Abstract
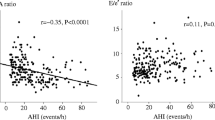
Prolonged P-wave duration, indicating atrial conduction delay, is a marker of left atrial abnormality and is reported as a potent precursor of atrial fibrillation (AF). Several studies have shown that obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with AF. We evaluated the relationship between OSA and prolonged P-wave duration. Consecutive subjects who underwent overnight polysomnography and showed a normal sinus rhythm, had no history of AF or ischemic heart disease, and showed no evidence of heart failure were enrolled. Apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) is defined as the number of apnea and hypopnea events per hour of sleep. P-wave duration was determined on the basis of the mean duration of three consecutive beats in lead II from a digitally stored electrocardiogram. A total of 250 subjects (middle-aged, predominantly male, mildly obese, with a mean P-wave duration of 106 ms) were enrolled. In addition to age, male gender, body mass index (BMI), hypertension, dyslipidemia, and uric acid and creatinine levels, AHI (r = 0.56; P < 0.001) had significant univariable relationship with P-wave duration. Multivariate regression analysis showed that age, BMI, male gender, and AHI (partial correlation coefficient, 0.47; P < 0.001) were significantly independently correlated to P-wave duration. Severity of OSA is significantly associated with delayed atrial conduction time. Obstructive sleep apnea may lead to progression of atrial remodeling as an AF substrate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (ACC/AHA/HRS Writing Committee to Develop Data Standards on Electrophysiology) (2006) ACC/AHA/HRS 2006 key data elements and definitions for electrophysiological studies and procedures: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (ACC/AHA/HRS Writing Committee to Develop Data Standards on Electrophysiology). Circulation 114:2534–2570
Ariyarajah V, Mercado K, Apiyasawat S, Puri P, Spodick DH (2005) Correlation of left atrial size with P-wave duration in interatrial block. Chest 128:2615–2618
Dagli N, Karaca I, Yavuzkir M, Balin M, Arslan N (2008) Are maximum P wave duration and P wave dispersion a marker of target organ damage in the hypertensive population? Clin Res Cardiol 97:98–104
Goyal SB, Spodick DH (2001) Electromechanical dysfunction of the left atrium associated with interatrial block. Am Heart J 142:823–827
Soliman EZ, Prineas RJ, Case LD, Zhang ZM, Goff DC Jr (2009) Ethnic distribution of ECG predictors of atrial fibrillation and its impact on understanding the ethnic distribution of ischemic stroke in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Stroke 40:1204–1211
Magnani JW, Johnson VM, Sullivan LM, Gorodeski EZ, Schnabel RB, Lubitz SA, Levy D, Ellinor PT, Benjamin EJ (2011) P wave duration and risk of longitudinal atrial fibrillation in persons ≥60 years old (from the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol 107:917–921
Magnani JW, Gorodeski EZ, Johnson VM, Sullivan LM, Hamburg NM, Benjamin EJ, Ellinor PT (2011) P wave duration is associated with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality outcomes: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Heart Rhythm 8:93–100
Bradley TD, Floras JS (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet 373:82–93
Naito R, Sakakura K, Kasai T, Dohi T, Wada H, Sugawara Y, Kubo N, Yamashita S, Narui K, Ishiwata S, Ohno M, Ako J, Momomura S (2012) Aortic dissection is associated with intermittent hypoxia and re-oxygenation. Heart Vessels 27:265–270
Saruhara H, Takata Y, Usui Y, Shiina K, Hashimura Y, Kato K, Asano K, Kawaguchi S, Obitsu Y, Shigematsu H, Yamashina A (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea as a potential risk factor for aortic disease. Heart Vessels 27:166–173
Dohi T, Narui K, Kasai T, Takaya H, Inoshita A, Maeno K, Kasagi S, Ishiwata S, Ohno M, Yamaguchi T, Momomura S (2011) Effects of olmesartan on blood pressure and insulin resistance in hypertensive patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Heart Vessels 26:603–608
Buda AJ, Pinsky MR, Ingels NB Jr, Daughters GT 2nd, Stinson EB, Alderman EL (1979) Effect of intrathoracic pressure on left ventricular performance. N Engl J Med 301:453–459
Zamagni M, Sforza E, Boudewijns A, Petiau C, Krieger J (1996) Respiratory effort. A factor contributing to sleep propensity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 109:651–658
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Yokoe T, Minoguchi K, Matsuo H, Oda N, Minoguchi H, Yoshino G, Hirano T, Adachi M (2003) Elevated levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome are decreased by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Circulation 107:1129–1134
Alonso-Fernández A, García-Río F, Arias MA, Hernanz A, de la Peña M, Piérola J, Barceló A, López-Collazo E, Agustí A (2009) Effects of CPAP on oxidative stress and nitrate efficiency in sleep apnoea: a randomised trial. Thorax 64:581–586
Ip MS, Tse HF, Lam B, Tsang KW, Lam WK (2004) Endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea and response to treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:348–353
Fletcher EC, DeBehnke RD, Lovoi MS, Gorin AB (1985) Undiagnosed sleep apnea in patients with essential hypertension. Ann Intern Med 103:190–195
