Abstract
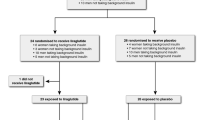
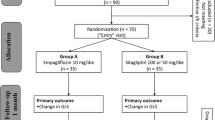
Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is observed frequently in patients with type 2 diabetes; however, few studies have focused on the effect of the Rho-associated kinase inhibitor fasudil on cardiac performance in humans. We conducted a prospective pilot study to assess the impact of fasudil on LV diastolic function in patients with diabetes without systolic dysfunction. Two hundred and fifty eligible patients with type 2 diabetes (149 men [61.3 %] and 94 women [38.7 %]) with a mean age of 57.2 years were randomly assigned to fasudil (n = 122, 30 mg intravenously twice a day for 14 days) or placebo (n = 121) groups. Echocardiographic variables were measured at the baseline and 1 month after the intervention. Compared with the placebo group, the fasudil group showed a significant decrease in diastolic blood pressure and in the peak of late diastolic transmitral flow (Am) (P < 0.05 for both). Deceleration time (DT), isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT), the peak of early diastolic annular velocity (e′), the peak of late diastolic annular velocity, and E/e′ also exhibited a significant improvement (all, P < 0.05) after fasudil administration. Furthermore, the Em/Am ratio and IVRT, DT, and E/e′ values recorded after fasudil treatment in the subgroup with impaired LV relaxation significantly differed from the corresponding values in the subgroup with normal LV relaxation (all, P < 0.05). Fasudil improves short-term echocardiographic parameters of LV diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snell-Bergeon JK, Wadwa RP (2012) Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Technol Ther 14:S51–S58
Çiftel S, Içağasıoğlu S, Yıldız G, Tekin G, Aydin H (2012) Association of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with elevated NT-proBNP in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with preserved ejection fraction: the supplemantary role of tissue doppler imaging parameters and NT-proBNP levels. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 96:179–186
von Bibra H, St John Sutton M (2010) Diastolic dysfunction in diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: promising potential for diagnosis and prognosis. Diabetologia 53:1033–1045
Reinhard H, Hansen PR, Wiinberg N, Kjær A, Petersen CL, Winther K, Parving HH, Rossing P, Jacobsen PK (2012) NT-proBNP, echocardiographic abnormalities and subclinical coronary artery disease in high risk type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:19
Raev DC (1994) Left ventricular function and specific diabetic complications in other target organs in young insulin-dependent diabetics: an echocardiographic study. Heart Vessels 9:121–128
Maréchaux S, Six-Carpentier MM, Bouabdallaoui N, Montaigne D, Bauchart JJ, Mouquet F, Auffray JL, Le Tourneau T, Asseman P, LeJemtel TH, Ennezat PV (2011) Prognostic importance of comorbidities in heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Heart Vessels 26:313–320
Arita R, Hata Y, Nakao S, Kita T, Miura M, Kawahara S, Zandi S, Almulki L, Tayyari F, Shimokawa H, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Ishibashi T (2009) Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil ameliorates diabetes-induced microvascular damage. Diabetes 58:215–226
Noma K, Oyama N, Liao JK (2006) Physiological role of ROCKs in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290:C661–C668
Ocaranza MP, Rivera P, Novoa U, Pinto M, González L, Chiong M, Lavandero S, Jalil JE (2011) Rho kinase inhibition activates the homologous angiotensin-converting enzyme angiotensin-(1–9) axis in experimental hypertension. J Hypertens 29:706–715
Dong M, Liao JK, Fang F, Lee AP, Yan BP, Liu M, Yu CM (2012) Increased Rho kinase activity in congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 14:965–973
Ocaranza MP, Gabrielli L, Mora I, Garcia L, McNab P, Godoy I, Braun S, Córdova S, Castro P, Novoa U, Chiong M, Lavandero S, Jalil JE (2011) Markedly increased Rho-kinase activity in circulating leukocytes in patients with chronic heart failure. Am Heart J 161:931–937
Guan SJ, Ma ZH, Wu YL, Zhang JP, Liang F, Weiss JW, Guo QY, Wang JY, Ji ES, Chu L (2012) Long-term administration of fasudil improves cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 50:1874–1882
Zhou H, Li YJ, Wang M, Zhang LH, Guo BY, Zhao ZS, Meng FL, Deng YG, Wang RY (2011) Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in myocardial fibrosis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:999–1008
