Abstract
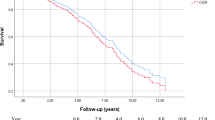
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is an alternative treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (rAAA) in hemodynamically (hd) stable patients. Treatment for patients with hd-unstable rAAA remains controversial. The aim of this study was to compare the outcomes of EVAR and open surgery (OS) in hd-stable and hd-unstable rAAA patients using meta-analysis. The first part of this study included 48 articles that reported the treatment outcomes of rAAA managed with EVAR (n = 9610) and OS (n = 93867). The second part, which is the focus of this study, included 5 out of 48 articles, which further reported treatment results in hd-stable (n = 198) and hd-unstable (n = 185) patients. When heterogeneity among the groups was observed, a random-effects model was used to calculate the adjusted odds ratios (OR) or in cases of non-heterogeneity, a fixed-effects model analysis was employed. In the first part of this study, the in-hospital mortality rate was found to be lower in the EVAR group than in the OS group (29.9 vs 40.8 %; OR 0.59; 95 % CI 0.52–0.66; P < 0.01). In the second part of this study, 383 patients from 5 articles were included: 152 patients were treated by EVAR, and 231 were treated by OS. The total mortality was 147/383 (38.4 %), while the mortality of the EVAR group and the OS group was 25.7 % (39/152) and 46.8 % (108/231), respectively. In the hd-stable group, the in-hospital mortality after EVAR was significantly lower than that after OS [18.9 % (18/95) vs 28.2 % (29/103); OR 0.47; 95 % CI 0.22–0.97; P = 0.04]. For the hd-unstable rAAA patients, the in-hospital mortality after EVAR was significantly lower than that after OS [36.8 % (21/57) vs 61.7 % (79/128); OR 0.40; 95 % CI 0.20–0.79; P < 0.01]. This study indicated that compared with OS, EVAR in hd-unstable rAAA patients is associated with improved outcomes. Available publications are currently limited; thus, the best treatment strategy for this subgroup of patients remains unclear. Further clinical studies are needed to provide more detailed data, such as the shock index and long-term results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Kwong GP, Powell JT, Thompson SG, EVAR trial participants (2004) Comparison of endovascular aneurysm repair with open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 1), 30-day operative mortality results: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364:843–848
Prinssen M, Verhoeven EL, Buth J, Cuypers PW, van Sambeek MR, Balm R, Buskens E, Grobbee DE, Blankensteijn JD; Dutch Randomized EndovascularAneurysm Management(DREAM)Trial Group (2004) A randomized trial comparing conventional and endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med 351:1607–1618
Yusuf SW, Whitaker SC, Chuter TA, Wenham PW, Hopkinson BR (1994) Emergency endovascular repair of leaking aortic aneurysm. Lancet 344:1645
Takagi H, Umemoto T (2011) A meta-analysis of randomized and risk-adjusted observational studies of endovascular versus open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Vasc Endovascular Surg 45:717–719
Karkos CD, Harkin DW, Giannakou A, Giannakou A, Gerassimidis TS (2009) Mortality after endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Surg 144:770–778
Antoniou GA, Georgiadis GS, Antoniou SA, Pavlidis P, Maras D, Sfyroeras GS, Georgakarakos EI, Lazarides MK (2013) Endovascular repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm confers an early survival benefit over open repair. J Vasc Surg 58:1091–1105
Hardman DT, Fisher CM, Patel MI, Neale M, Chambers J, Lane R, Appleberg M (1996) Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: who should be offered surgery? J Vasc Surg 23:123–129
Karkos CD, Karamanos D, Papazoglou KO, Kantas AS, Theochari EG, Kamparoudis AG, Gerassimidis TS (2008) Usefulness of the Hardman index in predicting outcome after endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 48(4):788–794
Sharif MA, Lee B, Makar RR, Loan W, Soong CV (2007) Role of the Hardman index in predicting mortality for open and endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Endovasc Ther 14:528–535
Larzon T, Lindgren R, Norgren L (2005) Endovascular treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: a shift of the paradigm? J Endovasc Ther 12:548–555
Acosta S, Ogren M, Bergqvist D, Lindblad B, Dencker M, Zdanowski Z (2006) The Hardman index in patients operated on for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review. J Vasc Surg 44:949–954
