Abstract
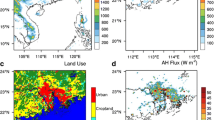
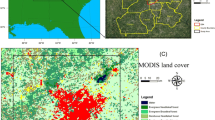
We simulated the impact of anthropogenic heat release (AHR) on the regional climate in three vast city agglomerations in China using the Weather Research and Forecasting model with nested high-resolution modeling. Based on energy consumption and high-quality land use data, we designed two scenarios to represent no-AHR and current-AHR conditions. By comparing the results of the two numerical experiments, changes of surface air temperature and precipitation due to AHR were quantified and analyzed. We concluded that AHR increases the temperature in these urbanized areas by about 0.5°C—1°C, and this increase is more pronounced in winter than in other seasons. The inclusion of AHR enhances the convergence of water vapor over urbanized areas. Together with the warming of the lower troposphere and the enhancement of ascending motions caused by AHR, the average convective available potential energy in urbanized areas is increased. Rainfall amounts in summer over urbanized areas are likely to increase and regional precipitation patterns to be altered to some extent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao, X. Y., X. J. Ren, J. P. Tang, and X. Q. Yang, 2011: Simulation study of urbanization effects on summer daily precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 31(4), 451–459. (in Chinese)
Barriopedro, D., E. M. Fischer, J. Luterbacher, R. M. Trigo, and R. García-Herrera, 2011: The hot summer of 2010: Redrawing the temperature record map of Europe. Science, 332, 220–224.
Block, A., K. Keuler, and E. Schaller, 2004: Impacts of anthropogenic heat on regional climate patterns. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, L12211, doi: 10.1029/2004GL019852.
Carter, M., J. M. Shepherd, S. Burian, and I. Jeyachandran, 2011: Integration of lidar data into a coupled mesoscale-land surface model: A theoretical assessment of sensitivity of urbancoastal mesoscale circulations to urban canopy parameters. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 29, 328–346.
Chen, T. C., S. Y. Wang, and M. C. Yen, 2007: Enhancement of afternoon thunderstorm activity by urbanization in a Valley: Taipei. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 46, 1324–1340.
Chinese National Bureau of Statistics, 2009: China Energy Statistics Yearbook. China Statistics Press, 284 pp. (in Chinese)
Crutzen, P. J., 2004: New directions: The growing urban heat and pollution “island” effect-impact on chemistry and climate. Atmos. Environ., 38, 3539–3540.
de Munck, C., and Coauthors, 2013: How much can air conditioning increase air temperatures for a city like Paris, France? Inter. J. Climatol., 33, 210–227.
Fan, H. L., and D. J. Sailor, 2005: Modeling the impacts of anthropogenic heating on the urban climate of Philadelphia: A comparison of implementations in two PBL schemes. Atmos. Environ., 39, 73–84.
Feng, J. M., Y. L. Wang, Z. G. Ma, and Y. H. Liu, 2012: Simulating the regional impacts of urbanization and anthropogenic heat release on climate across China. J. Climate, 25, 7187–7203.
Flanner, M. G., 2009: Integrating anthropogenic heat flux with global climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L02801, doi: 10.1029/2008GL036465.
Hu, Y. H., and G. S. Jia, 2010: Influence of land use change on urban heat island derived from multi-sensor data. Inter. J. Climatol., 30, 1382–1395.
Ichinose, T., K. Shimodozono, and K. Hanaki, 1999: Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmos. Environ., 33, 3897–3909.
Jin, M. L., and J. M. Shepherd, 2008: Aerosol relationships to warm season clouds and rainfall at monthly scales over east China: Urban land versus ocean. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D24S90, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010276.
Jin, M. L., J. M. Shepherd, and M. D. King, 2005: Urban aerosols and their variations with clouds and rainfall: A case study for New York and Houston. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D10S20, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005081.
Kusaka, H., and F. Kimura, 2004: Coupling a single-layer urban canopy model with a simple atmospheric model: Impact on urban heat island simulation for an idealized case. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 82, 67–80.
Kusaka, H., H. Kondo, Y. Kikegawa, and F. Kimura, 2001: A simple single-layer urban canopy model for atmospheric models: Comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Bound.- Layer Meteor., 101, 329–358.
Li, X., X. Q. Yang, J. P. Tang, X. G. Sun, and J. B. Fang, 2011: Multiple urban heat islands and surface energy balance during summer in Yangtze River Delta city cluster region simulated with WRF/NCAR. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 31(4), 441–450. (in Chinese)
Li, Z., and Z. W. Yan, 2009: Homogenized daily mean/maximum/minimum temperature series for China from 1960–2008. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 2, 237–243.