Arias MA, García-Río F, Alonso-Fernández A, Mediano O, Martínez I, Villamor J (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome affects left ventricular diastolic function: effects of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in men. Circulation 112:375–383
Baguet JP, Barone-Rochette G, Lévy P, Vautrin E, Pierre H, Ormezzano O, Pépin JL (2010) Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is linked to severity of obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 36:1323–1329
Can I, Aytemir K, Demir AU, Deniz A, Ciftci O, Tokgozoglu L, Oto A, Sahin A (2009) P-wave duration and dispersion in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Cardiol 133:e85–e89
Baranchuk A, Parfrey B, Lim L, Morriello F, Simpson CS, Hopman WM, Redfearn DP, Fitzpatrick M (2011) Interatrial block in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Cardiol J 18:171–175
Cagirci G, Cay S, Gulsoy KG, Bayindir C, Vural MG, Firat H, Kilic H, Yeter E, Akdemir R, Ardic S (2011) Tissue Doppler atrial conduction times and electrocardiogram interlead P-wave durations with varying severity of obstructive sleep apnea. J Electrocardiol 44:478–482
Rechtschaffen A, Kales AA (1968) Manual of standardized terminology, techniques, and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. NIH Publication No. 204, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
The American Sleep Disorders Association Atlas Task Force (1992) EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples. Sleep 15:173–184
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendation for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–689
Kasai T, Narui K, Dohi T, Ishiwata S, Yoshimura K, Nishiyama S, Yamaguchi T, Momomura S (2005) Efficacy of nasal bi-level positive airway pressure in congestive heart failure patients with Cheyne–Stokes respiration and central sleep apnea. Circ J 69:913–921
Sokolow M, Lyon T (1949) The ventricular complex in left ventricular hypertrophy as obtained by unipolar precordial and limb leads. Am Heart J 37:161–186
Mirvis DM, Goldberger AL (2001) Electrocardiography. In: Braunwald E, Zipes DP, Libby P (eds) Heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 6th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 82–125
Kistler PM, Sanders P, Fynn SP, Stevenson IH, Spence SJ, Vohra JK, Sparks PB, Kalman JM (2004) Electrophysiologic and electroanatomic changes in the human atrium associated with age. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:109–116
Magnani JW, Johnson VM, Sullivan LM, Lubitz SA, Schnabel RB, Ellinor PT, Benjamin EJ (2010) P-wave indices: derivation of reference values from the Framingham Heart Study. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 15:344–352
Seyfeli E, Duru M, Kuvandik G, Kaya H, Yalcin F (2006) Effect of obesity on P-wave dispersion and QT dispersion in women. Int J Obes (Lond) 30:957–961
Song J, Kalus JS, Caron MF, Kluger J, White CM (2002) Effect of diuresis on P-wave duration and dispersion. Pharmacotherapy 22:564–568
Faggiano P, D’Aloia A, Zanelli E, Gualeni A, Musatti P, Giordano A (1997) Contribution of left atrial pressure and dimension to signal-averaged P-wave duration in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 79:219–222
Burstein B, Nattel S (2008) Atrial fibrosis: mechanisms and clinical relevance in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:802–809
Kijima K, Matsubara H, Murasawa S, Maruyama K, Mori Y, Ohkubo N, Komuro I, Yazaki Y, Iwasaka T, Inada M (1996) Mechanical stretch induces enhanced expression of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 79:887–897
Goette A, Staack T, Röcken C, Arndt M, Geller JC, Huth C, Ansorge S, Klein HU, Lendeckel U (2000) Increased expression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and angiotensin-converting enzyme in human atria during atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 35:1669–1677
Kim SJ, Choisy SC, Barman P, Zhang H, Hancox JC, Jones SA, James AF (2011) Atrial remodeling and the substrate for atrial fibrillation in rat hearts with elevated afterload. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 4:761–769
London GM, Marchais SJ, Guerin AP, Pannier B (2004) Arterial stiffness: pathophysiology and clinical impact. Clin Exp Hypertens 26:689–699
Van Wagoner DR (2008) Oxidative stress and inflammation in atrial fibrillation: role in pathogenesis and potential as a therapeutic target. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52:306–313
Oliveira W, Campos O, Bezerra Lira-Filho E, Cintra FD, Vieira M, Ponchirolli A, de Paola A, Tufik S, Poyares D (2008) Left atrial volume and function in patients with obstructive sleep apnea assessed by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 21:1355–1361
Dilaveris P, Batchvarov V, Gialafos J, Malik M (1999) Comparison of different methods for manual P wave duration measurement in 12-lead electrocardiograms. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 22:1532–1538
Spodick DH (2004) Unappreciated prevalence of interatrial block and associated consequences: a poorly perceived pandemic. Mayo Clin Proc 79:668–670
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeno, Ki., Kasai, T., Kasagi, S. et al. Relationship between atrial conduction delay and obstructive sleep apnea. Heart Vessels 28, 639–645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0288-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-012-0288-8