Kizub IV, Pavlova OO, Johnson CD, Soloviev AI, Zholos AV (2010) Rho kinase and protein kinase C involvement in vascular smooth muscle myofilament calcium sensitization in arteries from diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 159:1724–1731
Bach LA (2008) Rho kinase inhibition: a new approach for treating diabetic nephropathy? Diabetes 57:532–533
Komers R (2011) Rho kinase inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20:77–83
Ishida T, Takanashi Y, Kiwada H (2006) Safe and efficient drug delivery system with liposomes for intrathecal application of an antivasospastic drug, fasudil. Biol Pharm Bull 29:397–402
Omeis I, Neil JA, Murali R, Abrahams JM (2008) Treatment of cerebral vasospasm with biocompatible controlled-release systems for intracranial drug delivery. Neurosurgery 63:1011–1019 (discussion 1019–1021)
Fujita H, Fukumoto Y, Saji K, Sugimura K, Demachi J, Nawata J, Shimokawa H (2010) Acute vasodilator effects of inhaled fasudil, a specific Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Vessels 25:144–149
Suzuki Y, Shibuya M, Satoh S, Sugimoto Y, Takakura K (2007) A postmarketing surveillance study of fasudil treatment after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 68:126–131 (discussion 131–132)
Nagueh SF, Appleton CP, Gillebert TC, Marino PN, Oh JK, Smiseth OA, Waggoner AD, Flachskampf FA, Pellikka PA, Evangelista A (2009) Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:107–133
Sherazi S, Zaręba W (2011) Diastolic heart failure: predictors of mortality. Cardiol J 18:222–232
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ, Chamber Quantification Writing Group; American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee; European Association of Echocardiography (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1440–1463
Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM (2006) Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 355:251–259
Füchtenbusch M, Standl E, Otter W, Hummel M (2007) Diabetes mellitus and heart failure. MMW Fortschr Med 149:41–44
Cleland JG, Tendera M, Adamus J, Freemantle N, Polonski L, Taylor J, PEP-CHF Investigators (2006) The perindopril in elderly people with chronic heart failure (PEP-CHF) study. Eur Heart J 27:2338–2345
Ahmed A, Rich MW, Fleg JL, Zile MR, Young JB, Kitzman DW, Love TE, Aronow WS, Adams KF Jr, Gheorghiade M (2006) Effects of digoxin on morbidity and mortality in diastolic heart failure: the ancillary Digitalis Investigation Group trial. Circulation 114:397–403
Massie BM, Carson PE, McMurray JJ, Komajda M, McKelvie R, Zile MR, Anderson S, Donovan M, Iverson E, Staiger C, Ptaszynska A, I-PRESERVE Investigators (2008) Irbesartan in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 359:2456–2467
Dong M, Yan BP, Liao JK, Lam YY, Yip GW, Yu CM (2010) Rho-kinase inhibition: a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Drug Discov Today 15:622–629
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (2000) Signal transduction by G-proteins, rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J Physiol 522:177–185
Fukui S, Fukumoto Y, Suzuki J, Saji K, Nawata J, Tawara S, Shinozaki T, Kagaya Y, Shimokawa H (2008) Acute vasodilator effects of inhaled fasudil, a specific Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase ameliorates diastolic heart failure in hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 51:317–326
Li H, Peng W, Jian W, Li Y, Li Q, Li W, Xu Y (2012) ROCK inhibitor fasudil attenuated high glucose-induced MCP-1 and VCAM-1 expression and monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:65
Yokoyama J, Sutoh N, Higuma T, Horiuchi D, Katoh C, Yokota T, Echizen T, Sasaki S, Hanada H, Osanai T, Okumura K (2007) Efficacy and safety of low-dose pioglitazone after primary coronary angioplasty with the use of bare metal stent in patients with acute myocardial infarction and with type 2 diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance. Heart Vessels 22:146–151
Hughes AD, Park C, March K, Coady E, Khir A, Chaturvedi N, Thom SA (2012) A randomized placebo controlled double blind crossover study of pioglitazone on left ventricular diastolic function in type 2 diabetes. Int J Cardiol. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.03.179
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070107).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
R. Guo, Y. Su contributed equally to this paper and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Su, Y., Yan, J. et al. Fasudil improves short-term echocardiographic parameters of diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: a pilot study. Heart Vessels 30, 89–97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-013-0458-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-013-0458-3