of recurrence of atrial fibrillation after transcatheter ablation? A meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol 167:1984–1989
Park J, Joung B, Uhm JS, Young Shim C, Hwang C, Hyoung Lee M, Pak HN (2014) High left atrial pressures are associated with advanced electroanatomical remodeling of left atrium and independent predictors for clinical recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Heart Rhythm 11:953–960
Naruse Y, Tada H, Sekiguchi Y, Machino T, Ozawa M, Yamasaki H, Igarashi M, Kuroki K, Itoh Y, Murakoshi N, Yamaguchi I, Aonuma K (2011) Concomitant chronic kidney disease increases the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a mid-term follow-up. Heart Rhythm 8:335–341
Li M, Liu T, Luo D, Li G (2014) Systematic review and meta-analysis of chronic kidney disease as predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence following catheter ablation. Cardiol J 21:89–95
Liu J, Fang PH, Dibs S, Hou Y, Li XF, Zhang S (2011) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after primary circumferential pulmonary vein isolation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 34:398–406
Smit MD, Maass AH, De Jong AM, Muller Kobold AC, Van Veldhuisen DJ, Van Gelder IC (2012) Role of inflammation in early atrial fibrillation recurrence. Europace 14:810–817
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81570364, 81873468] and in part by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau of Zhejiang Province of China [Y20150032, Y20160318, Y20170021].The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. No additional external funding received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. No commercial party having a direct or indirect interest in the subject matter of this research conferred a benefit on the authors or on any organization with which the authors are associated. This material has not previously been presented in any form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, X., Chen, L., Sun, L. et al. Serum relaxin level predicts recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation. Heart Vessels 34, 1543–1551 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-019-01386-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-019-01386-1