Abstract
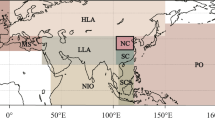
The climatological characteristics of the moisture budget over the joining area of Asia and the Indian-Pacific Ocean (AIPO) and its adjacent regions as well as their anomalies have been estimated in this study. The main results are as follows.
In the winter, the northeasterly moisture transport covers the extensive areas at the lower latitudes of the AIPO. The westerly and northerly moisture transport is the major source and the South Indian Ocean (SIO) is the moisture sink. In the summer, influenced by the southwesterly monsoonal wind, the cross-equatorial southwesterly moisture transport across Somali originating from the SIO is transported through the Arabian Sea (AS), the Bay of Bengal (BOB), and the South China Sea (SCS) to eastern China. The AIPO is controlled by the southwesterly moisture transport.
The net moisture influx over the AIPO has obvious interannual and interdecadal variations. From the mid- or late 1970s, the influxes over the SIO, the AS, the northern part of the western North Pacific (NWNP), and North China (NC) as well as South China (SC) begin to decrease abruptly, while those over Northeast China (NEC) and the Yangtze River-Huaihe River basins (YHRB) have increased remarkably. As a whole, the net moisture influxes over the BOB and the southern part of the western North Pacific (SWNP) in the recent 50 years take on a linear increasing trend. However, the transition timing for these two regions is different with the former being at the mid- or late 1980s and the latter occurring earlier, approximately at the early stage of the 1970s.
The anomalous moisture source associated with the precipitation anomalies is different from the normal conditions of the summer precipitation. For the drought or flood years or the years of El Niño and its following years, the anomalous moisture transport originating from the western North Pacific (WNP) is the vital source of the anomalous precipitation over eastern China, which is greatly related with the variation of the subtropical Pacific high.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, G. T. J., 1994: Large-scale circulations associated with the East Asian summer monsoon and Meiyu over south China and Taiwan. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 72, 959–983.
Ding, Y., 1994: Water vapor budget in monsoon area. Asia Monsoon, China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 105–133. (in Chinese)
Ding, Y., and G. Hu, 2003: A study on water vapor budget in China during the 1998 severe flood periods. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 61(2), 129–145. (in Chinese)
Ding, Y., and Y. Sun, 2002: Seasonal march of East Asian summer monsoon and the related moisture transport. Weather and Climate, 1(1), 18–33.
Ding, Y., and Y. Sun, 2003: Long-term climate variability in China. WMO/TD No. 1172, 18–33.
Gong, D., and S. Wang, 1999: Influence of ENSO on precipitation in China in recent 100 Years. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(3), 315–320. (in Chinese)
He, J., and T. Murakami, 1983: Water vapor flux over East and South Asia during June of 1979. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 6(2), 159–173. (in Chinese)
Huang, R., Z. Zhang, G. Huang, and B. Ren, 1998: Characteristics of the water vapor transport in East Asian monsoon region and its difference from that in South Asian monsoon Region in summer. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 22(4), 460–469. (in Chinese)
Jiang, X., Y. Li, and X. Wang, 2008: Water vapor transportation in China and its relationship with drought and flood in the Yangtze River Basin. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 63(5), 482–490. (in Chinese)
Liu, Y., and Y. Ding, 1995: Influence of ENSO events on weather and climate in China. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 19(2), 200–208. (in Chinese)
Liu, Y., J. He, and J. Liang, C. Li., 2006: Features of moisture transport in seasonal transition over Asian-Australian monsoon region. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 22(2), 138–146. (in Chinese)
Ma, J., B. Yu, X. Gao, and J. Li., 2008: Change of large-scale circulation and its impact on the water vapor over North China. Plateau Meteorology, 27(3), 517–523. (in Chinese)
Ninomiya, K., 1999: Moisture balance in China and the south China Sea during the summer monsoon in 1991 in relation to the intense rainfalls in China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 77(3), 737–751.
Qiao, Y., and M. Lin, 2006: The Characteristics of moisture transport over Asian-Australian monsoon region. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 45(6), 102–105. (in Chinese)
Shi, X., X. Xu, H. Wang, and D. Qin, 2008: Characteristics of moisture transport in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River and its variation trend. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 39(5), 596–603. (in Chinese)
Simmonds, I., D. Bi, and P. Hope, 1999: Atmospheric water vapor flux and its association with rainfall in China in summer. J. Climate, 22, 1353–1367.
