Abstract
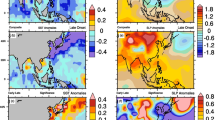
Beijing located at the junction of four major components of the Asian-Australia monsoon system (the Indian, the western North Pacific, the East Asian subtropical, and the Indonesian-Australian monsoons), the monsoon climate over the South China Sea (SCS) exhibits some unique features. Evidences are presented in this paper to reveal and document the following distinctive features in the temporal structure of the SCS summer monsoon:
-
(1)
pronounced monsoon singularities in the lower tropospheric monsoon flows which include the pre-onset and withdrawal easterly surges and the southwesterly monsoon bursts at Julian pentad 34-35 (June 15-24) and pentad 46-47 (August 14-23);
-
(2)
four prominent subseasonal cycles (alternative occurrences of climatological active and break monsoons);
-
(3)
considerably larger year-to-year variations in convectiye activity on intraseasonal time scale compared to those over the Bay of Bengal and the Philippine Sea;
-
(4)
the redness of the climatological mean spectrum of precipitation / deep convection on synoptic to intraseasonal time scales in the central SCS;
-
(5)
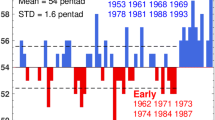
a remarkable asymmetry in the seasonal transitions between summer and winter monsoons and an extremely abrupt mid-May transition (the outburst of monsoon rain and the sudden switch in the lower troposphere winds from an easterly to a westerly regime);
-
(6)
the bi-modal interannual variation of summer monsoon onset (normal and delayed modes). In addition, the monsoon rainfall displays enormous east-west gradient over the central SCS. Possible causes for these features are discussed. A number of specific science questions concerning some of the peculiar features are raised for the forthcoming SCS monsoon experiment to address.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, Y.-H. (1992), Summer monsoon rainfall in China, J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,70: 373–396.
Garcia, O. (1985), Atlas of Highly Reflective Clouds for the Global Tropics: 1971-1983,U.S. Dept. of Commerce, NOAA, Environmental Research Lab., 365pp.
Gill, A.E. (1980), Some simple solutions for heat induced tropical circulation, Quart. J. Royal. Meteor. Soc,106: 447–463.
Huang, R.H., and W.J. Li (1988), The effect of heat source anomaly over the tropical western Pacific during summer, Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., Special issue.
Huang, Z. and S. Y. Tao (1992), Diagnostic study of the bursting processes of Asian summer monsoon in 1983, Ada Meteor. Sinica,50: 210–217 (in Chinese).
Kilonsky, B.J. and C.S. Ramage (1976), A technique for estimating tropical open-ocean rainfall from satellite obseryations, J. Appl. Meteor. 15:972–976.
Krishnamurti, T.N. (1985), Summer monsoon experiment, A review, Mon. Wea. Rev., 113:1590–1626.
Lau, K.-M. and L. Peng (1992), Dynamics of atmospheric teleconnection during northern summer, J. Atmos. Sci., 5:140–158.
Lau, K.-M., and S. Yang (1997), Climatology and interannual variability of Southeast Asian summer monsoon, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,14(2): 141–162.
Matsumoto, J. (1992), Climate over Asian and Australian monsoon regions, the University of Tokyo Project No, 03212-103.
Marissey, M.L. (1986), A statistical analysis of the relationships among rainfall, outgoing longwave radiation and the moisture budget during January–March 1979, Mon. Wea. Rev., 114: 931–994.
Motell, C.E., and B.C. Weare (1987), Estimating tropical Pacific rainfall using digital satellite data, J. Climate Appl. Meteor., 26:1436–1446.
Nitta, T. (1987), Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the Northern Hemisphere summer circulation, J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,41: 373–390.
Sadler, J.C., M.A. Lander, A.M. Hori and L.K. Oda (1987), Tropical marine climatic atlas, Vol. 2, Pacific Ocean, Report UHMET 87-02, Department of Meteorology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, 27pp.
Tao, S.Y. and L. Chen (1987), A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China, in Monsoon Meteorology,C.P. Chang and T.N. Krishnamurti eds., Oxford University Press, 60–92.
Tomita, T. and T. Yasunari (1996), Role of northeast winter monsoon on the biennial oscillation of the ENSO / monsoon system, J. Met. Soc. Japan,74: 399–413.
Wang, B. (1994), Climatic regimes of tropical convection and rainfall, J. Climate,7: 1109–1118.
Wang, B. and H. Rui (1990), Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies: 1975–1985, Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 44:43–62.
Wang, B. and X. Xie (1996), On the impacts of Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon on intraseasonal oscillation, J. Atmos. Sci..
Wang, B. and X. Xu (1997), Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon singularities and climatological intraseasonal oscillation, J. Climate,to be published.
Webster, P.J. and S. Yang (1992), Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems, Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc, 118:877–926.
Yasunari, T. (1991), “The monsoon year”—a new concept of the climatic year in the tropics, Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc, 72:1331–1338.
Zhu, Q., J. He and P. Wang (1986), A study of the circulation differences between East Asian and Indian summer monsoons with their interaction, Advances in Atmos. Sci., 3:466–477.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study is supported by the Climate Dynamics Program of NSF under grant number ATM-9400759 and the Marine Meteorology Program of ONR under the grant No N00014-96-1-0796. The authors thanks Mrs. Z. Fang and Y. Wang and Ms. H. Teng for preparation of part of the data and figures. This is the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology publication No. XXXX.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Wu, R. Peculiar temporal structure of the south china sea summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 14, 177–194 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-997-0018-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-997-0018-9