Abstract
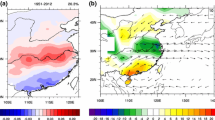
By examining the second leading mode (EOF2) of the summer rainfall in China during 1958–2001 and associated circulations, the authors found that this prominent mode was a dipole pattern with rainfall decreasing to the north of the Yangtze River and increasing to the south. This reverse relationship of the rainfalls to the north and to the south of the Yangtze River was related with the meridional circulations within East Asia and the neighboring region, excited by SST in the South China Sea-northwestern Pacific. When the SST was warmer, the geopotential heights at 500 hPa were positive in the low and high latitudes and negative in the middle latitudes. The anticyclone in the low latitudes favored the subtropical high over the northwestern Pacific (SHNP) shifting southwestward, leading to additional moisture transport over southern China. The anomalous atmospheric circulations along the East Asian coast tends to enhance upward movement over the region. Subsequently, rainfall in southern China is enhanced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, C. P., Y. S. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000a: Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: Roles of the subtropical ridge. J. Climate, 13, 4310–4325.
Chang, C. P., Y. S. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000b: Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical SSTs. Part II: Meridional structure of the monsoon. J. Climate, 13, 4326–4340.
Chen, L. T., and R. G. Wu, 2000: Interannual and decadal variations of snow cover over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and their relationships to summer monsoon rainfall in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 18–30.
Ding, Y. H., Z. Y. Wang, and Y. Sun, 2008: Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. International Journal of Climatology, 28, 1139–1161.
Fan, K., 2006: Atmospheric circulation in southern Hemisphere and summer rainfall over Yangtze River valley. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49, 672–679. (in Chinese)
Gong, D. Y., and C. H. Ho, 2002: Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 1436, doi: 10.1029/2001GL14523.
Hu, Z. Z, 1997: Inter-decadal variability of summer climate over East Asia and its association with 500 hPa height and global sea surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 19403–19412.
Huang, R. H., and F. Y. Sun, 1992: Impacts of the tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 243–256.
Huang, R. H., Y. H. Xu, and L. T. Zhou, 1999: Interdecadal variation and dry trend of summer precipitation in China. Plateau Meteorology, 18, 465–476. (in Chinese)
Liu, H. Q., Z. B. Sun, J. Wang, and J. Z. Min, 2004: A modeling study of the effects of anomalous snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau upon the South Asian summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21, 964–975.
Liu, X. D., and M. Yanai, 2002: Influence of Eurasian spring snow cover on Asian summer rainfall. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1075–1089.
Menon, S., J. Hansen, L. Nazarenko, and Y. F. Luo, 2002: Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 297, 2250–2253.
North, G. R., T. L. Bell, R. F. Cahalan, and F. J. Moeng, 1982: Sampling errors in the estimation of EOFs. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 699–706.
Simmons, A. J., and J. K. Gibson, 2000: The ERA-40 Project Plan. ERA-40 Project Report Series 1, ECMWF, Reading, United Kingdom, 62pp.
Smith, T. M., and R. W. Reynolds, 2003: Extended reconstruction of global sea surface temperatures based on COADS data (1854–1997). J. Climate, 16, 1495–1510.
Sun, J. Q., H. J. Wang, and W. Yuan, 2008: A possible mechanism for the co-variability of the boreal spring Antarctic Oscillation and the Yangtze River valley summer rainfall. International Journal of Climatology, doi: 10.1002/joc.1773. (in press)
Wang, H. J., 2001: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 376–386.
Wang, H. J., and K. Fan, 2005: Central-north China precipitation as reconstructed from the Qing Dynasty: Signal of the Antarctic atmospheric Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L24705, doi: 10.1029/2005GL024562.
Wang, Y. Q., and L. Zhou, 2005: Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in China during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L09707, doi: 10.1029/2005GL022574.
Weng, H. Y., K. M. Lau, and Y. K. Xue, 1999: Multiscale summer rainfall variability over China and its long-term link to global sea surface temperature variability. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 77, 845–857.
Wu, B. Y., and R. H. Zhang, 2007: Interdecadal shift in the western North Pacific summer SST anomaly in the late 1980s. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52, 2559–2564.
Wu, B. Y., R. H. Zhang, Y. H. Ding, and R. D Arrigo, 2008: Distinct modes of the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Climate, 21, 1122–1138.
Wu, B. Y., K. Yang, and R. H. Zhang, 2009: Eurasian snow cover variability and its association with summer rainfall in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26(1), 31–44, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-0031-2.
Wu, T. W., and Z. A. Qian, 2003: The relation between the Tibetan winter snow and the Asian summer monsoon and rainfall: An observational investigation. J. Climate, 16, 2038–2051.
Wu, R. G., and B. Wang, 2002: A contrast of the East Asian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship between 1962–77 and 1978–93. J. Climate, 15, 3266–3279.
Xu, Q., 2001: Abrupt change of the mid-summer climate in central east China by the influence of atmospheric pollution. Atmos. Environ., 35, 5029–5040.
Yang, F. L., and K.M. Lau, 2004: Trend and variability of China precipitation in spring and summer: Linkage to sea-surface temperature. International Journal of Climatology, 24, 1625–1644.
Yang, X. Q., Q. Xie, Y. M. Zhu, X. G. Sun, and Y. N. Guo, 2005: Decadal-to-interdecadal variability of precipitation in North China and associated atmospheric and oceanic anomaly patterns. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48, 789–797. (in Chinese)
Zhang, R. H., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the 86/87 and 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhang, R. H., B. Y. Wu, P. Zhao, and J. P. Han, 2008: The decadal shift of the summer climate in the Late 1980s over eastern China and its possible causes. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 22, 435–445.
Zhang, Y. S., T. Li, and B. Wang, 2004: Decadal change of the spring snow depth over the Tibetan Plateau: The associated circulation and its relationship to the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J. Climate, 17, 2780–2793.
Zhao, P., Z. J. Zhou, and J. P. Liu, 2007: Variability of Tibetan spring snow and its associations with the hemispheric extratropical circulation and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall: An observational investigation. J. Climate, 20, 3942–3955.
Zhou, S. W., and R. H. Zhang, 2005: Decadal variations of temperature and geopotential height over the Tibetan Plateau and their relations with Tibet ozone depletion. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L18705, doi: 10.1029/2005GL023496.
Zhou, T. J., and R. C. Yu, 2005: Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D08104, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Zhang, R. The dipole mode of the summer rainfall over East China during 1958–2001. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 26, 727–735 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9014-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9014-6