Tao, J., and J. Chen, 1994: Diagnosis of role of moisture sources and passages of Jianghuai meiyu. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 17, 443–447. (in Chinese)
Tao, S., and L. Chen, 1987: A review of recent research of the East Asian summer monsoon in China. Monsoon Meteorology, Oxford University Press, 60–92.
Tian, H., P. Guo, and W. Lu, 2002: Features of water vapor transfer by summer monsoon and their relations to rainfall anomalies in China. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 25(4), 496–502. (in Chinese)
Tian, H., P. Guo, and W. Lu, 2004: Characteristics of vapor inflow corridor related to summer rainfall in China and impact factors. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 20(4), 401–408. (in Chinese)
Wang, A., R. Feng, T. Tang, J. Li, Q. Fan, W. Meng, and R. Huang, 2003a: The discontinuity of atmospheric circulation for Asia in summer in the end of 1970s. The Research of Heavy Climatic Disasters and its Reason in China, Huang et al., Eds., China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 401–406. (in Chinese)
Wang, B., R. Wu, and X. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asia climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Wang, B., S. Clemens, and P. Liu, 2003b: Contrasting the Indian and East Asian monsoons: Implications on geologic timescales. Marine Geology, 201, 5–21.
Wang, H., 2001: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970s. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18(3), 376–386.
Wu, G., J. Chou, Y. Liu, and J. He, 2002: Dynamics of the Formation and Variation of Sub-tropical Anticyclones. Science Press, Beijing, 1–294. (in Chinese)
Wu, G., and Coauthors, 2006: The key region affecting the short-term climate variations in China: The joining area of Asia and Indian-Pacific Ocean. Advances in Earth Science, 21(11), 1109–1118. (in Chinese)
Xie, A., J. Mao, Y. Song, and Q. Ye, 2002: Climatological characteristics of moisture transport over Yangtze River Basin. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 13(1), 67–77. (in Chinese)
Xie, Y., and W. Dai, 1959: Certain computational results of water vapor transport over eastern China for a selected synoptic case. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 30, 173–185. (in Chinese)
Xu, Q., 2001: Abrupt change of the mid-summer climate in central east China by the influence of atmospheric pollution. Atmos. Environ., 35, 5029–5040.
Xu, S., 1958: Water vapor transport and balance in China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 29, 3–43. (in Chinese)
Yao, H., and D. Li, 1995: The relationship between El-Niño events and rainfall, historical drought and water logging in China. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 3(2), 228–234. (in Chinese)
Zhai, P., F. Ren, and Q. Zhang, 1999: Detection of trends in China’s precipitation extremes. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 57, 208–216. (in Chinese)
Zhai, P., X. Li, and F. Ren, 2003: El Niño. Series of Hot Topics for Global Climate Change, D. Qin, Ed., China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 180pp. (in Chinese)
Zhang, R., 1999: The role of Indian summer monsoon water vapor transportation on the summer rainfall anomalies in the northern part of China during the El Niño mature phase. Plateau Meteorology, 18(4), 567–574. (in Chinese)
Zhou, C., J. He, and W. Li, 2005: Climatological characteristics of water vapor transfer over East Asia in summer. Journal of Nanjing Institute Meteorology, 28(1), 18–27. (in Chinese)
Zhou, T., and R. Yu, 2005: Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D08104, doi: 10.1029/2004JD5413.
Zhou, X., Y. Ding, and P. Wang, 2008a: Moisture transport in Asian summer monsoon region and its relationship with summer precipitation in China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 66(1), 59–70. (in Chinese)
Zhou, X., Y. Ding, and P. Wang, 2008b: Features of moisture transport associated with the precipitation over north china during July–August. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 32(2), 345–357. (in Chinese)
Zhu, W., Y. Liu, and J. He, 2007: Characteristics of water vapor transport in averaged field and its difference from that in disturbed field in Yangtze and Huaihe valley. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 27(2), 155–161. (in Chinese)
Zhuo, D., Y. Zheng, and W. Li, and X. Li., 2006: The disquisition of atmospheric water vapor transports and income and expenses in the typical drought and flood summer in the Jiang-Huai valley. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 26(3), 244–251. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ding, Y., Song, Y. et al. Climatological characteristics of the moisture budget and their anomalies over the joining area of Asia and the Indian-Pacific Ocean. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 26, 642–655 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9010-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9010-x