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch v, Losos M, Tugwell P (2014) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analysis. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Assessed Mar 29 2014
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Lee RW, Rhodes JM, Singh MJ, Davies MG, Wolford HY, Diachun C, Norton R, Illig KA (2008) Is there a selection bias in applying endovascular aneurysm repair for rupture? Ann Vasc Surg 22:215–220
Anain PM, Anain JM Sr, Tiso M, Nader ND, Dosluoglu HH (2007) Early and mid-term results of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms in the endovascular era in a community hospital. J Vasc Surg 46:898–905
Moore R, Nutley M, Cina CS, Motamedi M, Faris P, Abuznadah W (2007) Improved survival after introduction of an emergency endovascular therapy protocol for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 45:443–450
Coppi G, Silingardi R, Gennai S, Saitta G, Ciardullo AV (2006) A single-center experience in open and endovascular treatment of hemodynamically unstable and stable patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 44:1140–1147
Visser JJ, Bosch JL, Hunink MG, van Dijk LC, Hendriks JM, Poldermans D, van Sambeek MR (2006) Endovascular repair versus open surgery in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: clinical outcomes with 1-year follow-up. J Vasc Surg 44:1148–1155
van der Vliet JA, van Aalst DL, Schultze Kool LJ, Schultze Kool LJ, Wever JJ, Blankensteijn JD (2007) Hypotensive hemostatis (permissive hypotension) for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: are we really in control? Vascular 15:197–200
Najjar SF, Mueller KH, Ujiki MB, Morasch MD, Matsumura JS, Eskandari MK (2007) Percutaneous endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arch Surg 142:1049–1052
Egorova N, Giacovelli J, Greco G, Gelijns A, Kent CK, McKinsey JF (2008) National outcomes for the treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: comparison of open versus endovascular repairs. J Vasc Surg 48:1092–1100
Van Schaik DE, Dolmans DE, Ho G, Geenen GP, Vos L, Van Der Waal JC, De Groot HG, Van Der Laan L (2011) Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: endovascular or open approach in a Dutch general hospital. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 52:363–369
Ten Bosch JA, Willigendael EM, Kruidenier LM, de Loos ER, Prins MH, Teijink JA (2012) Early and mid-term results of a prospective observational study comparing emergency endovascular aneurysm repair with open surgery in both ruptured and unruptured acute abdominal aortic aneurysms. Vascular 20:72–80
Wu CY, Chan CY, Huang SC, Chi NS, Wang SS, Wu IH (2014) Outcomes following endovascular or open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm in a Chinese population. Heart Vessels 29:71–77
Mehta M, Byrne J, Darling RC 3rd, Paty PS, Roddy SP, Kreienberg PB, Taggert JB, Feustel P (2013) Endovascular repair of ruptured infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with lower 30-day mortality and better 5-year survival rates than open surgical repair. J Vasc Surg 57:368–375
Investigators IT (2014) Endovascular or open repair strategy for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: 30 day outcomes from IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ 348:f7661
Karkos CD, Sutton AJ, Bown MJ, Sayers RD (2011) A meta-analysis and metaregression analysis of factors influencing mortality after endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 42:775–786
Karkos CD, Menexes GC, Patelis N, Kalogirou TE, Giagtzidis IT, Harkin DW (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of abdominal compartment syndrome after endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 59(3):829–842
Nakayama Atsuko, Morita Hiroyuki, Miyata Tetsuro, Hoshina Katsuyuki, Nagayama Masatoshi, Takanashi Shuichiro, Sumiyoshi Tetsuya, Komuro Issei, Nagai Ryozo (2014) Predictors of mortality after emergency or elective repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in a Japanese population. Heart Vessels 29(1):65–70
Ten Bosch JA, Cuypers PW, van Sambeek M, Teijink JA (2011) Current insights in endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Euro Intervention 7:852–858
Lloyd GM, Newton JD, Norwood MG, Franks SC, Bown MJ, Sayers RD (2004) Patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm: are we missing the opportunity for cardiovascular risk reduction? J Vasc Surg 40:691–697
Lachat ML, Pfammatter T, Witzke HJ, Bettex D, Künzli A, Wolfensberger U, Turina MI (2002) Endovascular repair with bifurcated stent-grafts under local anaesthesia to improve outcome of ruptured aortoiliac aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23:528–536
