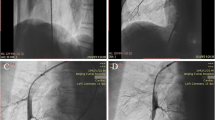
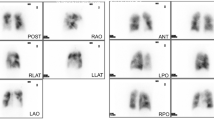
Abstract
Balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA) has emerged as a new treatment strategy for patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Improvements in hemodynamic parameters after BPA have been reported, but some patients continue to suffer from reduced exercise tolerance even after the normalization of hemodynamic parameters following BPA. As the amelioration of hemodynamic parameters is reportedly achieved via BPA, we hypothesized that the limiting factors for exercise tolerance in these patients are related to respiratory function. Therefore, we investigated the associations between respiratory function and exercise tolerance, and the mechanisms underlying respiratory dysfunction in patients after BPA. We analyzed 62 patients with CTEPH who underwent 1-year follow-up after BPA. Predictors for reduced exercise tolerance after BPA determined with six-minute walk test were sought from pulmonary hemodynamic and respiratory parameters using logistic regression analysis. After multivariate adjustments, high mean right atrium pressure (mRAP) and high alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient (A-aDO2) were significant predictors for reduced exercise tolerance. Next, we analyzed factors associated with high A-aDO2. Among the pathophysiological causes of high A-aDO2, including ventilation, diffusing capacity, and low ventilation-perfusion ratio, only low ventilation-perfusion ratio caused by high intrapulmonary shunt fraction was associated with high A-aDO2. Impaired oxygenation due to residual high intrapulmonary shunt fraction was associated with reduced exercise tolerance in patients with CTEPH, after receiving BPA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, Beghetti M, Corris P, Gaine S, Gibbs JS, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jondeau G, Klepetko W, Opitz C, Peacock A, Rubin L, Zellweger M, Simonneau G, ESC Committee for Practive Guidelines (CPG) (2009) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 30(20):2493–2537
Piazza G, Goldhaber SZ (2011) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med 364(4):351–360
Kataoka M, Inami T, Hayashida K, Shimura N, Ishiguro H, Abe T, Tamura Y, Ando M, Fukuda K, Yoshino H, Satoh T (2012) Percutaneous transluminal pulmonary angioplasty for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 5(6):756–762
Mizoguchi H, Ogawa A, Munemasa M, Mikouchi H, Ito H, Matsubara H (2012) Refined balloon pulmonary angioplasty for inoperable patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 5(6):748–755
Tsugu T, Murata M, Kawakami T, Yasuda R, Tokuda H, Minakata Y, Tamura Y, Kataoka M, Hayashida K, Tsuruta H, Maekawa Y, Inoue S, Fukuda K (2015) Significance of echocardiographic assessment for right ventricular function after balloon pulmonary angioplasty in patients with chronic thromboembolic induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol 115(2):256–261
Kawakami T, Kataoka M, Arai T, Yanagisawa R, Maekawa Y, Fukuda K (2016) Retrograde approach in balloon pulmonary angioplasty: useful novel strategy for chronic total occlusion lesions in pulmonary arteries. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 9(2):e19–e20
Kawakami T, Kataoka M, Yamada Y, Takei M, Yamada M, Jinzaki M, Fukuda K (2015) Impact of CT-guided balloon pulmonary angioplasty with identification of pulmonary arterial structures distal to target lesions. EuroIntervention 11(7):e1–e2
American Thoracic Society (1995) Standardization of spirometry 1994 update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152(3):1107–1136
West JB (1995) Single-breath carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (transfer factor). Recommendations for a standard technique—1995 update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152(6 Pt 1):2185–2198
West JB (2012) Respiratory physiology: the essentials. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 36–56
Austrap P, Severinghaus JW (1986) The history of blood gases, acids and bases, 1st edn. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp 128–156
Puente-Maestu L, Palange P, Casaburi R, Laveneziana P, Maltais F, Neder JA, O'Donnell DE, Onorati P, Porszasz J, Rabinovich R, Rossiter HB, Singh S, Troosters T, Ward S (2016) Use of exercise testing in the evaluation of interventional efficacy: an official ERS statement. Eur Respir J 47(2):429–460
Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M, Aboyans V, Vaz Carneiro A, Achenbach S, Agewall S, Allanore Y, Asteggiano R, Paolo Badano L, Albert Barbera J, Bouvaist H, Bueno H, Byrne RA, Carerj S, Castro G, Erol C, Falk V, Funck-Brentano C, Gorenflo M, Granton J, Iung B, Kiely DG, Kirchhof P, Kjellstrom B, Landmesser U, Lekakis J, Lionis C, Lip GY, Orfanos SE, Park MH, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Revel MP, Rigau D, Rosenkranz S, Voller H, Luis Zamorano J (2016) 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 37(1):67–119
Yanagisawa R, Kataoka M, Inami T, Shimura N, Ishiguro H, Fukuda K, Yoshino H, Satoh T (2014) Safety and efficacy of percutaneous transluminal pulmonary angioplasty in elderly patients. Int J Cardiol 175(2):285–289
Inami T, Kataoka M, Yanagisawa R, Ishiguro H, Shimura N, Fukuda K, Yoshino H, Satoh T (2016) Long-term outcomes after percutaneous transluminal pulmonary angioplasty for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 134(24):2030–2032
Aoki T, Sugimura K, Nochioka K, Miura M, Tatebe S, Yamamoto S, Yaoita N, Suzuki H, Sato H, Kozu K, Miyata S, Satoh K, Shimokawa H (2016) Effects of balloon pulmonary angioplasty on oxygenation in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension- importance of intrapulmonary shunt. Circ J 80(10):2227–2234
Acknowledgements
Authors thank staffs of department of respiratory physiology in Keio University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to declare regarding the contents of this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takei, M., Kawakami, T., Kataoka, M. et al. Residual high intrapulmonary shunt fraction limits exercise capacity in patients treated with balloon pulmonary angioplasty. Heart Vessels 34, 868–874 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1306-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1306-2