Lin, C. Y., W. C. Chen, S. C. Liu, Y. A. Liou, G. R. Liu, and T. H. Lin, 2008: Numerical study of the impact of urbanization on the precipitation over Taiwan. Atmos. Environ., 42, 2934–2947.
Lin, C. Y., W. C. Chen, P. L. Chang, and Y. F. Sheng, 2011: Impact of the urban heat island effect on precipitation over a complex geographic environment in Northern Taiwan. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 50, 339–353.
Lo, J. C. F., A. K. H. Lau, F. Chen, J. C. H. Fung, and K. K. M. Leung, 2007: Urban modification in a mesoscale model and the effects on the local circulation in the Pearl River Delta Region. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 46, 457–476.
Lu, X., K. C. Chow, T. Yao, A. K. H. Lau, and J. C. H. Fung, 2010: Effects of urbanization on the land sea breeze circulation over the Pearl River Delta region in winter. Inter. J. Climatol., 30, 1089–1104.
Offerle, B., C. S. B. Grimmond, and K. Fortuniak, 2005: Heat storage and anthropogenic heat flux in relation to the energy balance of a central European city centre. Inter. J. Climatol., 25, 1405–1419.
Ohashi, Y., Y. Genchi, H. Kondo, Y. Kikegawa, H. Yoshikado, and Y. Hirano, 2007: Influence of air-conditioning waste heat on air temperature in Tokyo during summer: Numerical experiments using an urban canopy model coupled with a building energy model. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 46, 66–81.
Pigeon, G., D. Legain, P. Durand, and V. Masson, 2007: Anthropogenic heat release in an old European agglomeration (Toulouse, France). Inter. J. Climatol., 27, 1969–1981.
Quah, A. K. L., and M. Roth, 2012: Diurnal and weekly variation of anthropogenic heat emissions in a tropical city, Singapore. Atmos. Environ., 46, 92–103.
Robine, J. M., S. L. K. Cheung, S. Le. Roy, H. Van. Oyen, C. Griffiths, J.-P. Michel, and F. R. Herrmann, 2008: Death toll exceeded 70,000 in Europe during the summer of 2003. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 331, 171–178.
Rosenfeld, D., 2000: Suppression of rain and snow by urban and industrial air pollution. Science, 287, 1793–1796.
Rosenfeld, D., J. Dai, X. Yu, X. H. Xu, X. Yang, C. L. Du, and Z. Yao, 2007: Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and orographic precipitation. Science, 315, 1396–1398.
Sailor, D. J., and L. Lu, 2004: A top-down methodology for developing diurnal and seasonal anthropogenic heating profiles for urban areas. Atmos. Environ., 38, 2737–2748.
Shem, W., and M. Shepherd, 2009: On the impact of urbanization on summertime thunderstorms in Atlanta: Two numerical model case studies. Atmospheric Research., 92, 172–189.
Shepherd, J. M., 2005: A review of current investigations of urban-induced rainfall and recommendations for the future. Earth Interactions, 9, 1–27.
Shepherd, J. M., and S. J. Burian, 2003: Detection of urban-induced rainfall anomalies in a major coastal city. Earth Interactions, 7, 1–17.
Stunder, B. J. B., 1997: NCEP model output-FNL archive data. Tech. Rep. TD-6141, NOAA Air Resour. Lab., Sliver Spring, Md. [Available online at http://www.ready.noaa.gov/fnl.php]
Washington, W. M., 1972: Numerical climate-change experiments: The effect of man’s production of thermal energy. J. Appl. Meteor., 11, 768–772.
Washington, W. M., and R. M. Chervin, 1979: Regional climatic effects of large-scale thermal pollution: Simulation studies with the NCAR general circulation model. J. Appl. Meteor., 18, 3–16.
Wu, K., and X. Q. Yang, 2013: Urbanization and heterogeneous surface warming in eastern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58, 1363–1373, doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5627-8.
Zhang, C. L., F. Chen, S. G. Miao, Q. C. Li, X. A. Xia, and C. Y. Xuan, 2009: Impacts of urban expansion and future green planting on summer precipitation in the Beijing metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D02116, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010328.
Zhang, L., X. Q. Yang, J. P. Tang, J. B. Fang, and X. G. Sun, 2011: Simulation of urban heat island effect and its impact on atmospheric boundary layer structure over Yangtze River Delta region in summer. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 31(4), 431–440. (in Chinese)
Zhang, N., Z. Q. Gao, X. M. Wang, and Y. Chen, 2010: Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 102, 331–342.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Wang, J. & Yan, Z. Impact of anthropogenic heat release on regional climate in three vast urban agglomerations in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 31, 363–373 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3041-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-013-3041-z