Peppelenbosch N, Cuypers PW, Vahl AC, Vermassen F, Buth J (2005) Emergency endovascular treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm and the risk of spinal cord ischemia. J Vasc Surg 42:608–614
Peppelenbosch N, Yilmaz N, van Marrewijk C, Buth J, Cuypers P, Duijm L, Tielbeek A (2003) Emergency treatment of acute symptomatic or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Outcome of a prospective intent-to-treat by EVAR protocol. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 26:303–310
Mehta M, Darling RC 3rd, Roddy SP, Fecteau S, Ozsvath KJ, Kreienberg PB, Paty PS, Chang BB, Shah DM (2005) Factors associated with abdominal compartment syndrome complicating endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 42(6):1047–1051
Hunter JD, Damani Z (2004) Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. Anaesthesia 59:899–907
Karkos CD, Menexes GC, Patelis N, Kalogirou TE, Giagtzidis IT, Harkin DW (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of abdominal compartment syndrome after endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 59(3):829–842
Alsac JM, Desgranges P, Kobeiter H, Becquemin JP (2005) Emergency endovascular repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: feasibility and comparison of early results with conventional open repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 30:632–639
Hinchliffe RJ, Yusuf SW, Macierewicz JA, MacSweeney ST, Wenham PW, Hopkinson BR (2001) Endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm–a challenge to open repair? Results of a single centre experience in 20 patients. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 22:528–534
Gerassimidis TS, Papazoglou KO, Kamparoudis AG, Konstantinidis K, Karkos CD, Karamanos D, Sfyroeras G (2005) Endovascular management of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: 6-year experience from a Greek center. J Vasc Surg 42:615–623
Orend KH, Kotsis T, Scharrer-Pamler R, Kapfer X, Liewald F, Görich J, Sunder-Plassmann L (2002) Endovascular repair of aortic rupture due to trauma and aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23:61–67
Egorova N, Giacovelli J, Greco G, Gelijns A, Kent CK, McKinsey JF (2008) National outcomes for the treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: comparison of open versus endovascular repairs. J Vasc Surg 48:1092–1100
Hannan EL, O’Donnell JF, Kilburn H, Bernard HR, Yazici A (1989) Investigation of the relationship between volume and mortality for surgical procedures performed in New York State hospitals. JAMA 262:503–510
Kazmers A, Jacobs L, Perkins A, Lindenauer SM, Bates E (1996) Abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in Veterans Affairs medical centers. J Vasc Surg 23:191–200
Wen SW, Simunovic M, Williams JI, Johnston KW, Naylor CD (1996) Hospital volume, calendar age, and short term outcomes in patients undergoing repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: the Ontario experience, 1988–92. J Epidemiol Commun Health 50:207–213
Manheim LM, Sohn MW, Feinglass J, Ujiki M, Parker MA, Pearce WH (1998) Hospital vascular surgery volume and procedure mortality rates in California, 1982–1994. J Vasc Surg 28:45–56
Huber TS, Seeger JM (2001) Dartmouth Atlas of Vascular Health Care review: impact of hospital volume, surgeon volume, and training on outcome. J Vasc Surg 34:751–756
Greco G, Egorova N, Anderson PL, Gelijns A, Moskowitz A, Nowygrod R, Arons R, McKinsey J, Morrissey NJ, Kent KC (2006) Outcomes of endovascular treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 43:453–459
Acknowledgments
Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81330034, 81270386, 81170291] and the 1255 Project of Changhai Hospital [CH125520200, CH125550300].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No relationship with industry. There is no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All human studies have been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and have, therefore, been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Additional information
S. Zhang, J. Feng, and H. Li authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Feng, J., Li, H. et al. Open surgery (OS) versus endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) for hemodynamically stable and unstable ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (rAAA). Heart Vessels 31, 1291–1302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0736-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0736-3